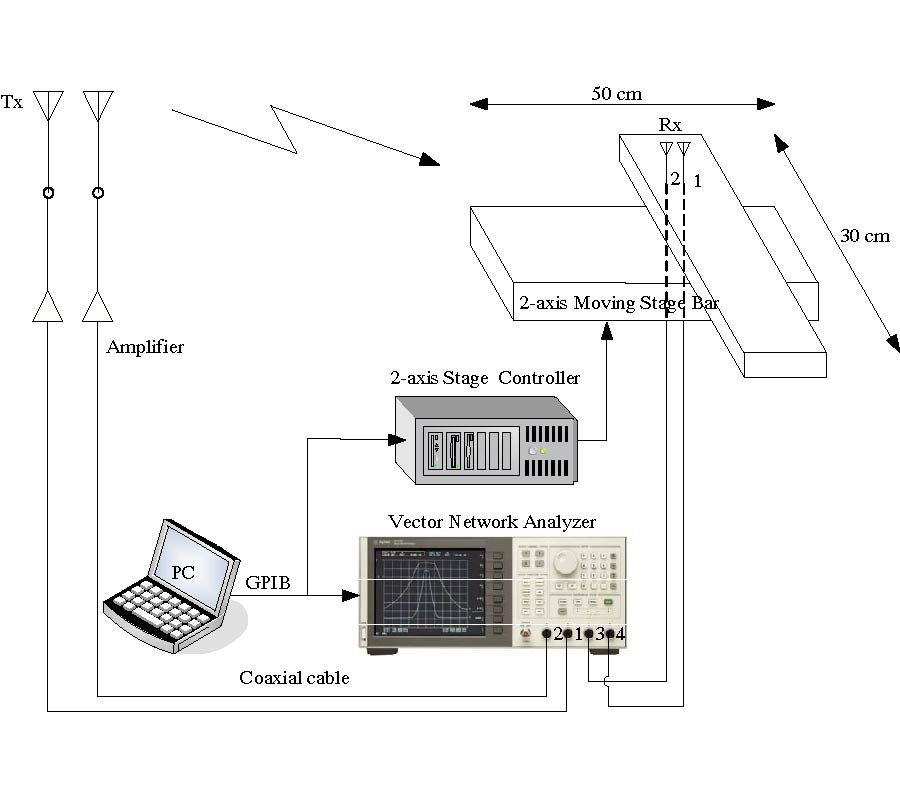
A Design of Vehicular GPS and LTE Antenna Considering the Vehicular Body Effects
Patchaikani Sindhuja,
Yoshihiko Kuwahara,
Kiyotaka Kumaki and
Yoshiyuki Hiramatsu
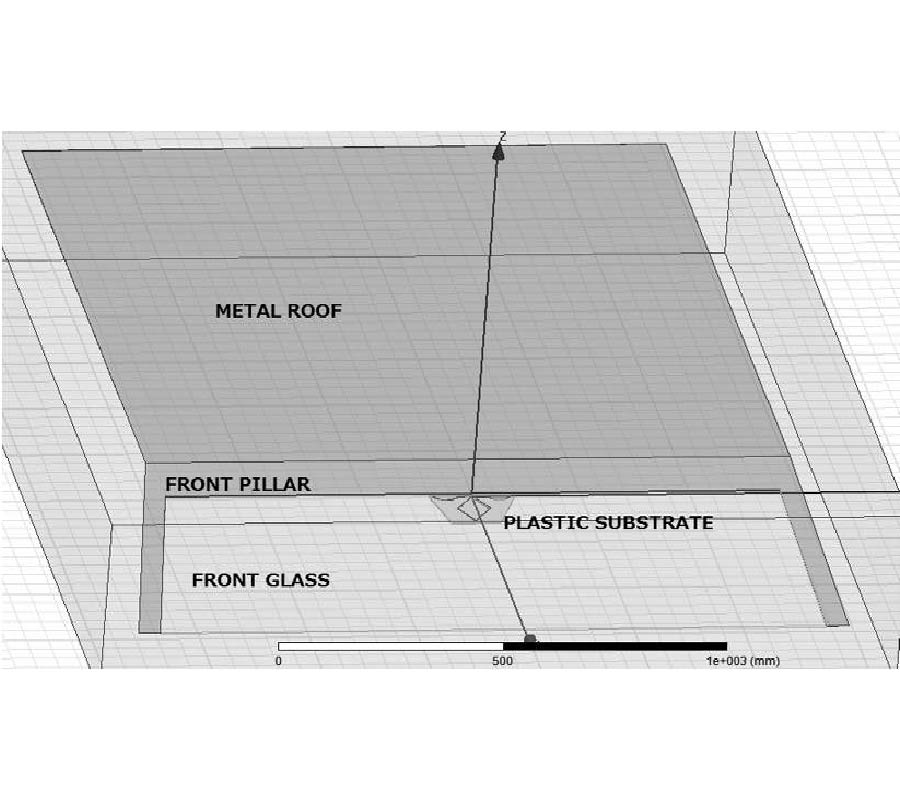
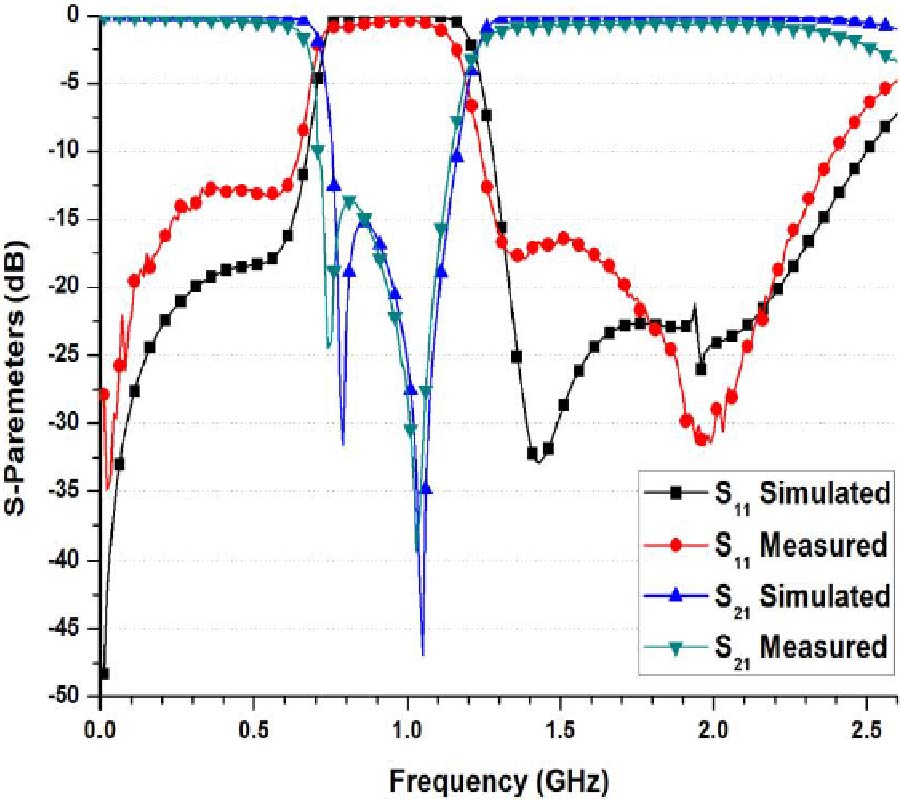
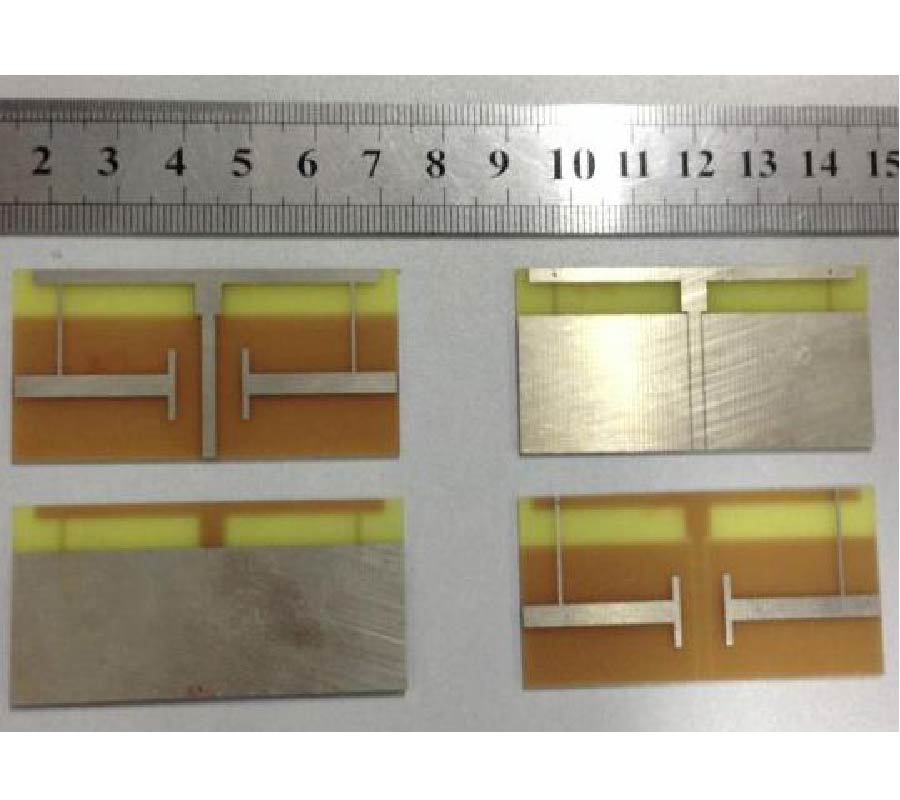
In this paper, a vehicular antenna design scheme considering the vehicular body effects is proposed. A wire antenna for GPS and LTE is implemented on the plastic plate, then it is mounted on the front glass. The outputs are commonly used to share the feed. It is necessary for GPS to increase the right hand circularly polarization (RHCP) gain near the zenith and to reduce the axis ratio while for LTE to increase the horizontal and vertical polarization (HP and VP) gain in the horizontal plane. Also for LTE, multiband characteristics are required. In order to achieve the specified performance, the antenna shape is optimized by Parato genetic algorithm (PGA). When the antenna is mounted on the body, the performance is seriously changed. To evaluate performance of the antenna mounted on the body with a complex shape, a commercial electromagnetic simulator (Ansoft HFSS) is used. To apply electromagnetic results output by HFSS to PGA algorithm operating on the MATLAB, MATLAB to HFSS linking program via Visual BASIC (VB) script was used. It is difficult to carry out the electromagnetic analysis with the whole body because of limitations of the calculating load and memory size. To overcome the limitation, we consider only a predominant part where it has an influence on the performance. It is presented that degradations caused by the body are improved through a series of optimization stages. The simulation results obtained clearly show that it is well optimized at 1.575 for GPS and 766.5 MHz and 2.135 GHz for LTE, respectively.