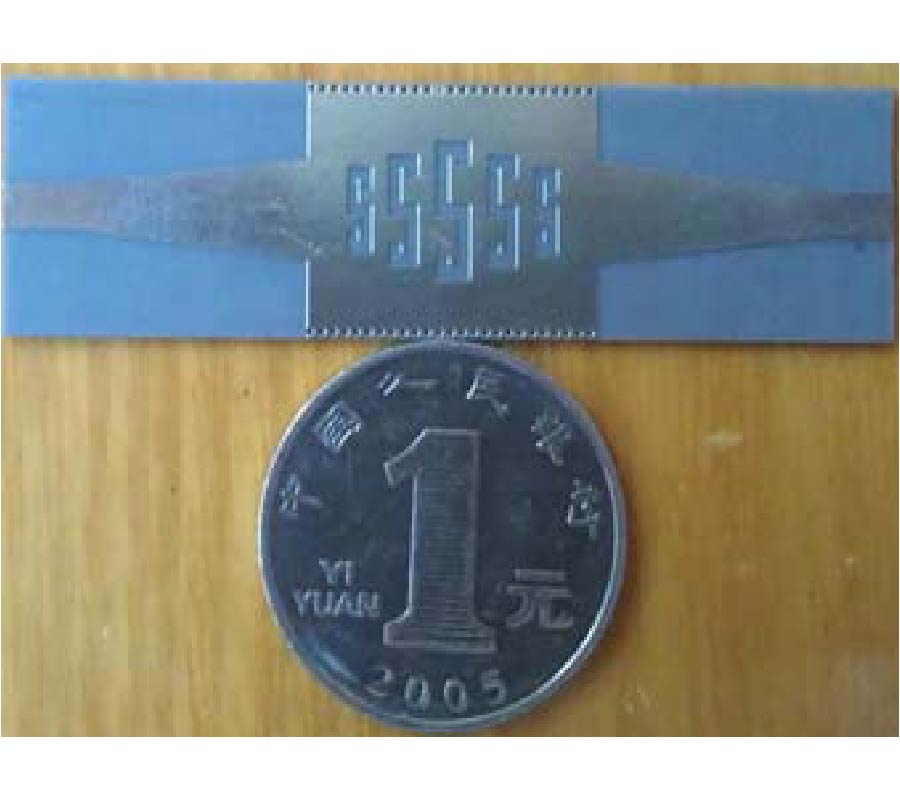
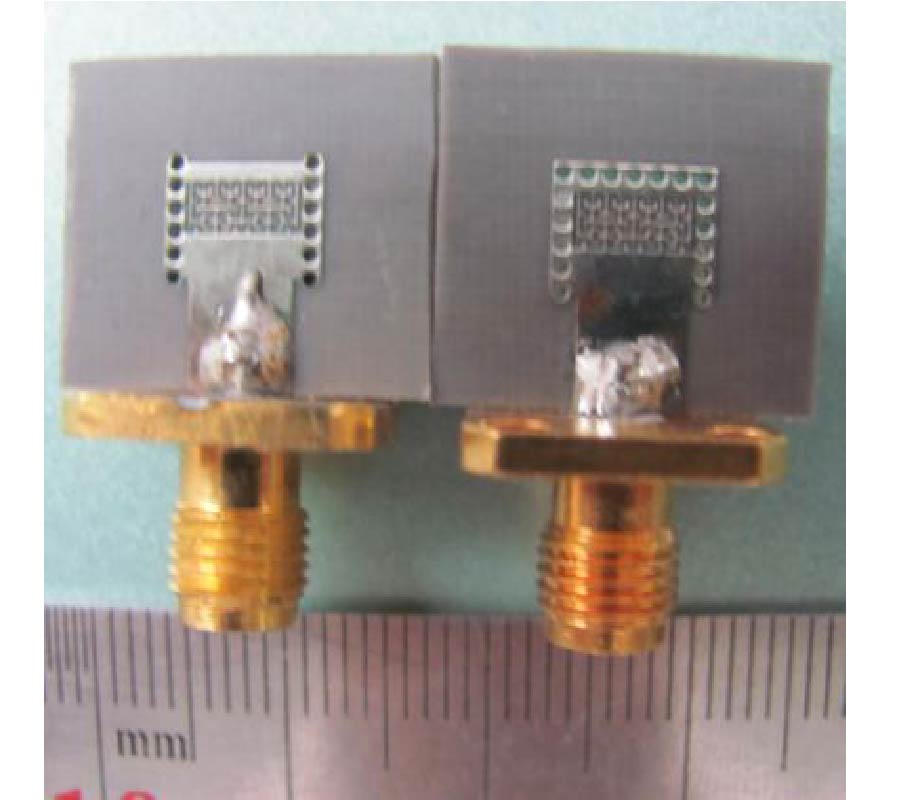
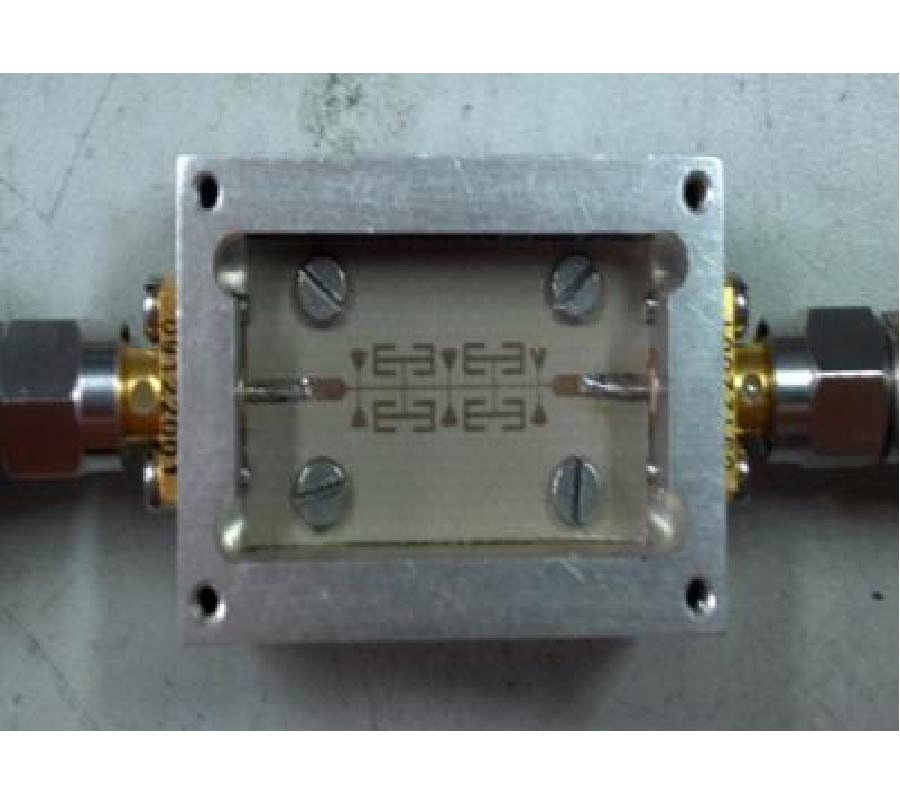
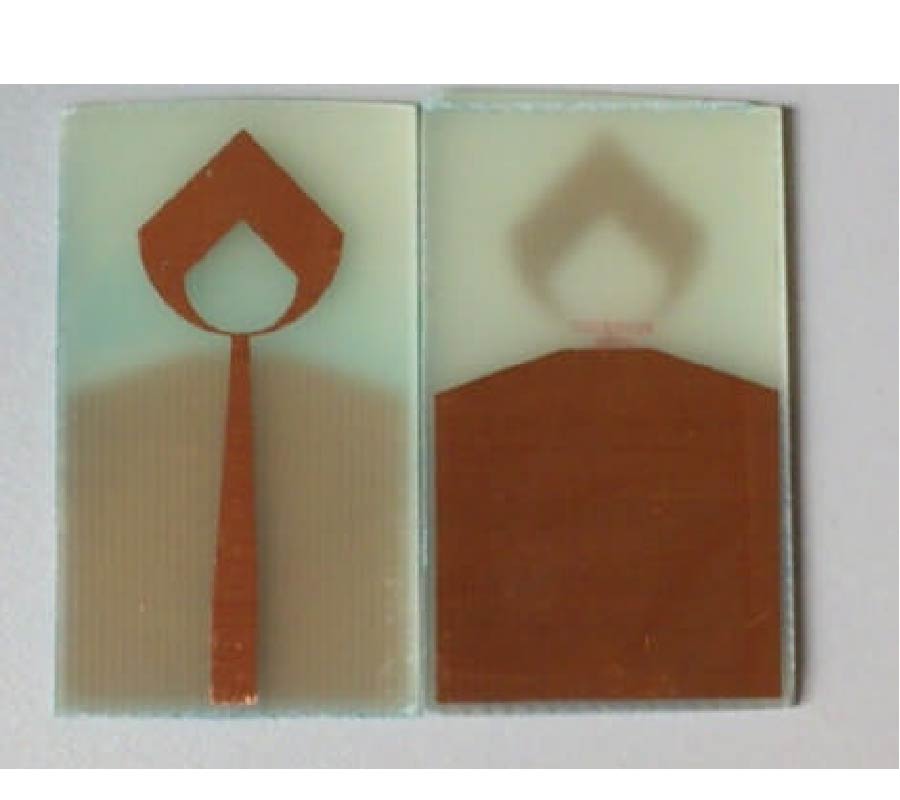
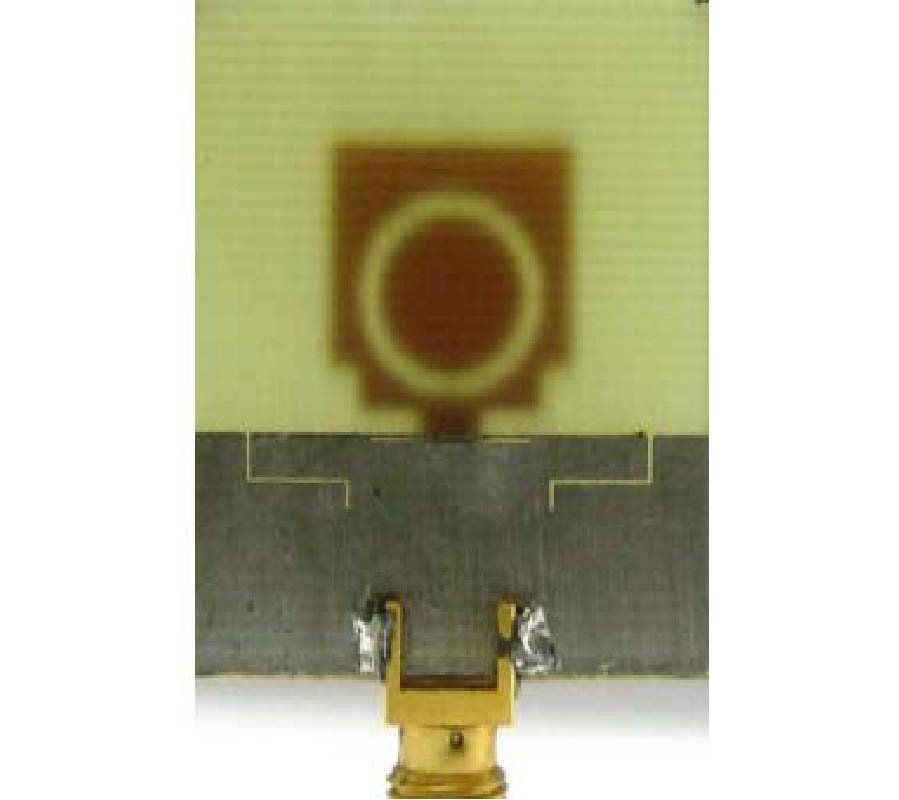
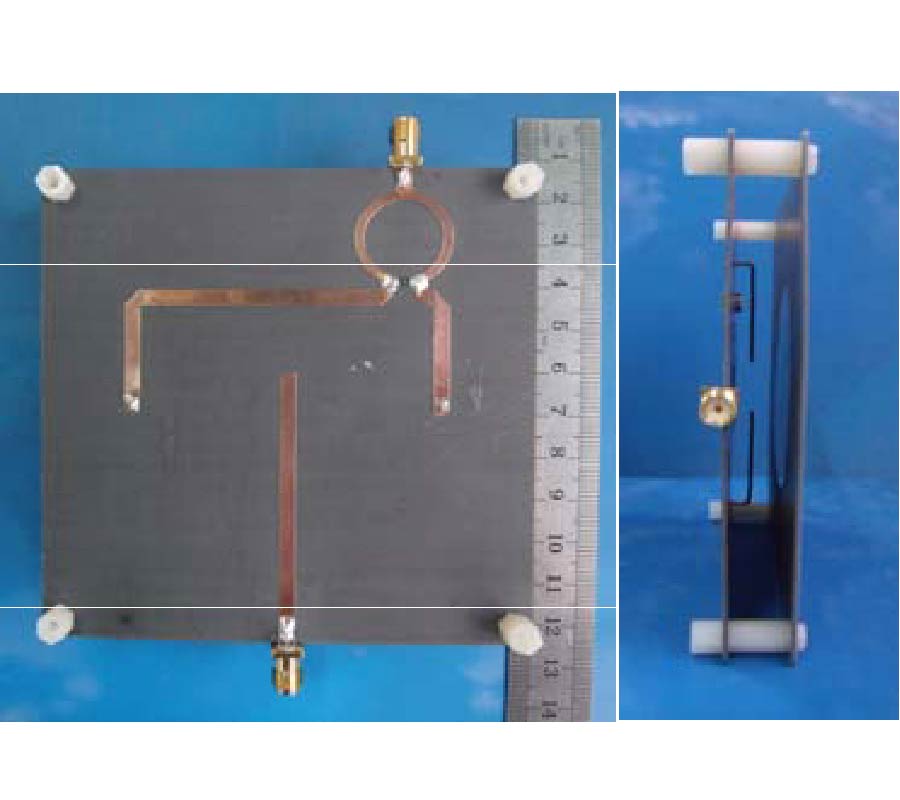
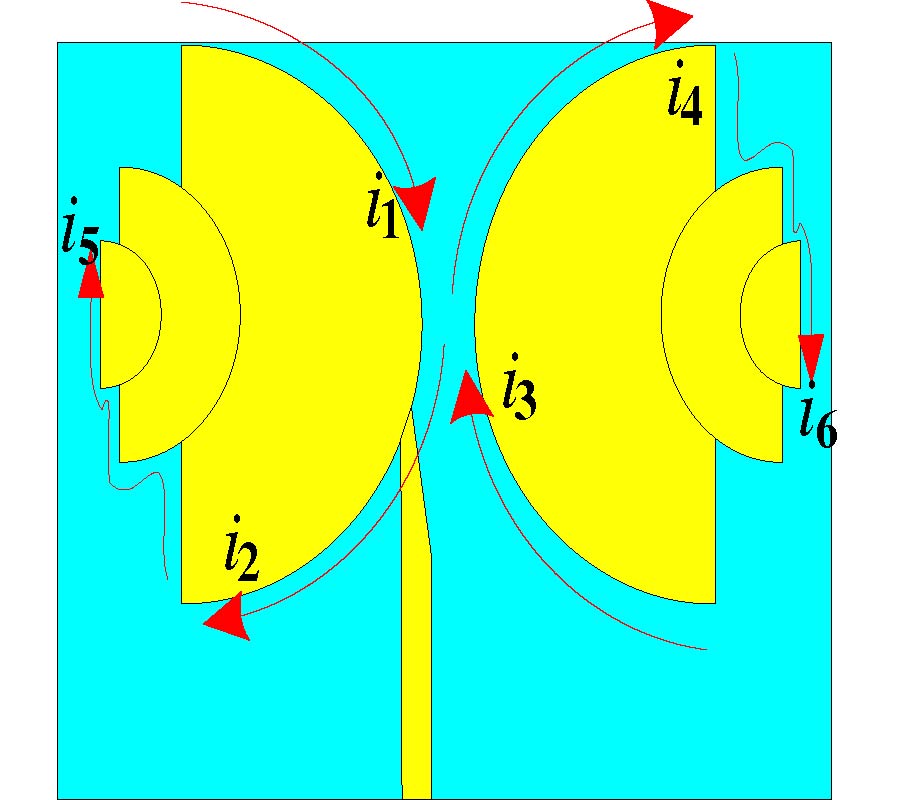
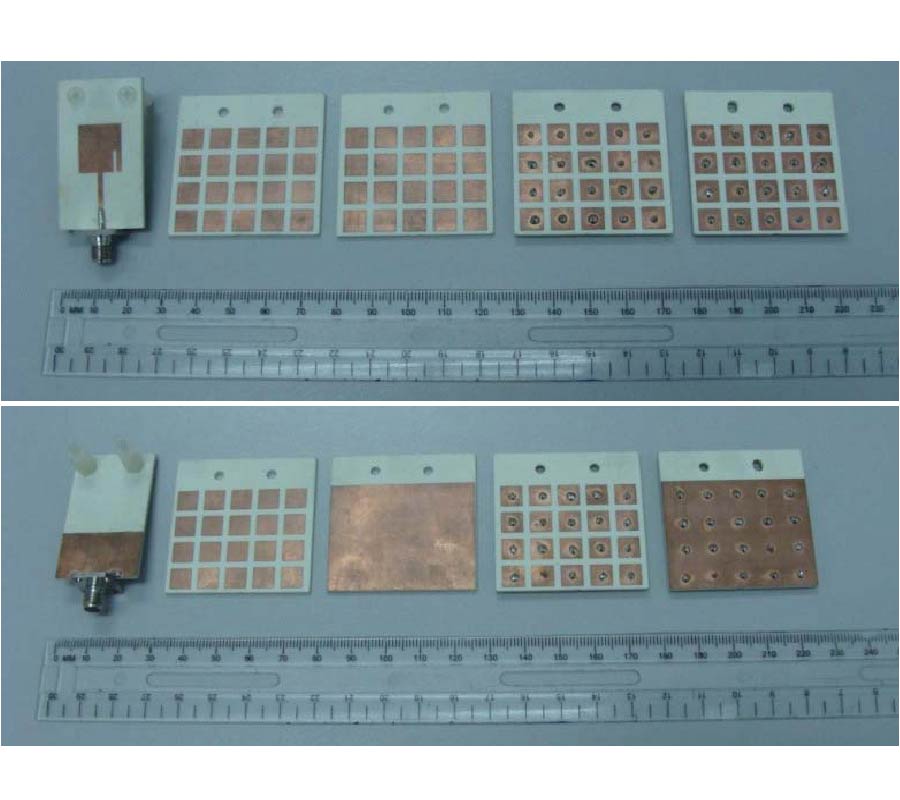
Compact Lowpass Filter with Wide Stopband Using Novel Double-Folded Scmrc Structure with Parallel Open-Ended Stub
Ke Li,
Minghua Zhao,
Yong Fan,
Zhong Bo Zhu and
Wan-Zhao Cui
Nowadays, there is expanding interest in planar compact microstrip filters applied in microwave wireless system nowadays. The compact microstrip resonant cell (CMRC) and spiral compact microstrip resonant cell (SCMRC) are more and more popular in filter design due to their slow-wave and band-stop effects. In this paper, a novel double-folded SCMRC (DSCMRC) is proposed, analyzed and measured, which turns out to have more compact dimensions and distinctly broader stopband than CMRC and SCMRC. Furthermore, an improved DSCMRC circuit with two parallel open-ended stubs that are added into the DSCMRC structure is presented, which could introduce more transmission zeros in the stopband for better out-of-band rejection than the original DSCMRC. The measured results show the excellent performance of the improved DSCMRC circuit structure. Finally, a novel low-pass filter incorporating two improved DSCMRC in series is simulated and measured, which proves to have an excellent performance of out-of-band rejection up to 25 GHz with a really compact circuit size.