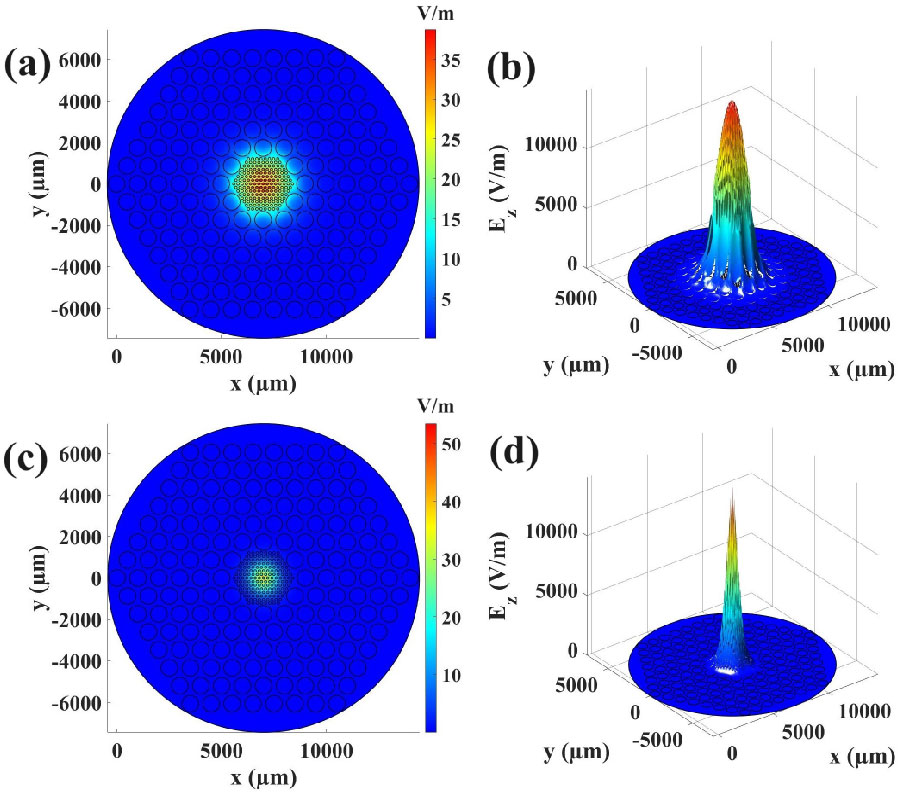
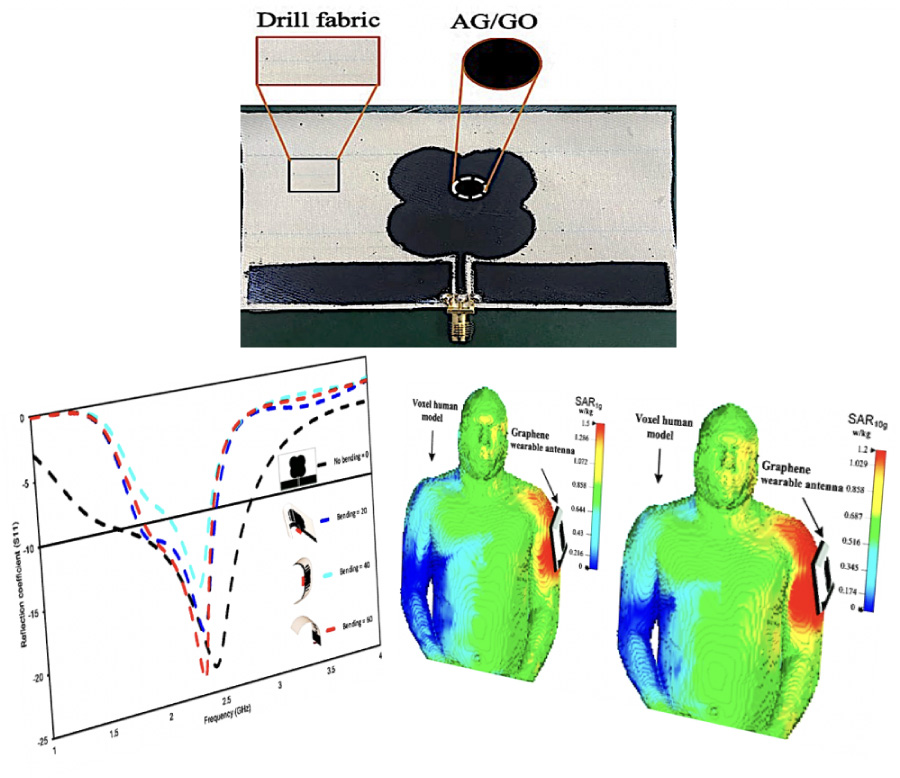
SAR Flexible Antenna Advancements: Highly Conductive Polymer-Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanocomposites
Ahmed Jamal Abdullah Al-Gburi,
Mohd Muzafar Ismail,
Naba Jasim Mohammed and
Thamer A. H. Alghamdi
In the past, copper served as the material for conductive patches in antennas, but its use was limited due to high costs, susceptibility to fading, bulkiness, environmental sensitivity, and manufacturing challenges. The emergence of graphene nanotechnology has positioned graphene as a viable alternative, offering outstanding electrical conductivity, strength, and adaptability. In this investigation, graphene is employed to fabricate conductive silver nanocomposites. The silver-graphene (Ag/GO) sample exhibits an electrical conductivity of approximately 21.386 S/cm as determined by the four-point probe method. The proposed flexible antenna, characterized by four carefully selected cylindrical shapes were used to construct the antenna patch. for enhanced bandwidth, resonates at 2.45 GHz. It achieves amazing performance characteristics, with a high gain of 11.78 dBi and a return loss greater than -20 dB. Safety considerations are addressed by evaluating the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR). For an input power of 0.5 W, the SAR is calculated to be 1.2 W/kg per 10 g of tissue, affirming the safety of integrating the suggested graphene flexible antenna into flexible devices. In this study, the bending of the antenna was assessed by subjecting the structure to bending at various radii and angles along both the X and Y axes. These findings underscore the promising utility of Ag/GO nanocomposites in the development of flexible antennas for wireless systems.