2021-03-22 Latest Published
By Ahmed Imad Imran
Taha Ahmed Elwi
Ali J. Salim
Progress In Electromagnetics Research M, Vol. 101, 219-239, 2021
Abstract
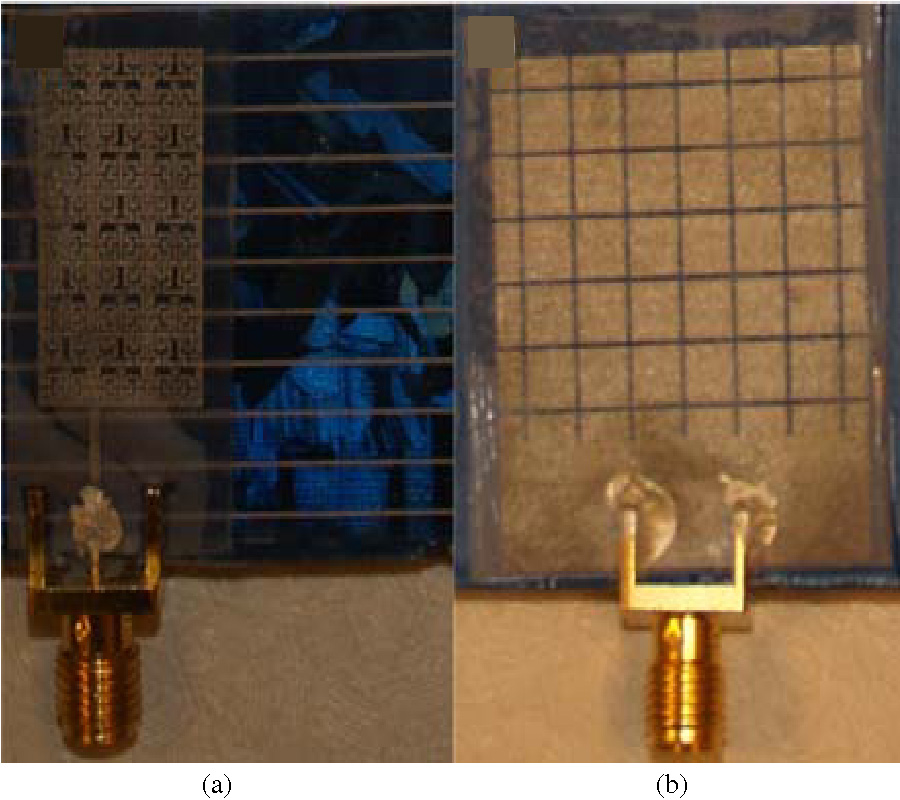
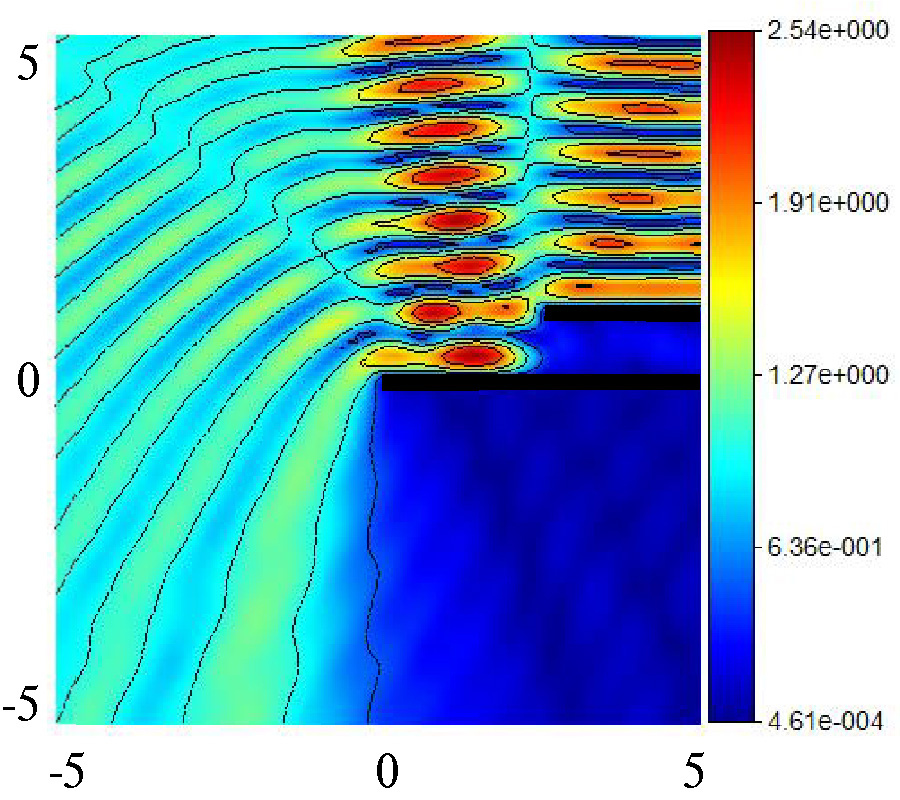
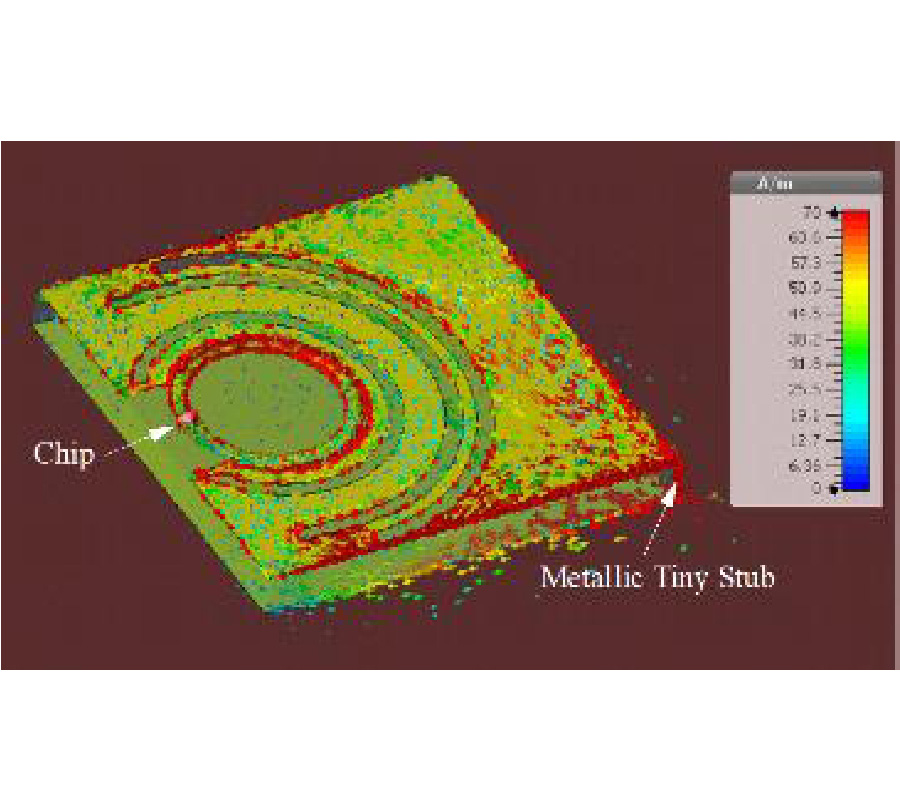
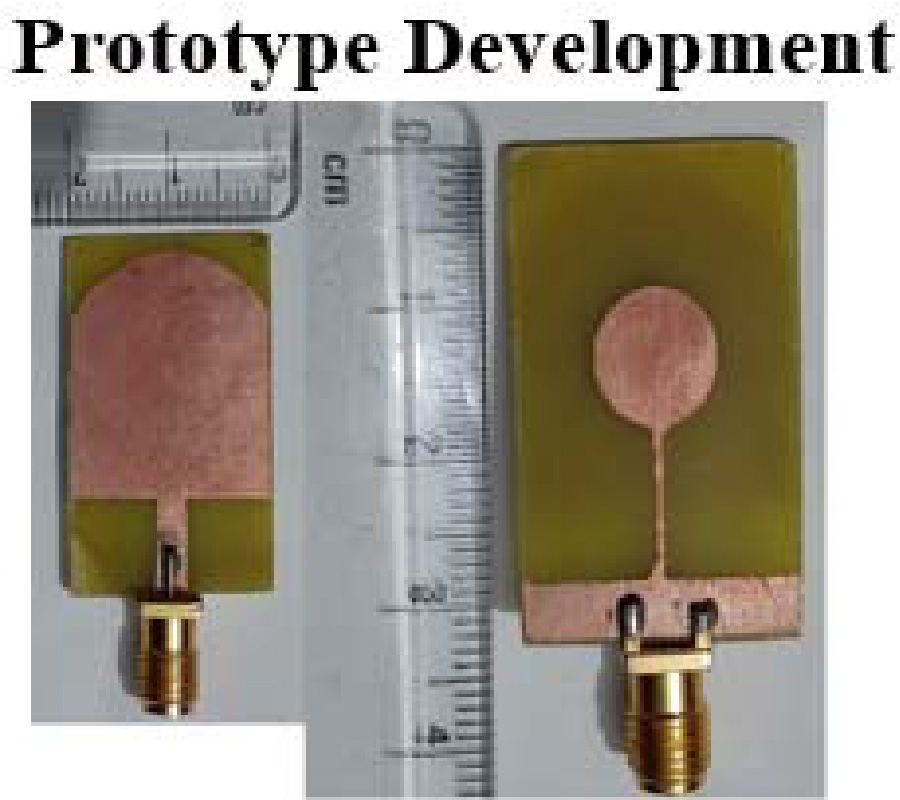
This paper presents a miniaturized antenna-based wearable self-powered wireless systems; the proposed study identifies the possibility to compact a flexible Solant-Rectenna integrated to low energy devices. The proposed system uses the obtained DC currents from RF rectifier and solar panel to recharge batteries. A low-profile Hilbert-shaped metamaterial (MTM) array forming a rectangular patch is conducted to minimize the shadowing effects to 13.3% on the solar panel area. Nevertheless, an Electromagnetic Bandgap (EBG) square pads array is introduced as defects on the ground plane to remove the negative effects, in terms of losses, of the solar panel bus-bar on the antenna performance. Moreover, the proposed EBG ground plane is utilized to isolate the human body from the undesired electromagnetic radiation leakage in addition to minimize the antenna impedance mismatch caused by the proximity to human tissues. For this, the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) is analysed numerically to assess the feasibility of the proposed EBG layer. The antenna expresses a frequency bandwidth, S11 < -10 dB, from 0.8 GHz up to 10 GHz; moreover, the EBG inclusions increase the front to back ratio to provide the gains of -10 dBi, -4 dBi, 0 dBi at 0.915 GHz, 1.88 GHz, and 2.45 GHz, respectively. Moreover, a SAR reduction is achieved up to 64% down after the EBG layer introduction. In addition, the antenna distortion effect in terms of group delay (Gd) after 3.1 GHz up to 10 GHz is tested; the maximum variation is found to be less than 1ns which shows a linear phase response with distortionless waveforms. Such a feature is found very suitable for UWB applications in modern wireless systems. The antenna performance improvement after introducing the proposed EBG defects is validated experimentally and numerically. The solar panel I-V characteristics are measured after the antenna structure introduction. Next, the solant RF port is connected to a rectifier circuit to realize the rectenna performance port that collects the RF energy at three bands in terms of efficiency spectra. Finally, it is proofed that the proposed Solant-Rectenna offers an excellent, compacted, and flexible candidate for the wearable self-powered devices at different bands.