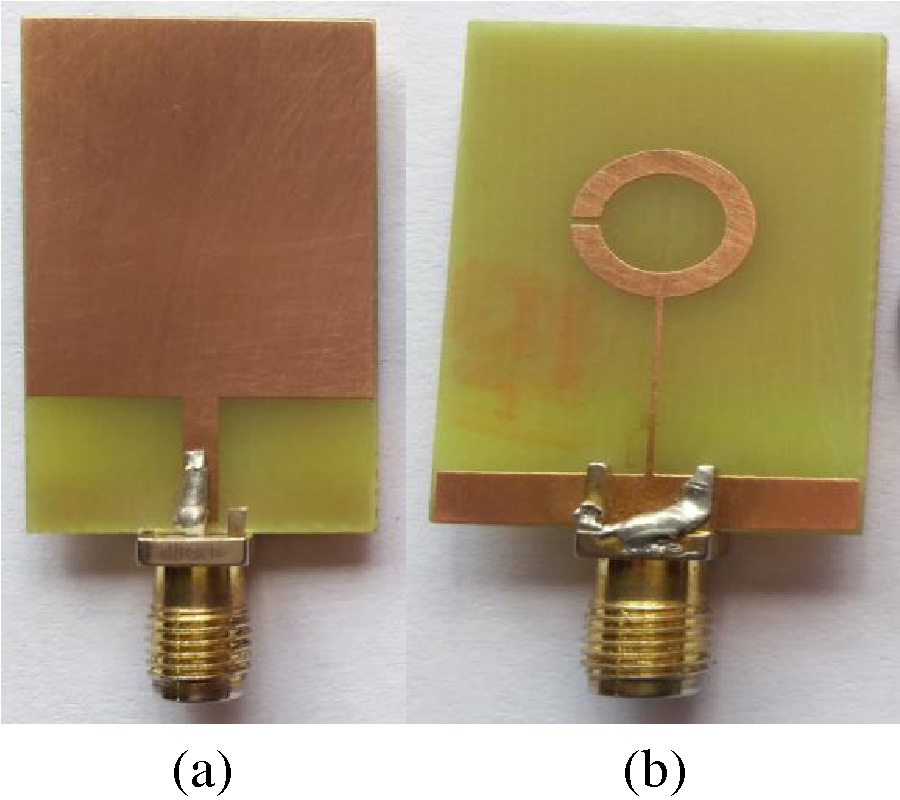
A Tuning Fork Shaped Differential Dipole Antenna with Floating Reflectors
Rida Gadhafi,
Dan Cracan,
Ademola Akeem Mustapha and
Mihai Sanduleanu
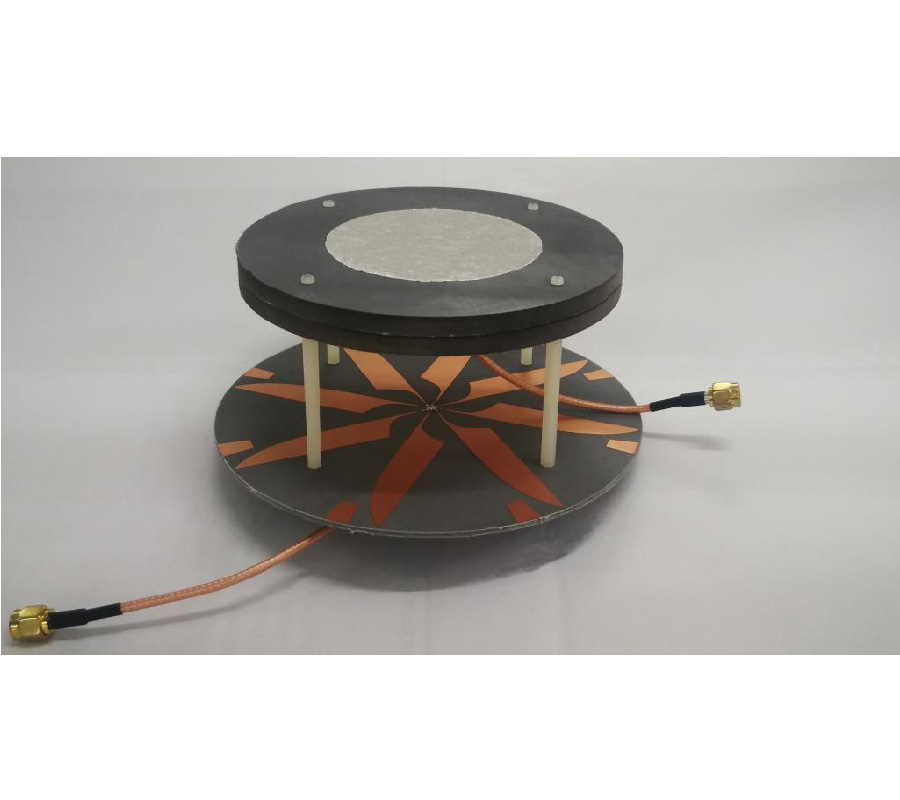
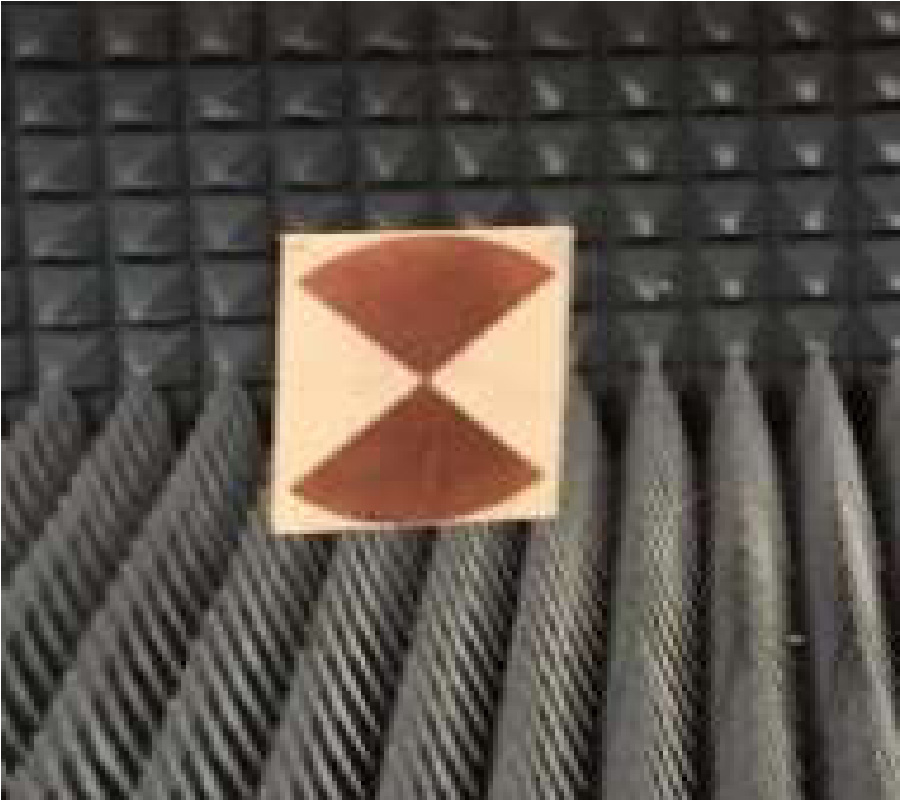
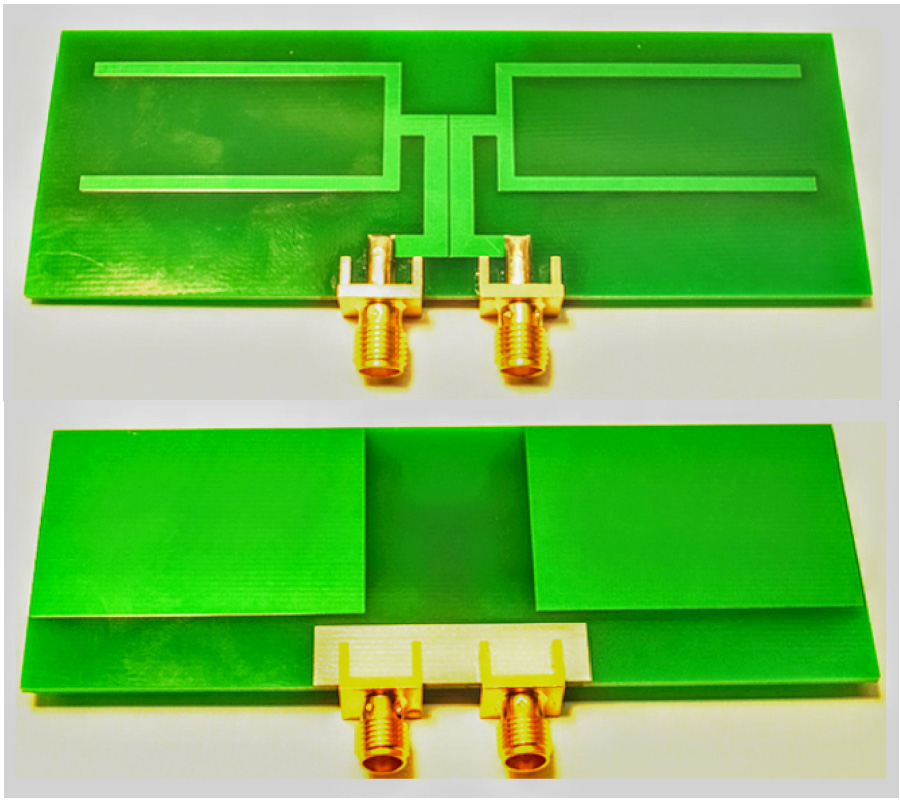
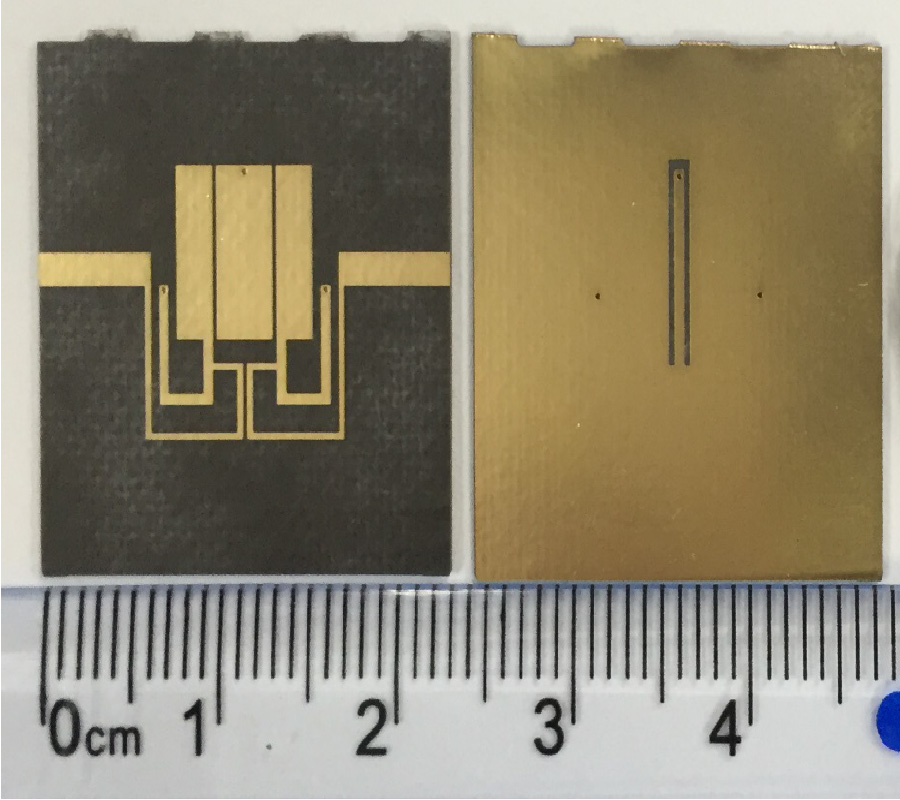
In this letter, a tuning fork shaped, differential dipole antenna, with two floating reflectors, is presented. The dipole antenna resonates at 1.22 GHz and has a fractional bandwidth (FBW) of 16.39% and a differential impedance of 100 Ω. The proposed antenna is composed of quarter wavelength tuning fork shaped dipole arms in the top layer. To improve robustness, while connecting to the differential circuits, two floating reflectors are used on the bottom layer, beneath the dipole arm. This method helps improving the gain by 7%. A microstrip-to-coplanar strip line (CPS) transition is designed to measure the stand-alone differential antenna. The measured gain and efficiency of the antenna are 2.14 dBi and 84%, respectively, at the resonant frequency. The possible targeted applications are circuits with differential inputs/outputs, like energy harvesting circuits, radio frequency tags, wireless communications and any other wireless sensor network nodes. Details of the design along with simulated and experimental results are presented and discussed.