A Tunable Left-Handed Metamaterial Based on Modified Broadside-Coupled Split-Ring Resonators
Jiafu Wang,
Shaobo Qu,
Jieqiu Zhang,
Hua Ma,
Yiming Yang,
Chao Gu,
Xiang Wu and
Zhuo Xu
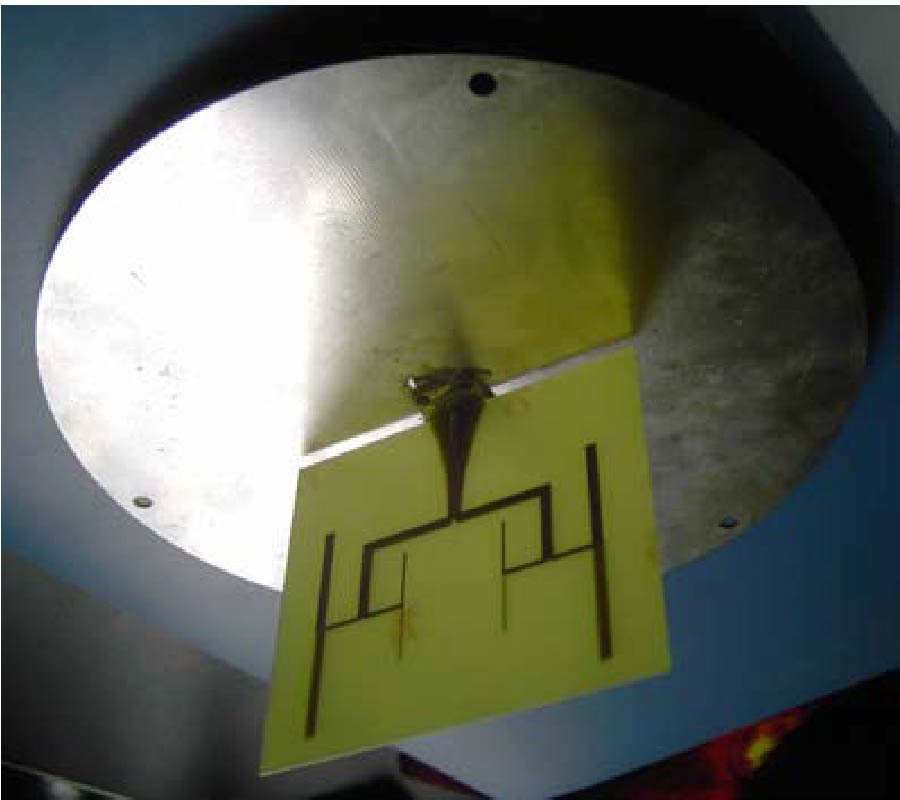
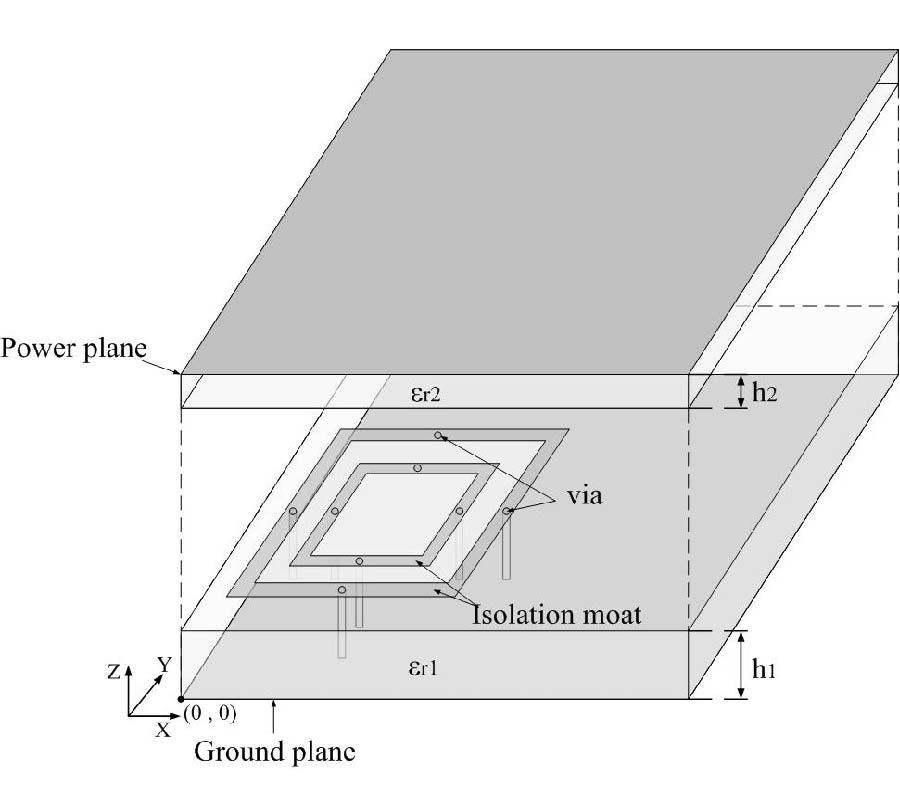
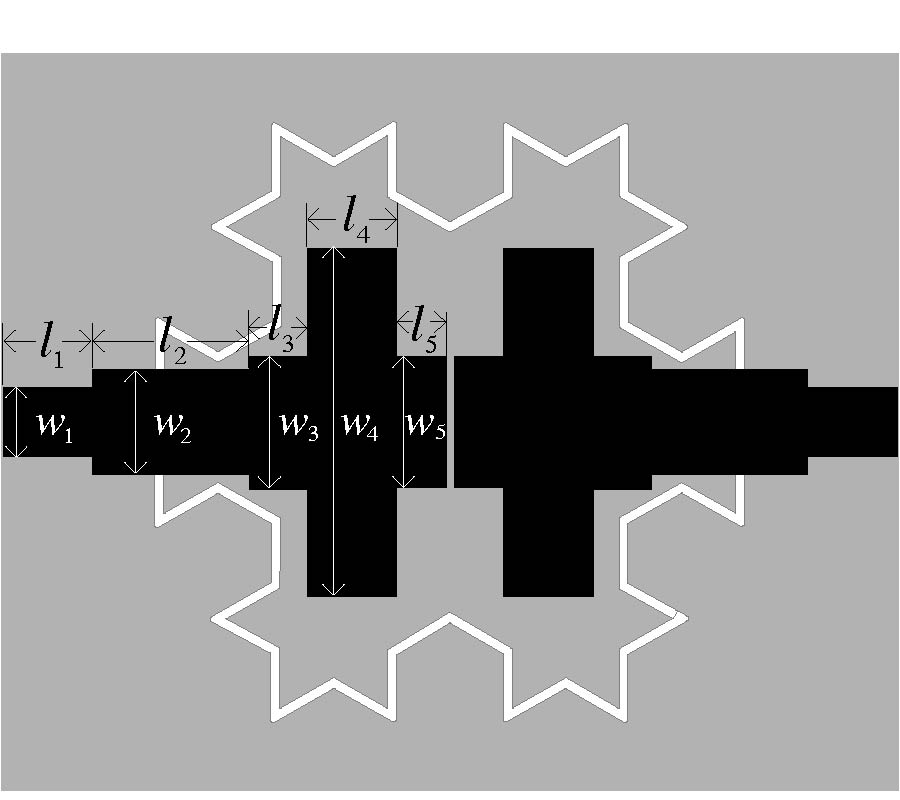
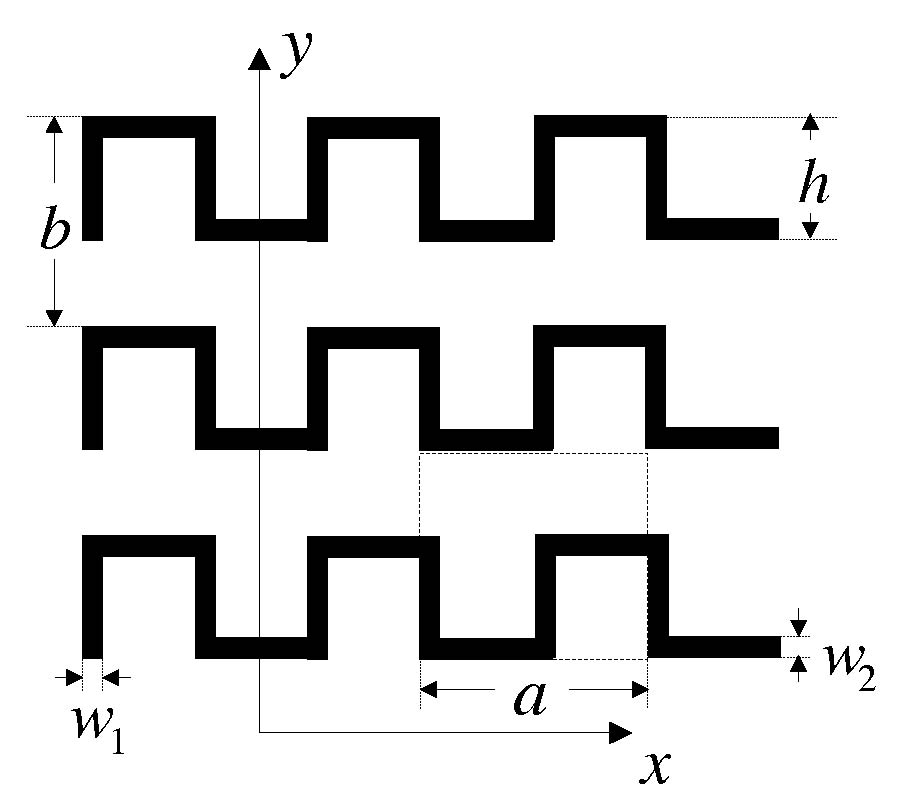
Based on the broadside-coupled split-ring resonator (BC-SRR), a tunable left-handed metamaterial (LHM) was proposed in this paper. The two rings of BC-SRR are etched on two separate substrates so that the coupling between the two rings can be adjusted by slightly slip one of the two substrates relative to the other one. Thus, the magnetic resonance frequency of the modified BC-SRR can be tuned. By combining the modified BC-SRR (MBC-SRR) with continuous conducting wires, a tunable LHM can be realized. The tunable LHM can realize both rough and minor tunings by minor slips along and perpendicular to the gap direction of BC-SRR, respectively. The proposed tunable LHM has many potential applications in microwave devices.