2016-09-12 Latest Published
By Mayank Kumar Chaudhari
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 49, 211-219, 2016
Abstract
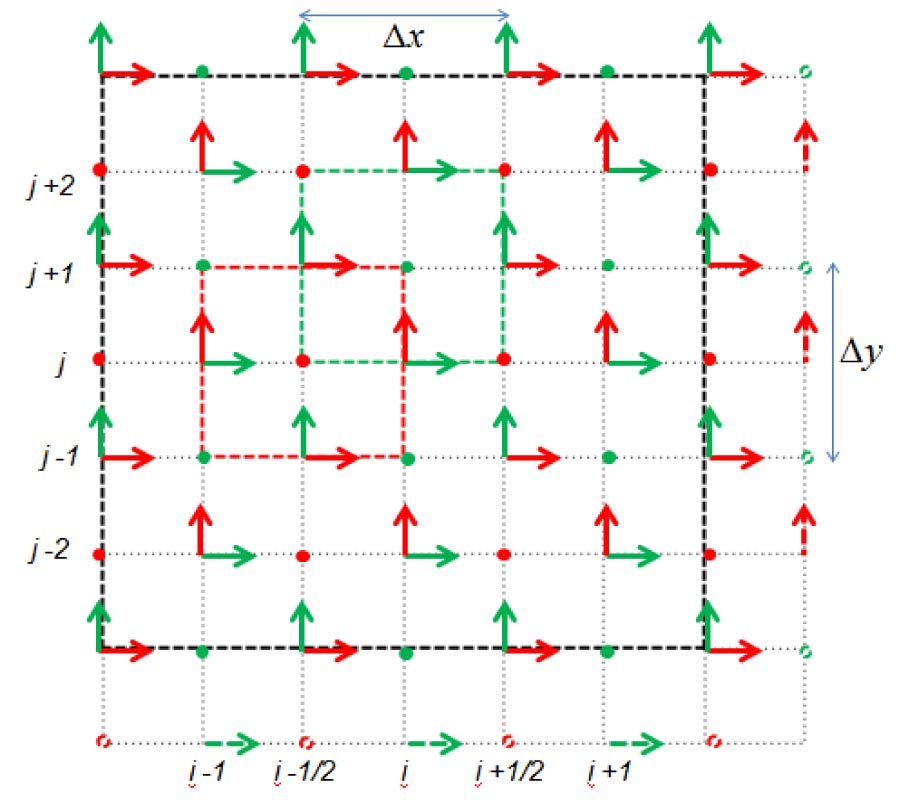
Photonic band gaps of plasma metallic photonic crystals can be tuned dynamically by subjecting it to external magnetic field leading to variety of applications. Dispersion characteristics of 2D photonic crystals are often studied by Finite Difference Time Domain (FDTD) method based on standard Yee's grid discretization schema, in which x- and y-components of fields are defined on different edges of the Yee's cell. However, finite difference equations for electromagnetic wave propagation in magnetized plasma involve interdependence of polarization currents and electric field in a manner that requires both x- and y-components of fields to be evaluated at the same spatial location. A non-conventional discretization technique is presented in which x- and y-components of fields are evaluated at the same spatial location. In this paper analysis of magnetized plasma metallic photonic crystals (PMPC) is presented using the new grid. However, the proposed discretization scheme can be used to introduce magnetized plasmas in any type of structures that can be studied on the basis of standard Yee's grid. For example, topics such as photonic band gap (PBG) cavities based on PMPC, PBG waveguides involving plasma, meta-materials, etc. can be very effectively studied using the approach presented in this paper. Interesting results are found when PMPC is subject to external magnetic field. Several new bands including two dispersion-less flat bands appear and the existing bands with an exception of first band slightly shift upward when PMPC is subjected to an external transverse magnetic field. The location of flat bands and the location and width of forbidden band gaps can be controlled by external magnetic field as well as plasma parameters. New band gaps appearing for lower r/a for magnetized PMPC can be utilized for several applications such as PBG cavity design for gyrotron devices.