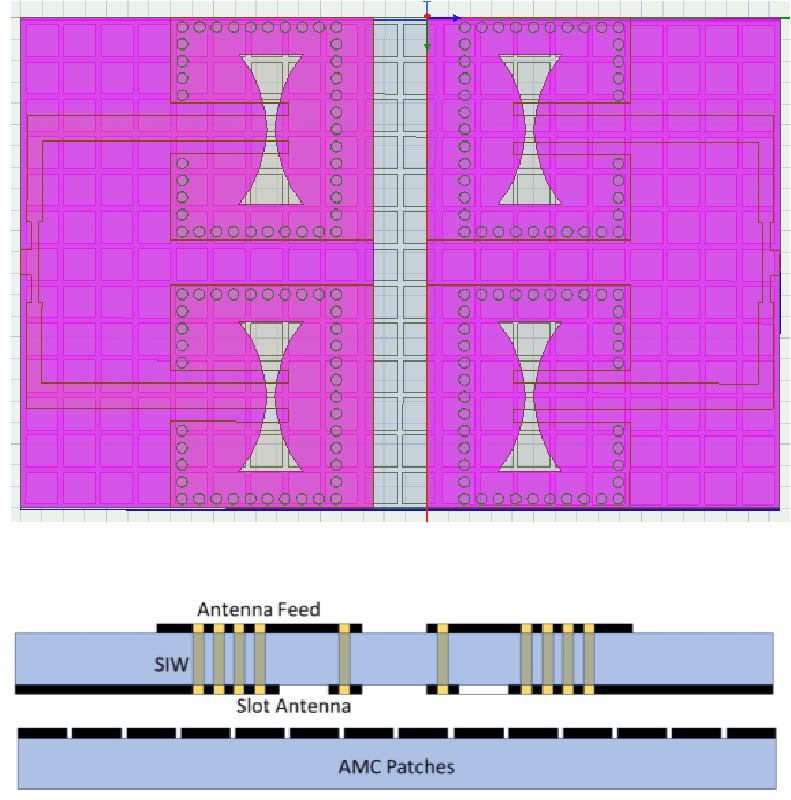
Parameter Enhancement of Vivaldi Slot 1×2 Array MIMO Antenna Using AMC
Ameet Mukund Mehta,
Shankar B. Deosarkar,
Anil Bapusa Nandgaonkar and
Avinash R. Vaidya
A wide band, high gain 1 × 2 array Vivaldi shaped slot Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) antenna with square shaped periodic Artificial Magnetic Conductor (AMC) placed beneath the antenna for applications in X band is presented. A two-port MIMO antenna backed by AMC patches is designed and realized for enhanced gain and bandwidth. The single antenna 1 × 2 array has electrical dimensions of 1.57λr × 1.13λr × 0.027λr. The designed antenna structure has bandwidth of 1.39 GHz (8.79 GHz-10.18 GHz) with a percentage bandwidth of 14.65% and Gain of 11.67 dBi. The edge to edge distance between the MIMO antenna elements is 5 mm (λr/4). The periodic AMC patches improve vital MIMO antenna performance metrics like Isolation, Envelope Correlation Coefficient (ECC), Diversity Gain (DG), Channel Capacity Loss (CCL) and radiation pattern. The unit cell analysis of periodic square AMC patch and a polynomial regression model to find the best goodness of fit for Gain-Bandwidth product versus square AMC patch size is studied. Antenna gain variation seen over the complete bandwidth is < 1 dBi which makes it a flat gain response antenna. The proposed high-gain, wide-band 1 × 2 Vivaldi-slot SIW MIMO antenna with AMC is suitable for X-band radar, point-to-point high-throughput wireless links, and compact platform communication systems requiring robust diversity performance.