2023-08-01 Latest Published
By Hanhan Guo
Dan Zhang
Yue Juan
Zhendong Ding
Jin He
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 111, 121-129, 2023
Abstract
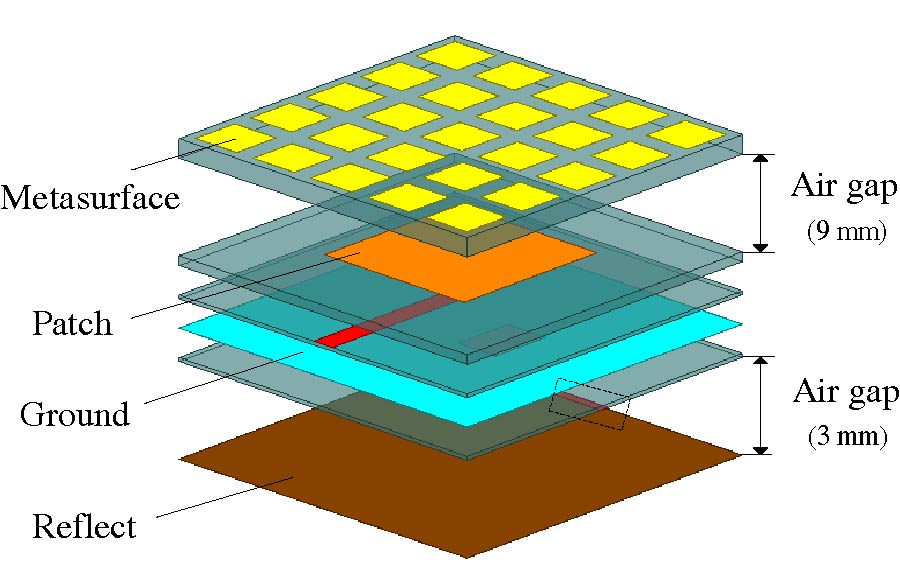
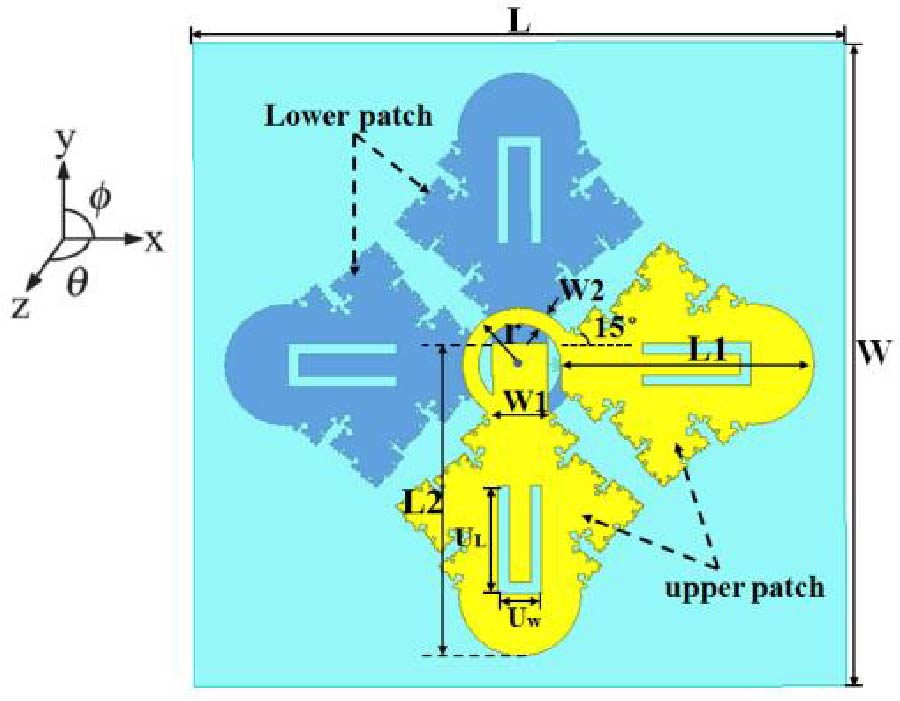
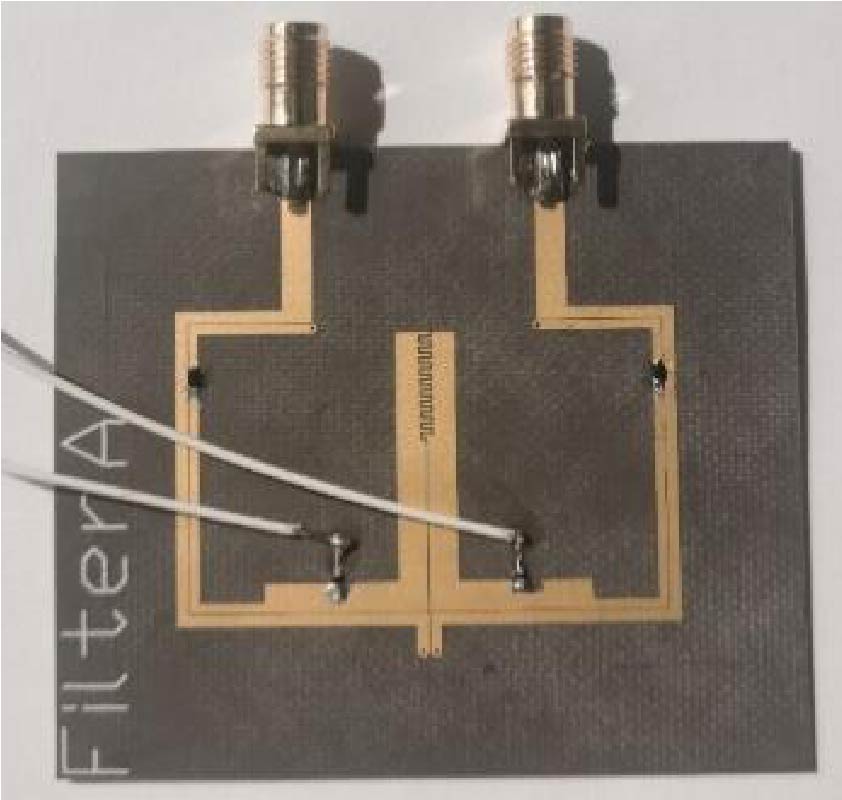
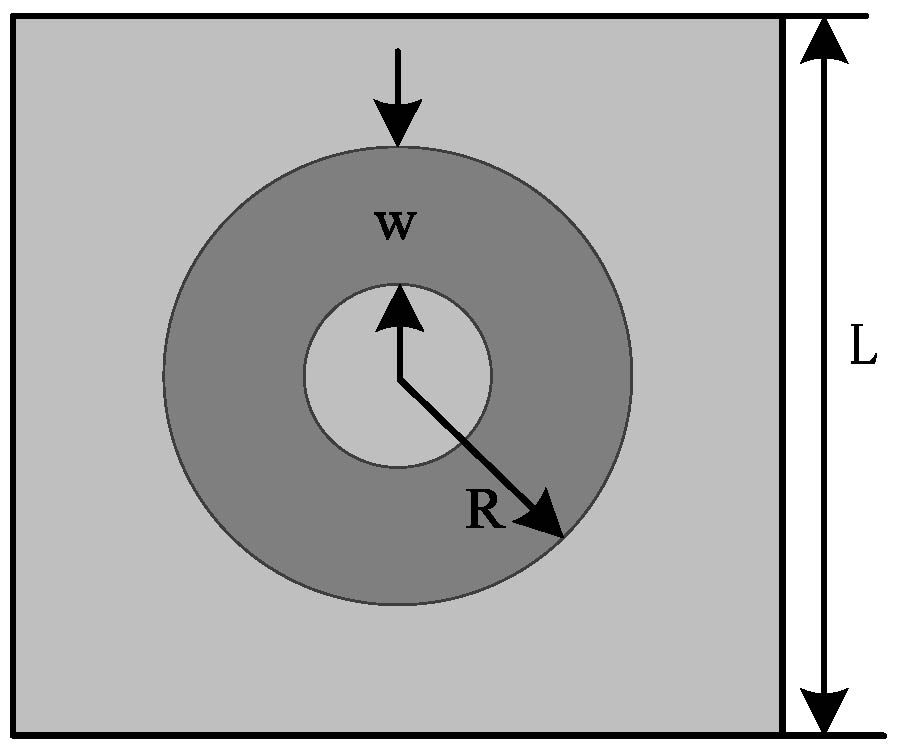
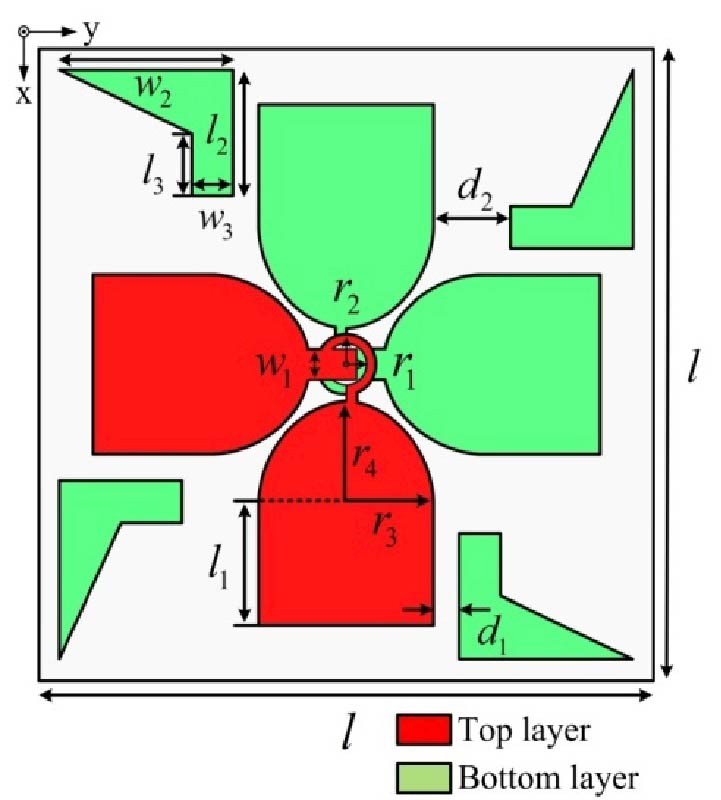
A hybrid-fed dual-polarized antenna with matesurface coverage is proposed in this paper, which can be used for 5G mobile communication base station antennas. By placing the two feeding ports on different layers of dielectric plates in an orthogonal manner, and using electromagnetic coupling and slit coupling for feeding respectively, the antenna can achieve inter-port isolation higher than 35 dB in the operating frequency band. In order to widen the bandwidth and obtain higher gain, the metasurface covering unit is loaded above the patch. The metasurface layer contains an array of 5 × 5 square patch units printed on the top surface of the dielectric plate. The measurement results show that the proposed antenna has an impedance bandwidth of 12% (3.24 to 3.66 GHz). In addition, the antenna obtains a stable gain of about 5.32 dBi at 3.5 GHz. The proposed antenna meets all the requirements of base station antennas and can be a promising candidate for application in 5G base station systems.