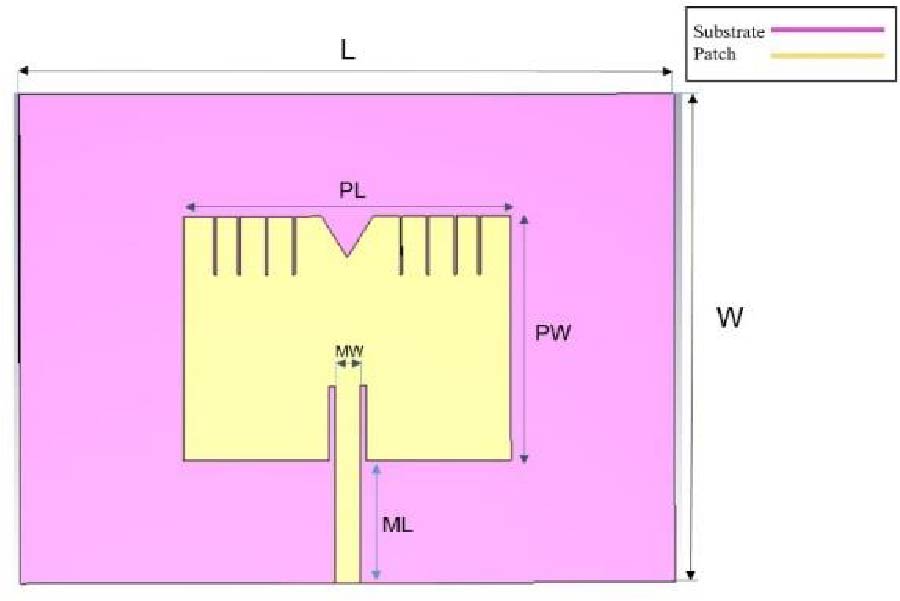
Development of Novel and High Gain Microstrip Patch Antennas at Different Frequency Bands for 6G Applications
Niyaz Mahmud Sayem,
Abul Kalam Muhammed Baki,
Fahim Faysal,
Sheikh Tanvi Mahmud,
Ahmed Jubayer and
Tawsif Ahmed Rifat
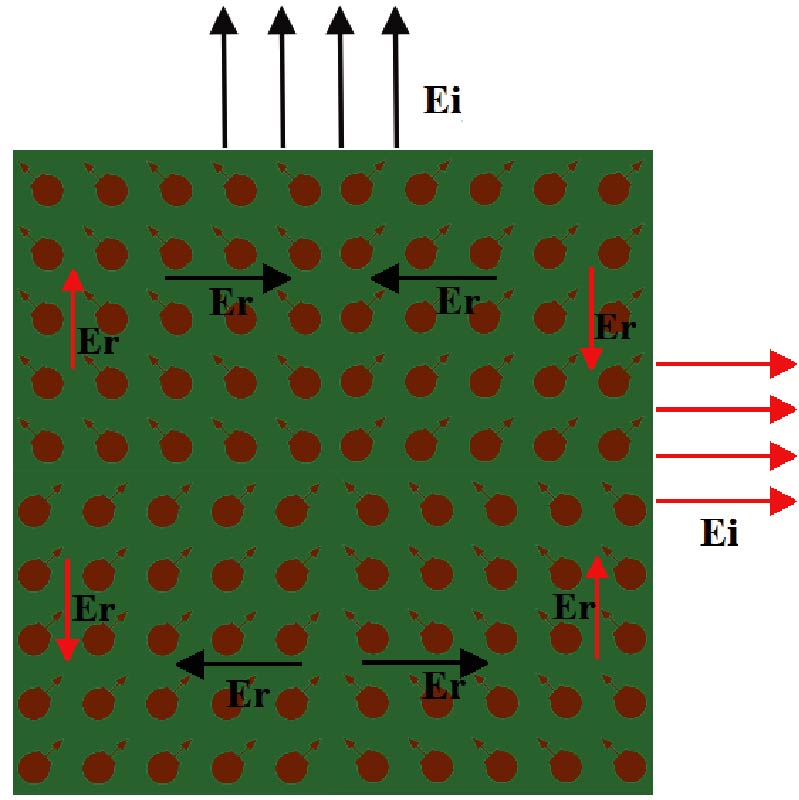
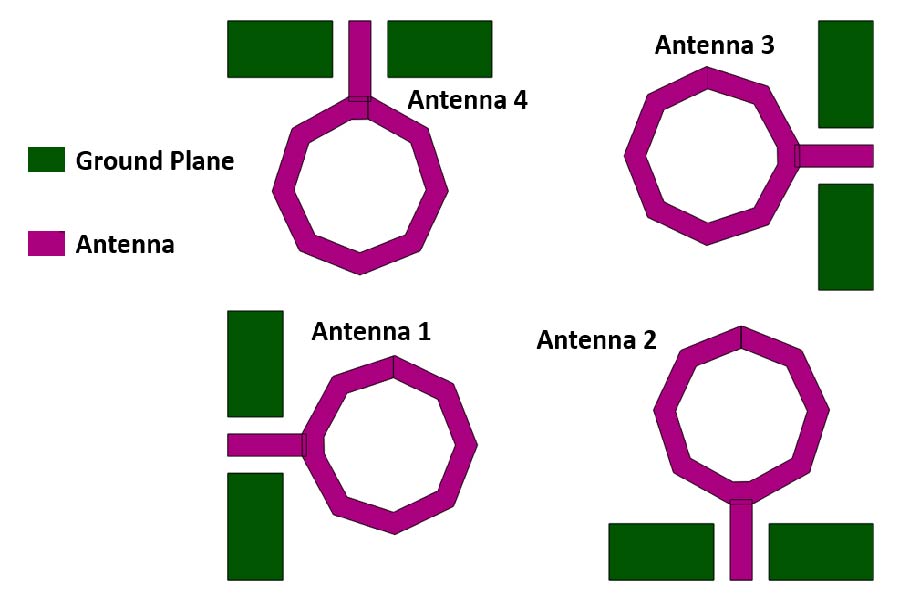
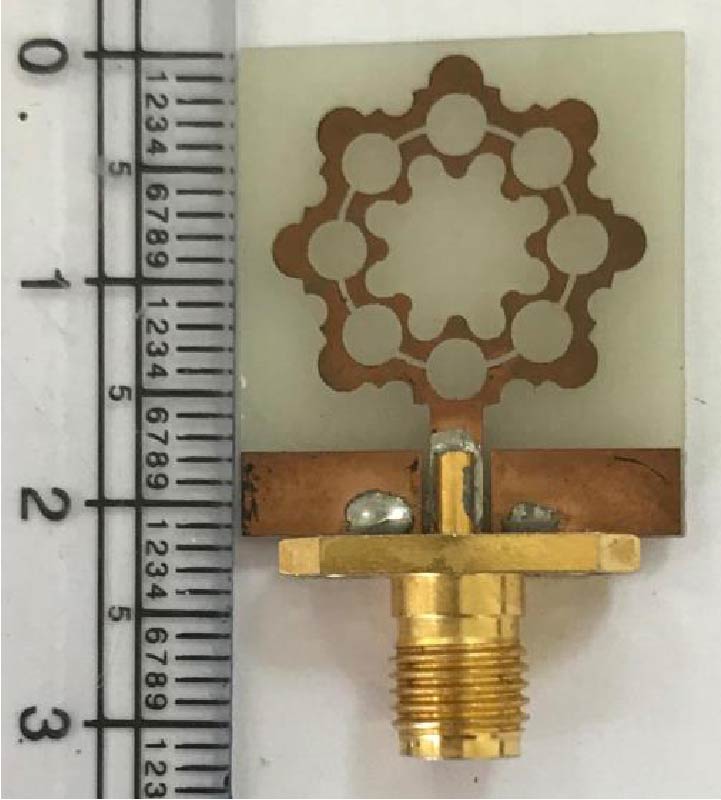
Wireless communications need antennas of different sizes, shapes, frequency-bands, bandwidths, and radiation patterns due to technical requirements, physical constraints, and FCC (Federal Communication Commission) regulations. For example, S-band antennas (2 GHz~4 GHz) are used in navigation, C-band antennas (4 GHz~8 GHz) used in Air-borne RADAR, X (8~12) band antennas used in Satellite communications, and millimeter wave (40 GHz and above) antennas used in autonomous vehicles. Ultrawide Band (UWB) antennas of different frequency bands have also applications in different fields such as medical imaging, radar imaging, software defined radios, surveillance, and health monitoring of different equipment. Microstrip patch antennas of different gains, bandwidths, shapes, and radiation patterns will play a vital role in different wireless applications of future 6G systems. In this paper, we have discussed different novel designs of patch antennas at different frequency bands: V-shaped patch antenna at 2.4 GHz, and hexagonal slotted half-circular patch antenna at 4.29 GHz. We have designed antennas of different shapes for different frequencies since some applications require UWB; some applications require narrow band but higher gain; and some applications require different gain/radiation patterns at the same frequency. We have designed a patch antenna at 2.4 GHz that can be used in Wi-Fi, and UWB patch at 4.29 GHz with omnidirectional radiation pattern that can be used in energy harvesting or biomedical applications. In this paper, we have also discussed the prototype development and testing results of the novel hexagonal slotted half-circular patch antenna at 4.29 GHz.