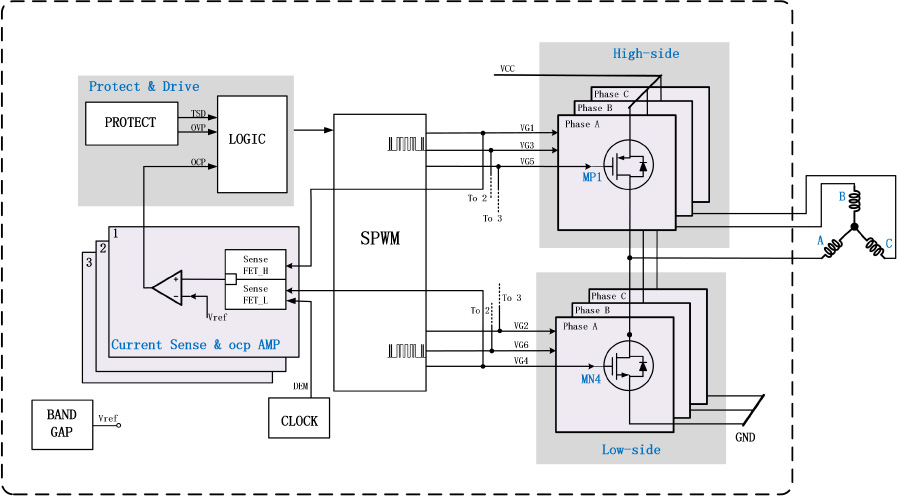
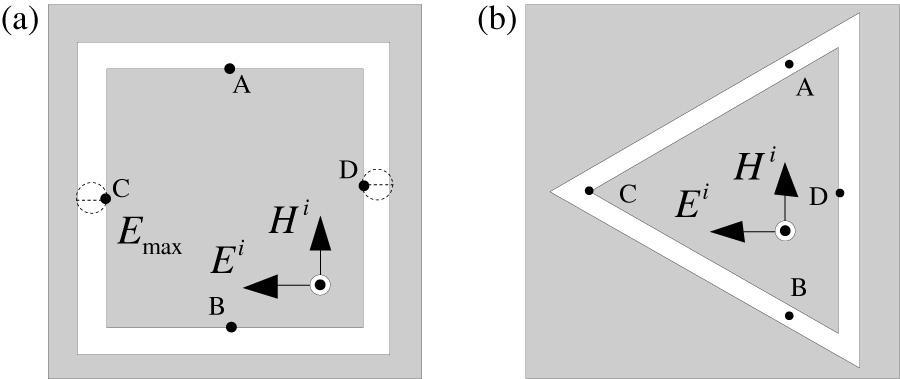
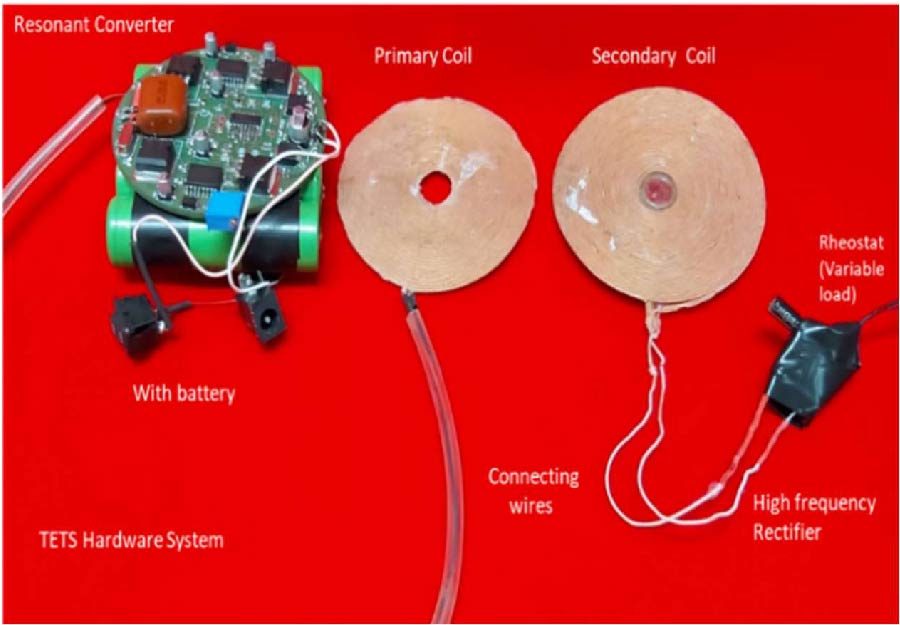
Li Liu,
Yufeng Liu,
Zhiyuan Yang and
Liping Han
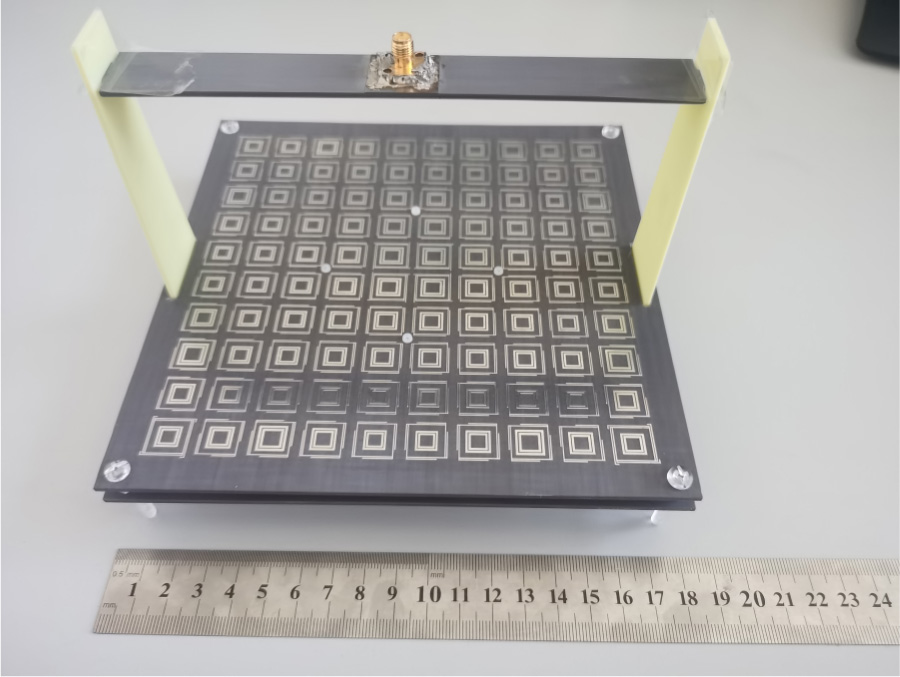
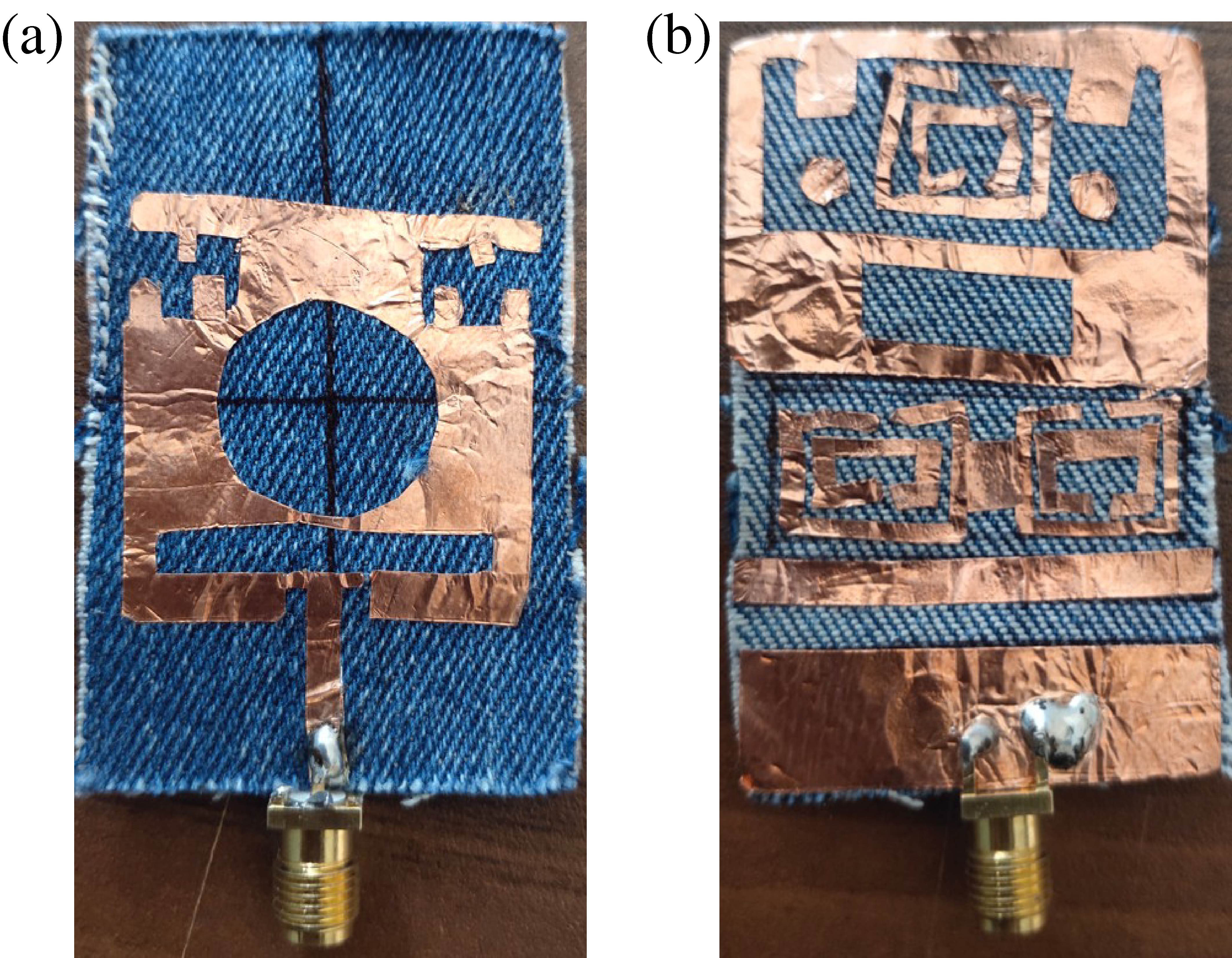
A single-layer reflectarray antenna working at C- and X-bands is designed in this paper. The proposed reflectarray element is mainly composed of three square rings. Four phase delay lines are attached to the outer ring to obtain the phase shift at C-band, and the inner two square rings are utilized to extend the phase range at X-band. The phase shift of the element reaches up to 375° and 560° at 5.9 GHz and 10.4 GHz, respectively. The cross-polarization level of the reflectarray is effectively suppressed by using a mirror symmetric element arrangement. To experimentally validate the proposed design, a center-fed dual-band prototype reflectarray with the size of 180 mm×180 mm is designed, fabricated, and tested. The measured peak gains are 16.5 dBi at 6.2 GHz and 17.1 dBi at 10.3 GHz, respectively. Besides, the measured 1-dB gain bandwidth is 9.15% (5.83-6.37 GHz) at the lower band and 3.27% (10.12-10.46 GHz) at the upper band, respectively.
16Dual-band shared aperture reflectarray and patch antenna array for s- and ka-bandsSerup, Daniel Edelgaard and Pedersen, Gert Frolund and Zhang, Shuai2340-2345SerupDaniel EdelgaardGert Frolund Pedersen, Shuai ZhangIEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation7023402345Mar.2022journal10.1109/TAP.2021.31111713 Moreover, the cross polarizations at both bands are under -21 dB.