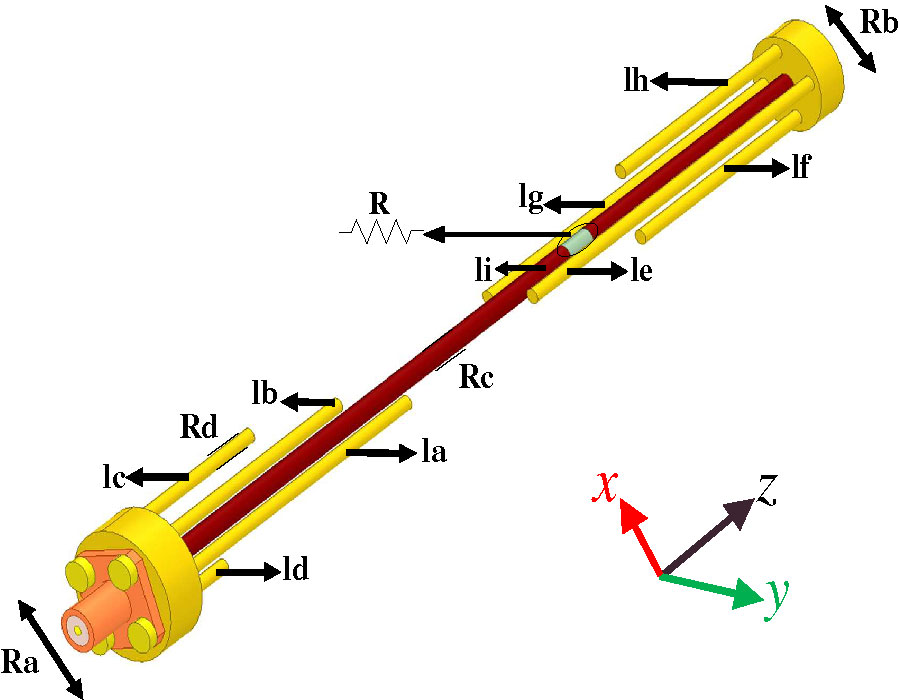
A Novel Compact Dual Open-Sleeve Multiband Antenna for Coal Mine Communication with Large Frequency Ratio
Bo Yin,
Xiangdong Fu,
Lilong Tan,
Xiaolang Sheng and
Peng Chen
In this paper, a novel compact dual open-sleeve multiband monopole omnidirectional antenna specifically designed for coal mine communication is proposed. Its core innovation lies in the structural optimization that enables multiband operation across a wide frequency range. To adapt to the confined mine tunnel environment, the antenna employs an ultra-small diameter design, which poses significant challenges for impedance matching below 1 GHz. Additionally, the substantial electrical size disparity between the sub-1 GHz and above-5 GHz bands further complicates multiband matching. The proposed open-sleeve monopole antenna consists of top and bottom dual open-sleeve structures along with resistive loads. Four length-adjustable thin copper columns replace the conventional sleeve, forming an open-sleeve structure. Through coordinated tuning of the two longest columns in the bottom open-sleeve structure together with the resistor loads, the antenna achieves favorable impedance matching in the low-frequency band (0.515-0.845 GHz). Furthermore, by adjusting the dimensions of the second-longest and shortest columns in the bottom open-sleeve, the antenna covers the 1.370-1.485 GHz and 4.660-6.000 GHz bands, respectively, while tuning the central monopole enables matching in the 2.210-2.525 GHz band. Ultimately, through independent adjustment of the four bottom column lengths and coordinated optimization of the resistor loads, the antenna effectively operates in four bands: 0.515-0.845 GHz, 1.370-1.485 GHz, 2.210-2.525 GHz, and 4.660-6.000 GHz, with the ratio between the lowest and highest operating frequencies reaching 10:1. Simultaneously, the top open-sleeve structure enhances the antenna's gain in the low-frequency band. Measured results show good agreement with simulation, demonstrating a gain of 1.21-4.59 dBi and radiation efficiency of 44%-77.7%. Moreover, the antenna exhibits omnidirectional radiation characteristics. This antenna shows potential for coal mine communication applications and also supports WLAN (2.4/5.2/5.8 GHz), WiMAX (2.3/5.8 GHz), and 5G NR (n5/n12/n28/n71/n79).