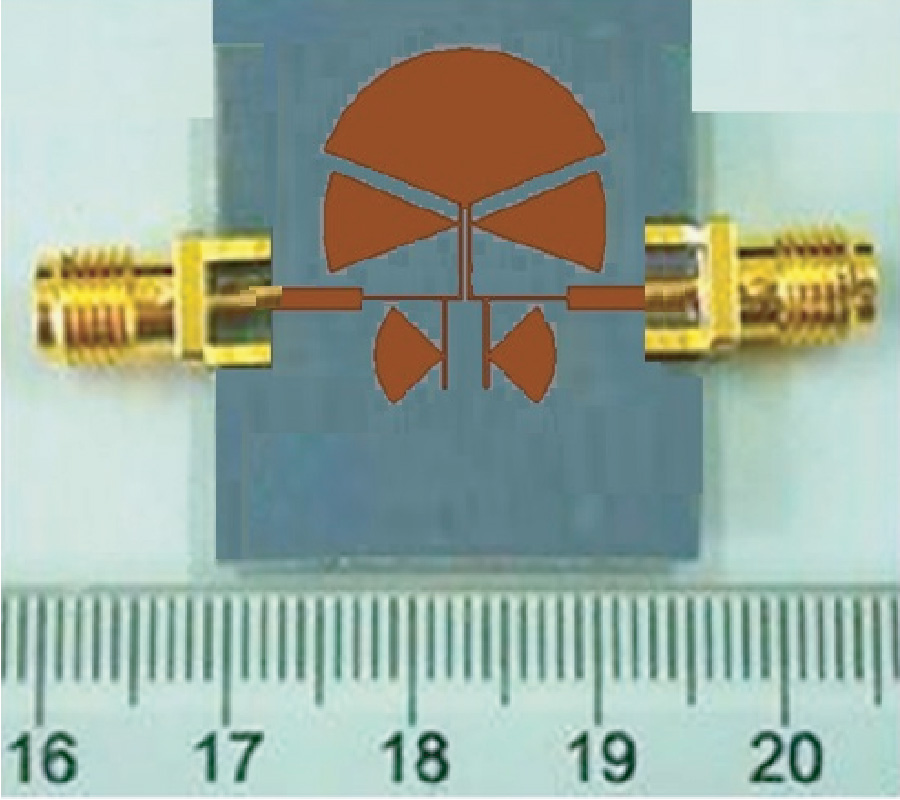
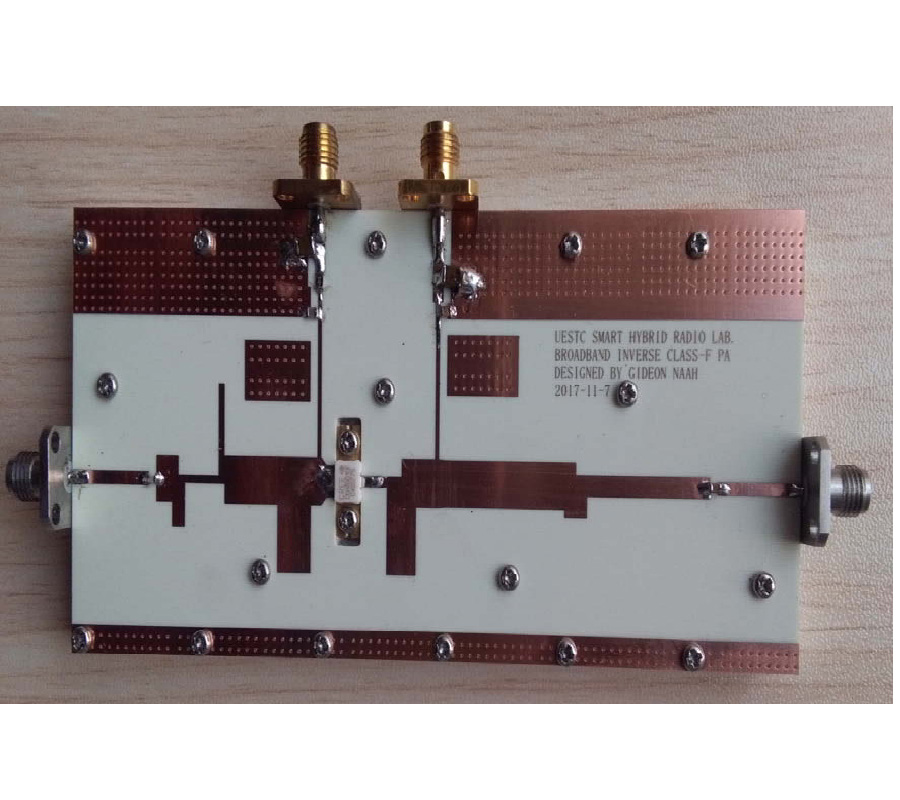
Broadband Class-j/F-1 Continuum Mode Design Utilizing Harmonic Efficiency Selectivity Circuit
Gideon Naah,
Songbai He,
Weimin Shi,
Bin Song,
Tian Qi and
Shaddrack Yaw Nusenu
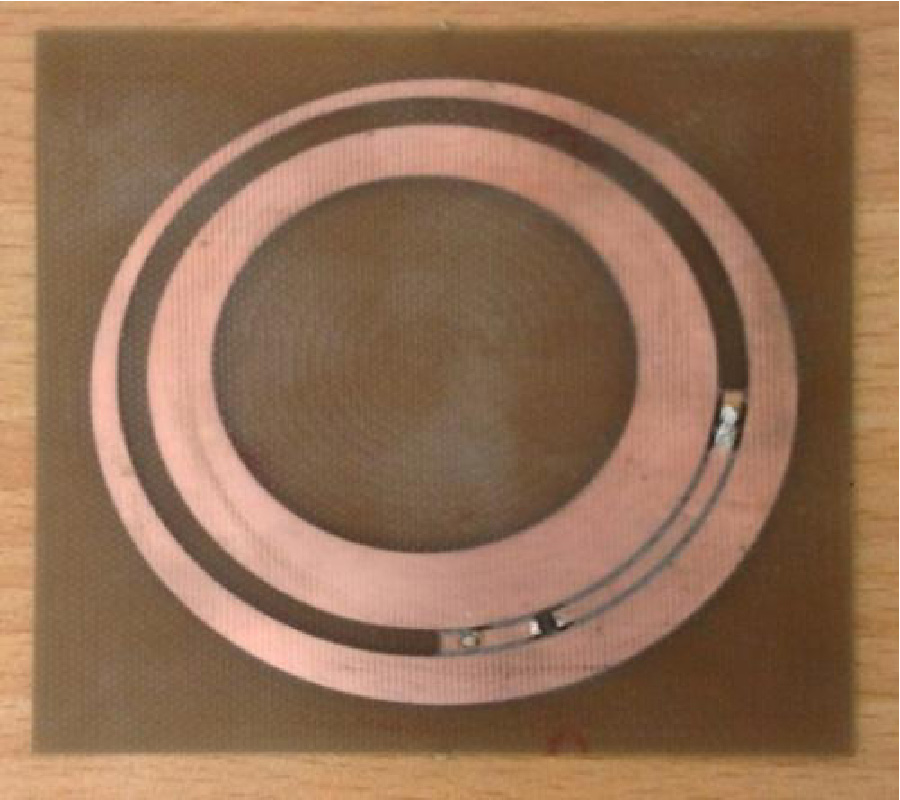
This paper proposes a harmonic efficiency selectivity circuit (HESC) for achieving a broadband Class-J/F-1 continuum mode power amplifier (PA) with enhanced efficiency. Design equations are derived through continuum mode condition analysis and are used in implementing the HESC. The implemented HESC topology is then used in attaining the broadband Class-J/F-1 continuum mode PA. A theoretical parameter termed harmonic-alpha (ρh) acting as a sub-unit structure in HESC is introduced. Considering harmonic losses, ρh possesses a lookup table containing information on the harmonics. ρh operates in unison with the HESC in selecting the suitable harmonics with the best efficiencies. With ρh, the relationship among the HESC, the optimal impedance at the device's drain, and the terminal load impedance is defined for a greater freedom of harmonic impedance solutions space, efficiency improvement, and bandwidth extension, thus, indicating an increased flexibility in the design of broadband continuum mode PAs. This method is validated with a realized PA prototype operating from 1.3 to 2.4 GHz corresponding to a fractional bandwidth of 59.5%. The experimental results under continuous wave signals indicate that 79% peak efficiency, 42.68 dBm peak output power, and 16.96 dB peak gain are recorded. Moreover, at 1.7 GHz, when being tested with modulated signals at an average output power of 34.83 dBm, the lower and higher adjacent channel power ratios (ACPRs) without digital predistortion (DPD) are -34.9 dBc and -33.9 dBc, respectively, and a drain effifficiency (DE) of 45% is recorded. With DPD, -50.8 dBc and -50.3 dBc are respectively obtained at lower and higher ACPRs at an average output power of 34.6 dBm, and a DE of 44% is achieved.