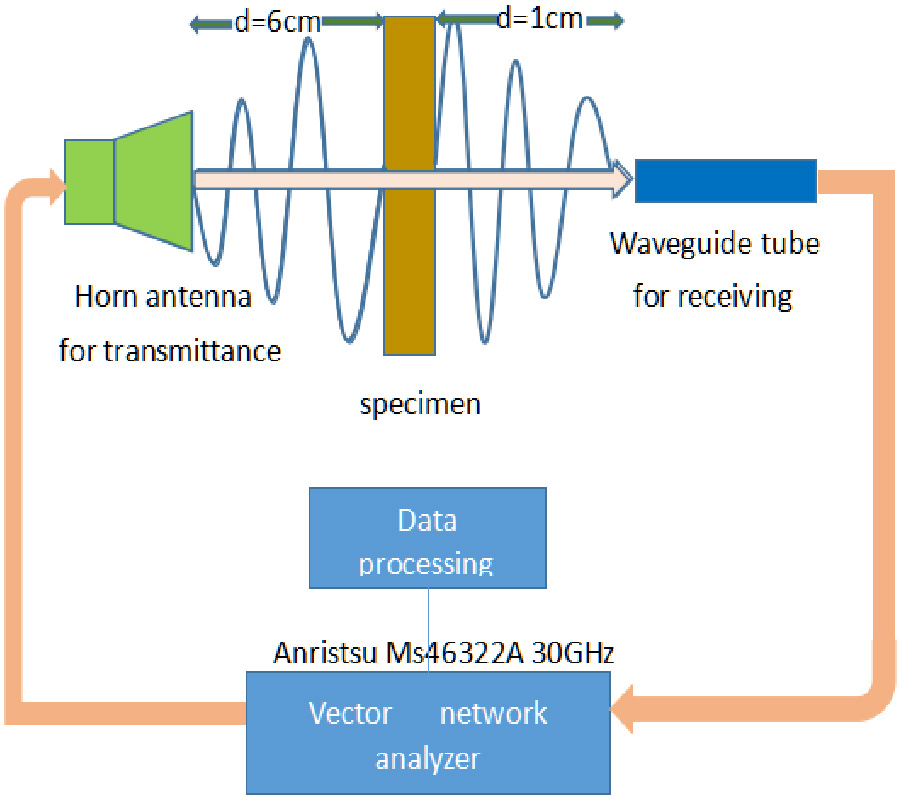
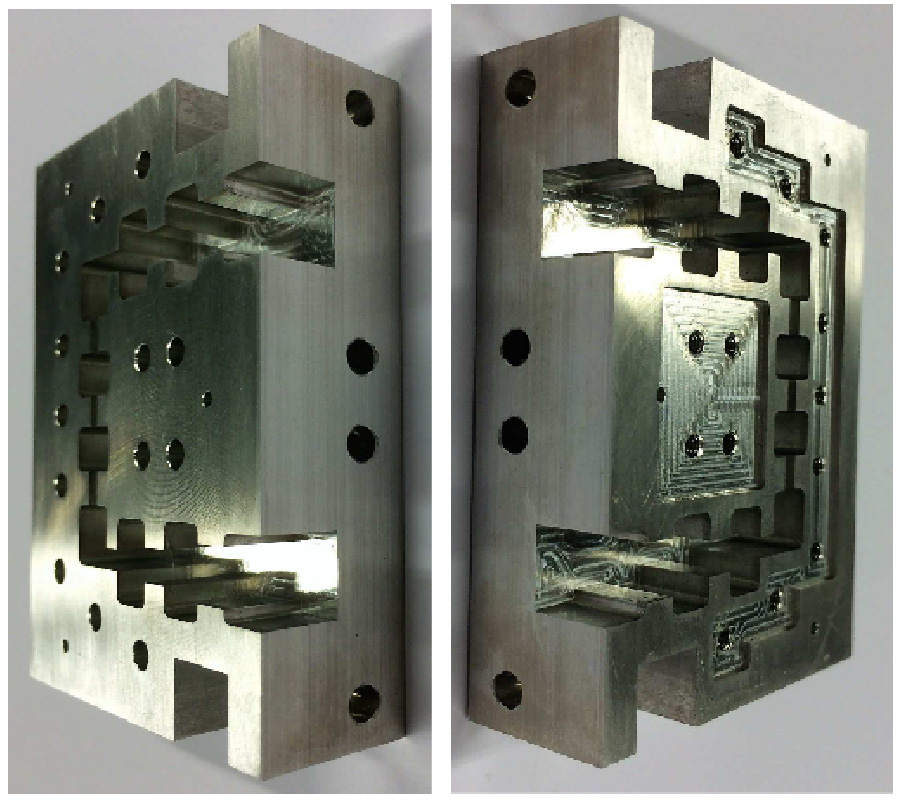
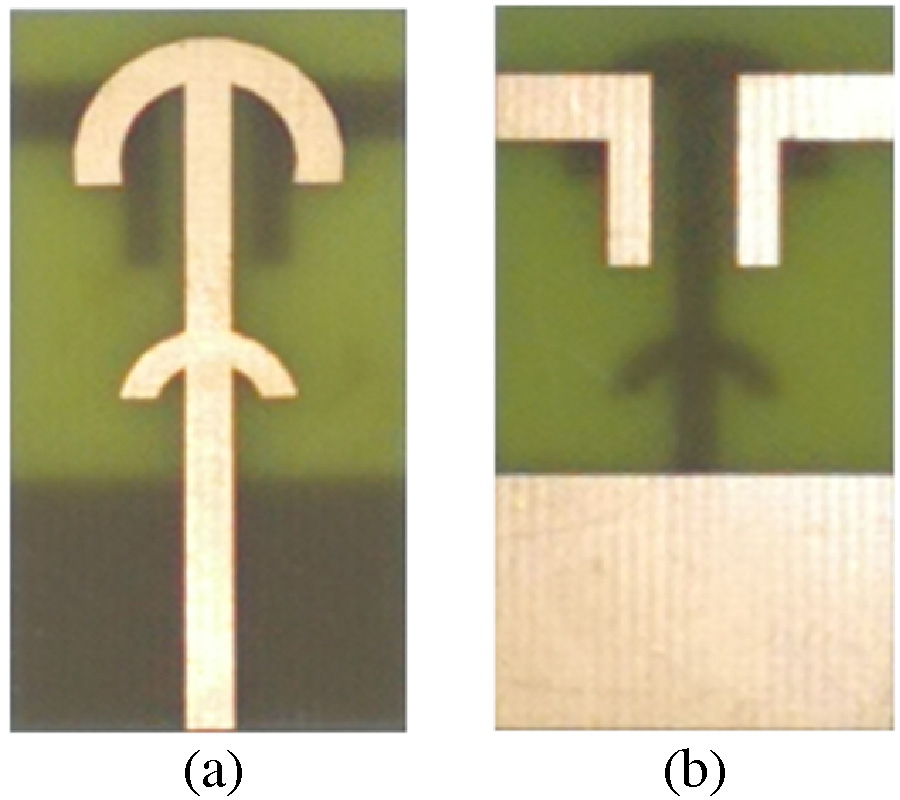
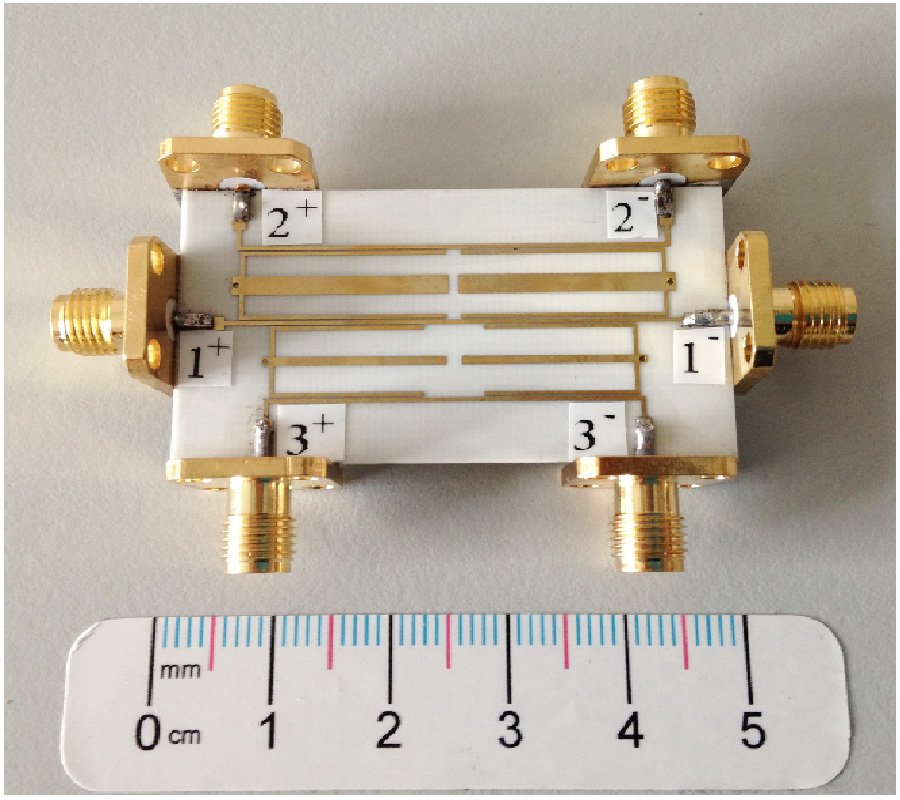
Effect of Superstrate on a Cylindrical Microstrip Antenna
Prasanna Kumar Singh and
Jasmine Saini
A microstrip patch antenna can be readily installed on any non-planar surface due to its conformal property, and this feature enhances its applicability in many areas. Moreover, in some specific applications, it is desirable and mandatory to provide protection of antenna from the unfriendly surroundings. Therefore, the present work focuses on the antenna with a dielectric cover and analyzes its effect on directivity, gain, and bandwidth at various superstrate air gaps. Two antenna models of single and dual elements are considered here separately, and both are conformal to the cylindrical surface. The antenna parameters are studied under varying superstrate gaps with equal intervals up to a quarter wavelength under fixed cylindrical curvature. It is noted that there is a significant improvement of 6% and 12% in bandwidth at quarter wavelength gap as compared to simple single and dual antenna models without dielectric loading, respectively. Also, both the calculated and measured results show the other important constructive effect of superstrate on the antenna performance.