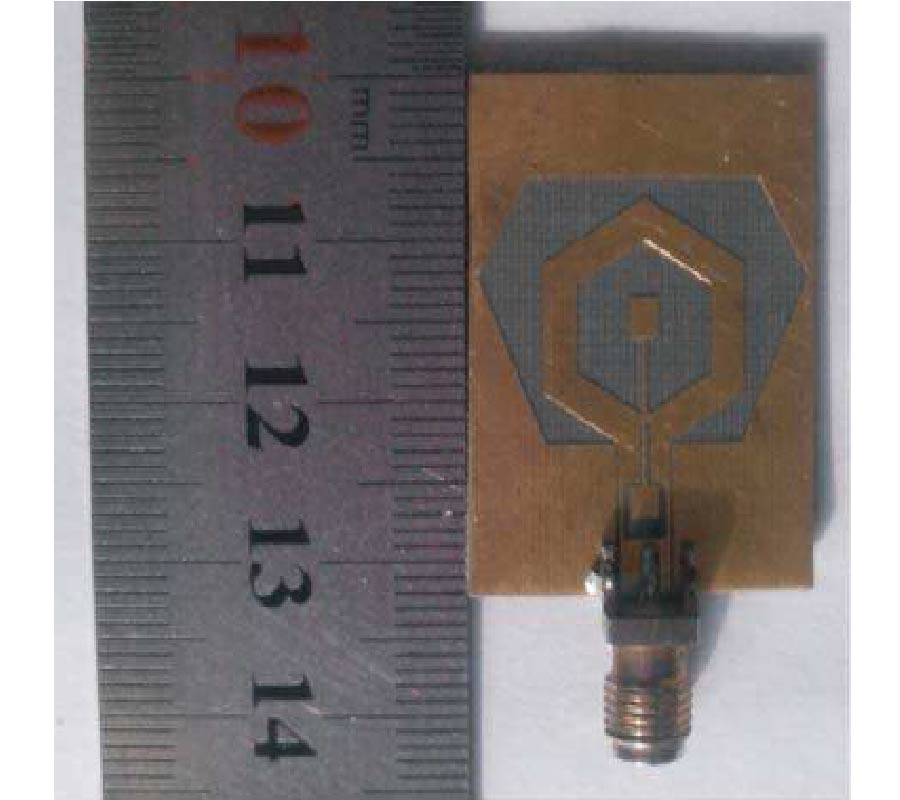
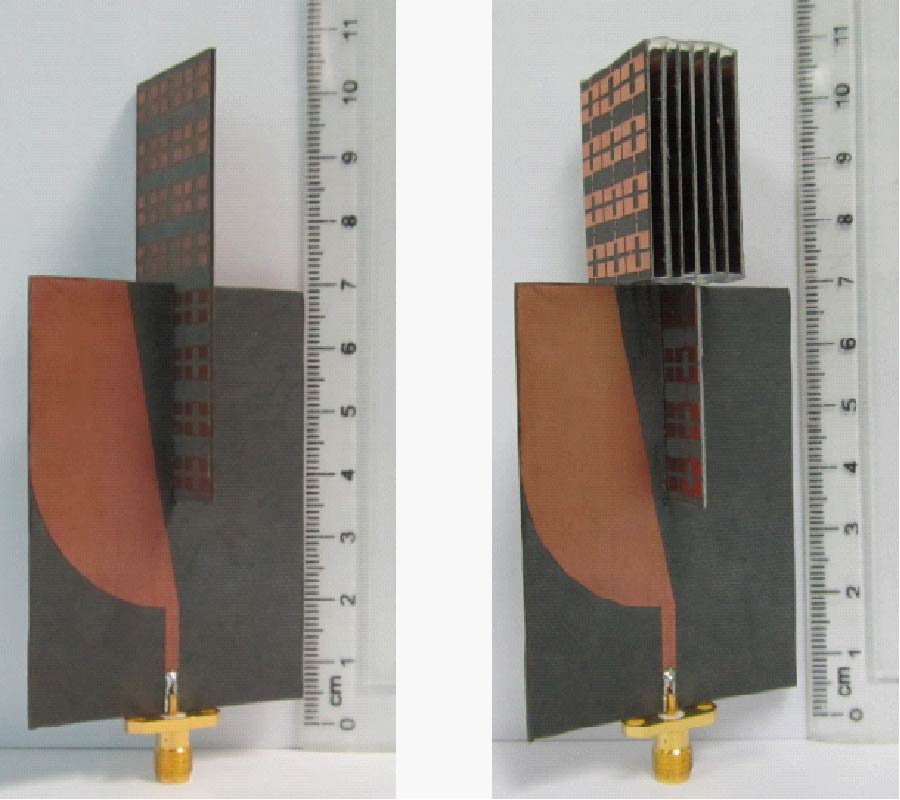
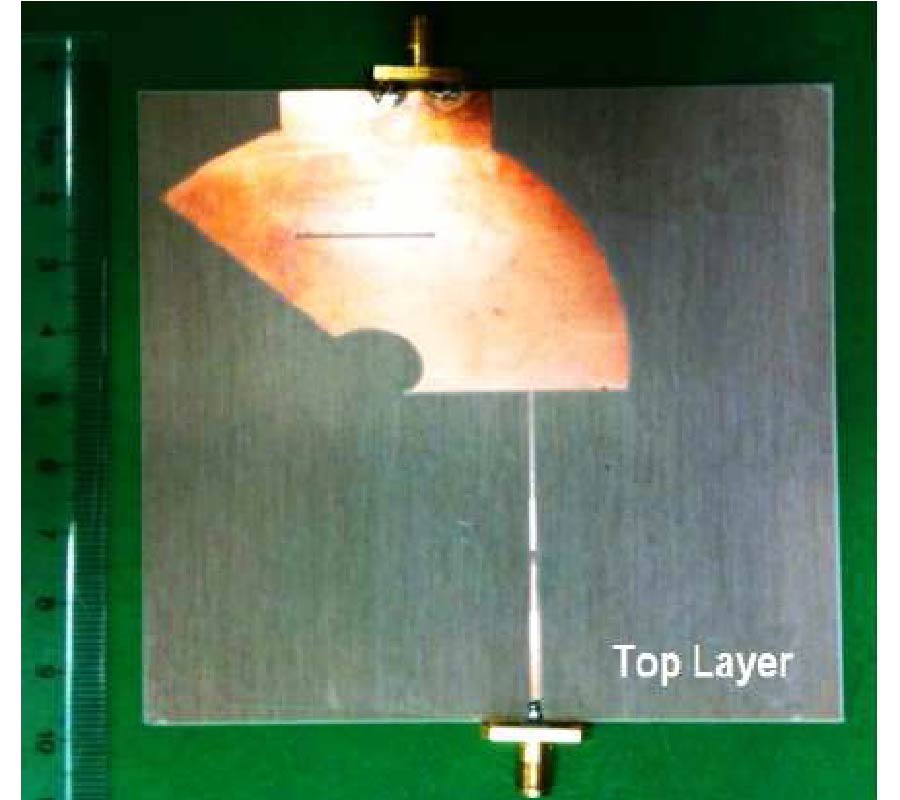
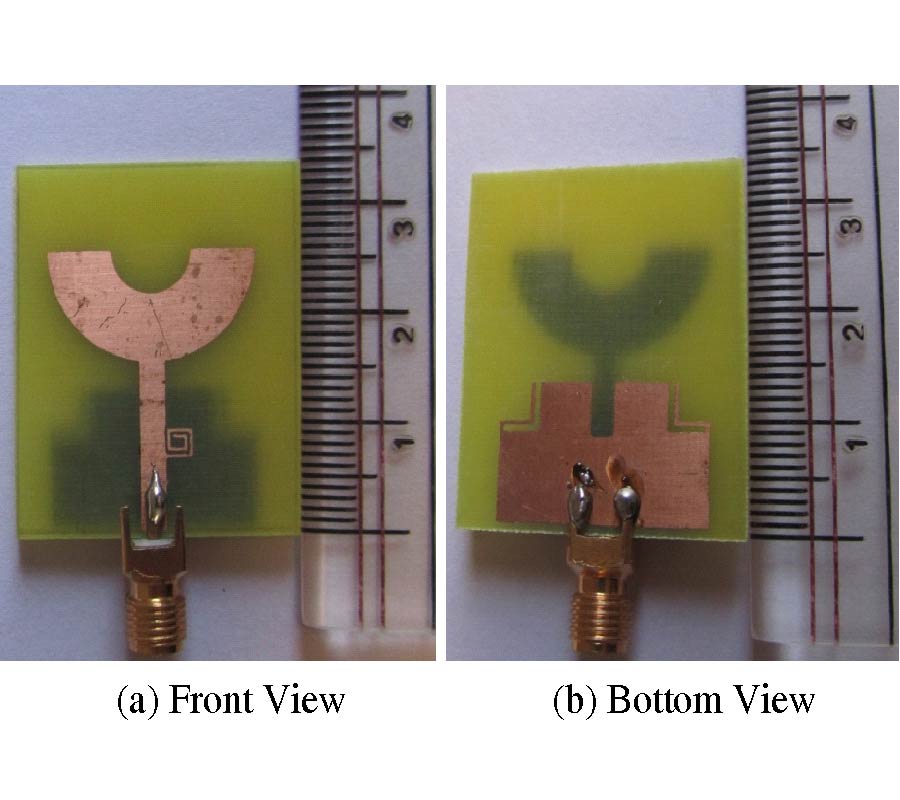
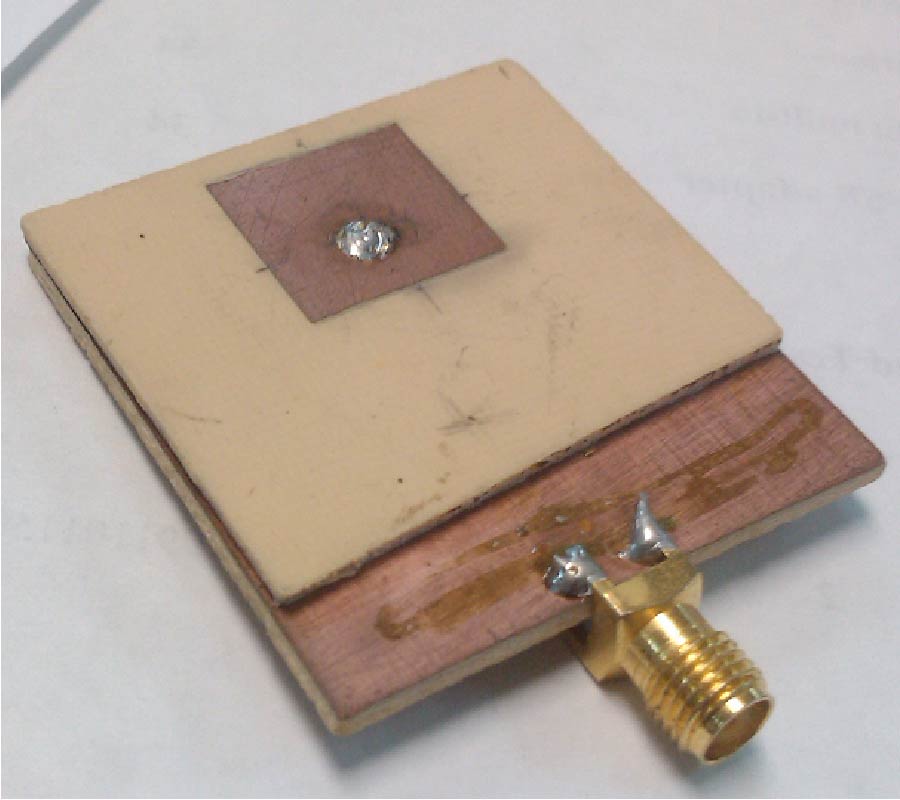
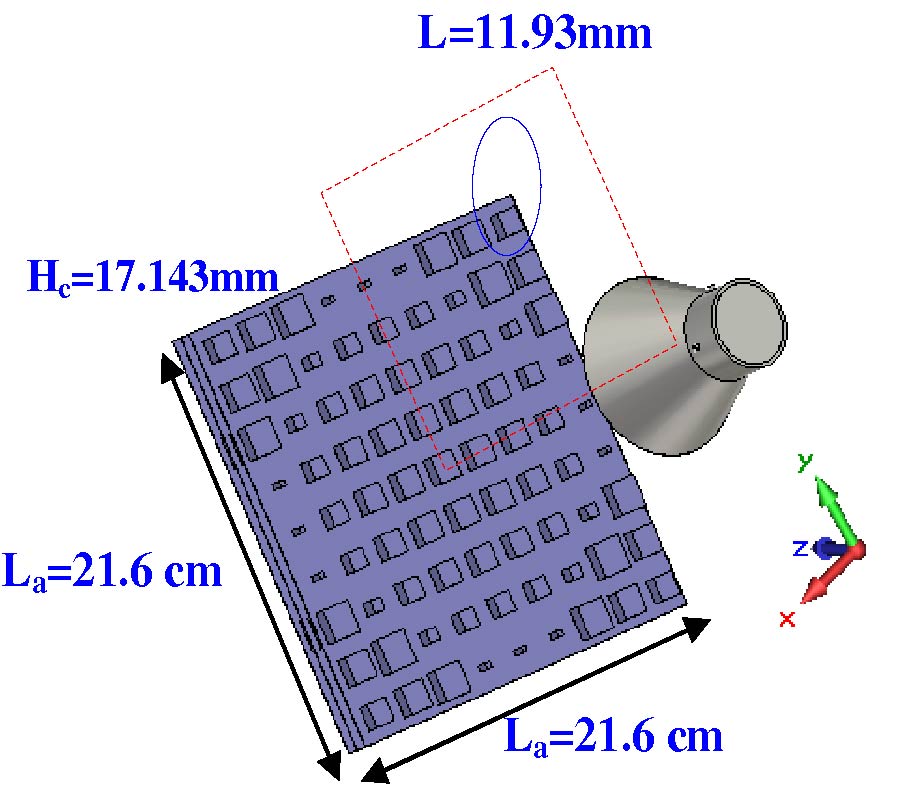
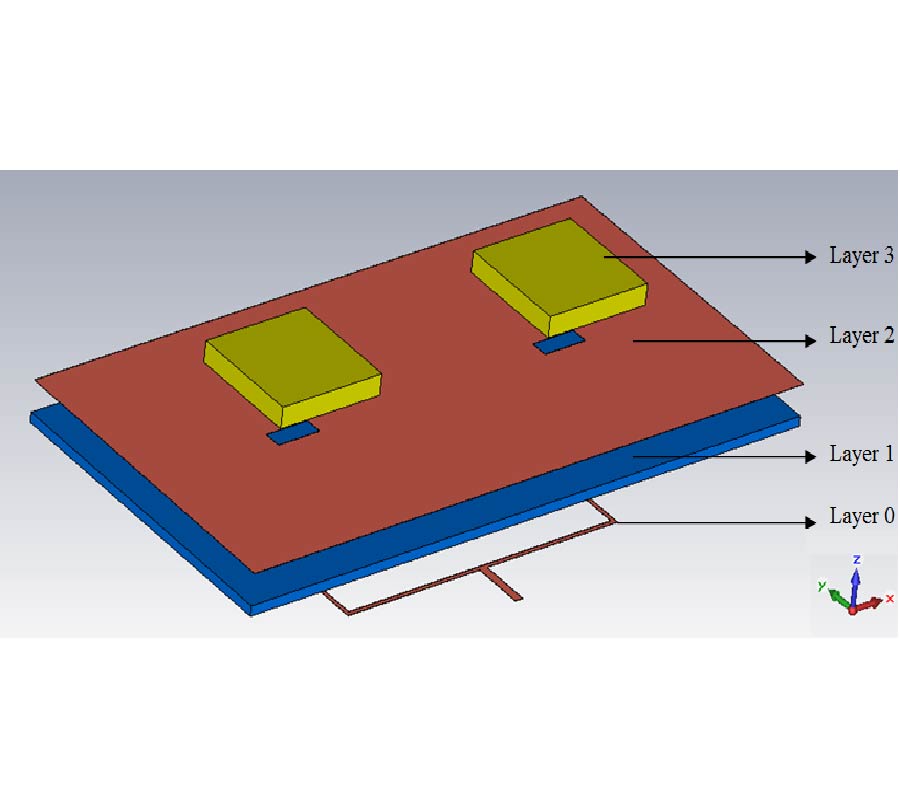
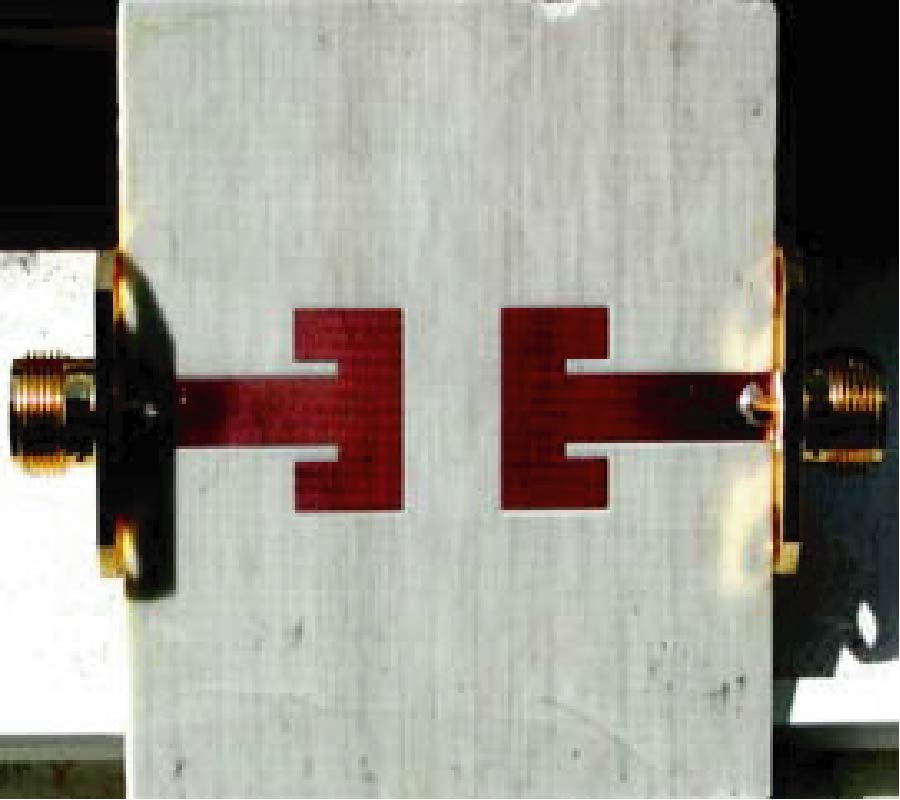
Antipodal Vivaldi Antenna Performance Booster Exploiting Snug-in Negative Index Metamaterial
Adam Reda Hasan Alhawari,
Alyani Ismail,
Mohd Adzir Mahdi and
Raja Syamsul Azmir Raja Abdullah
Despite its popularity, the conventional Vivaldi antenna has long suffered from some design problems, such as tilted beam, low or inconsistent directivity and gain, complicated design and fabrication methods, and limited size reduction. These setbacks make its progress lag on the fast track of technological demand. Thus, the antenna overall performance is anticipated to improve by incorporating negative index metamaterial (NIM) into the design method, plus, it is also tunable. In this study, the design uses linearly-tapered shape-loading structure, as its projected performance crucially depends on the space in between the antenna arms, a prerequisite to further boost its performance when combined with NIM technology. A unique slitting approach synchronizes the integration between the Vivaldi antenna and NIM where a single layer NIM piece is simply snugged into the slit perpendicular to the middle antenna substrate. The major improvement in the spotlight is the capability of NIM to focus the entire beam so that it can radiate to the targeted direction. The measurement results are similar to the simulations in terms of high gain, where the gain and directivity of the antenna are increased up to 4 dB. The contrast of overall performance between the plain modified Vivaldi antenna and the ones with NIM evidently asserts the expected contribution of snug and boost method applied and attests its significant potentials for a broad range of ultra-wideband applications.