2013-05-01 Latest Published
By Bazil Taha-Ahmed
Ignacio Alvarez Calvo
Jose Luis Masa-Campos
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 39, 199-205, 2013
Abstract
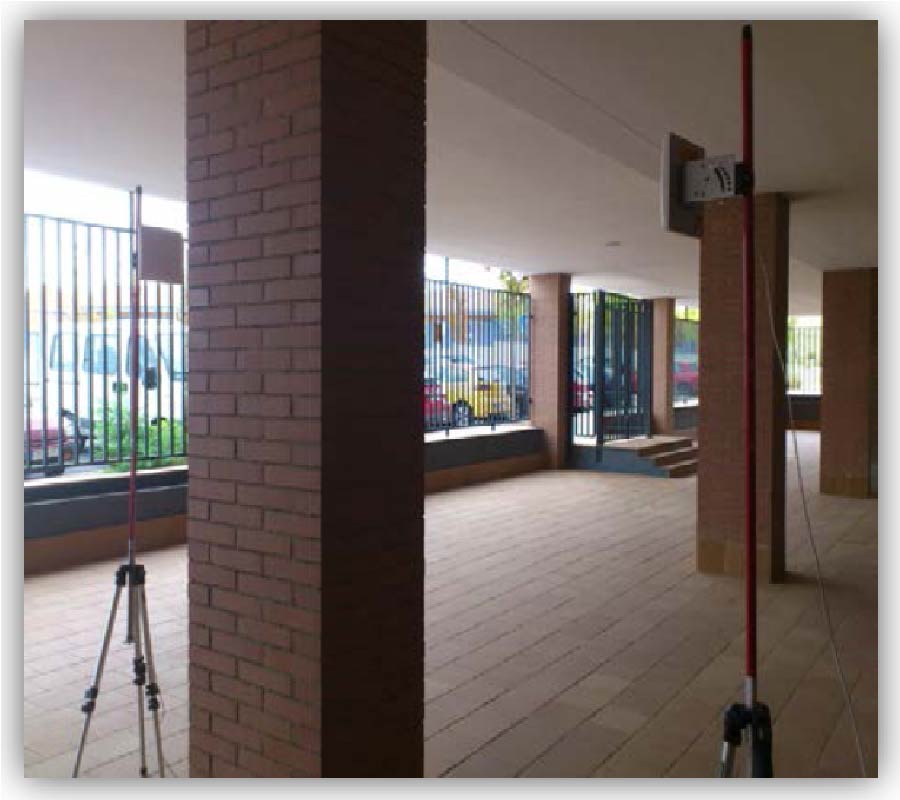
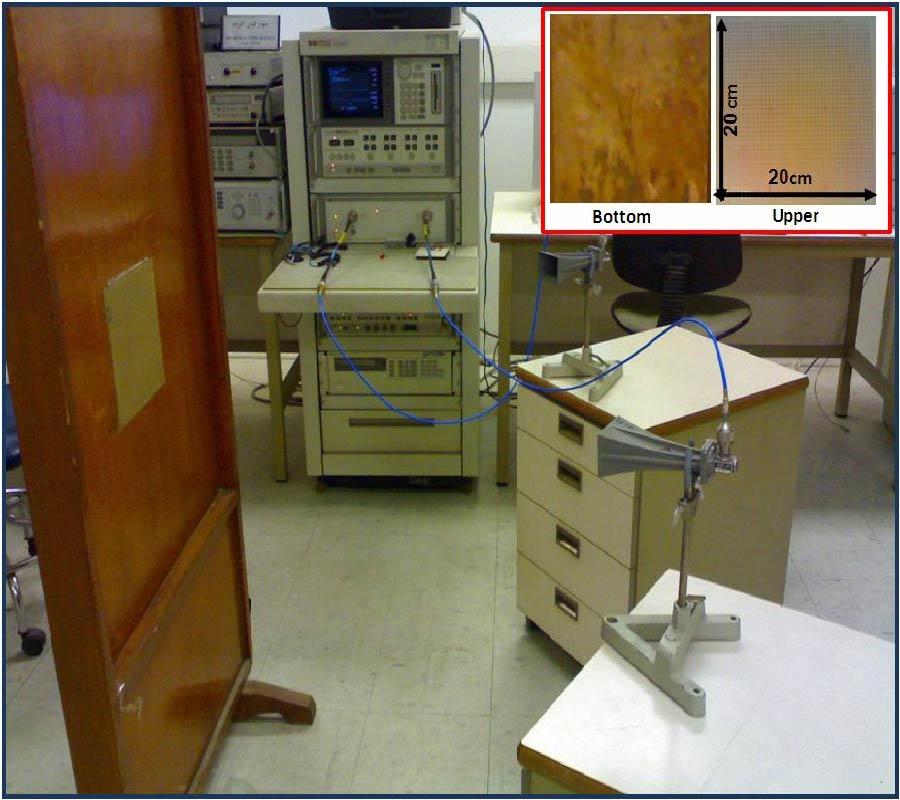
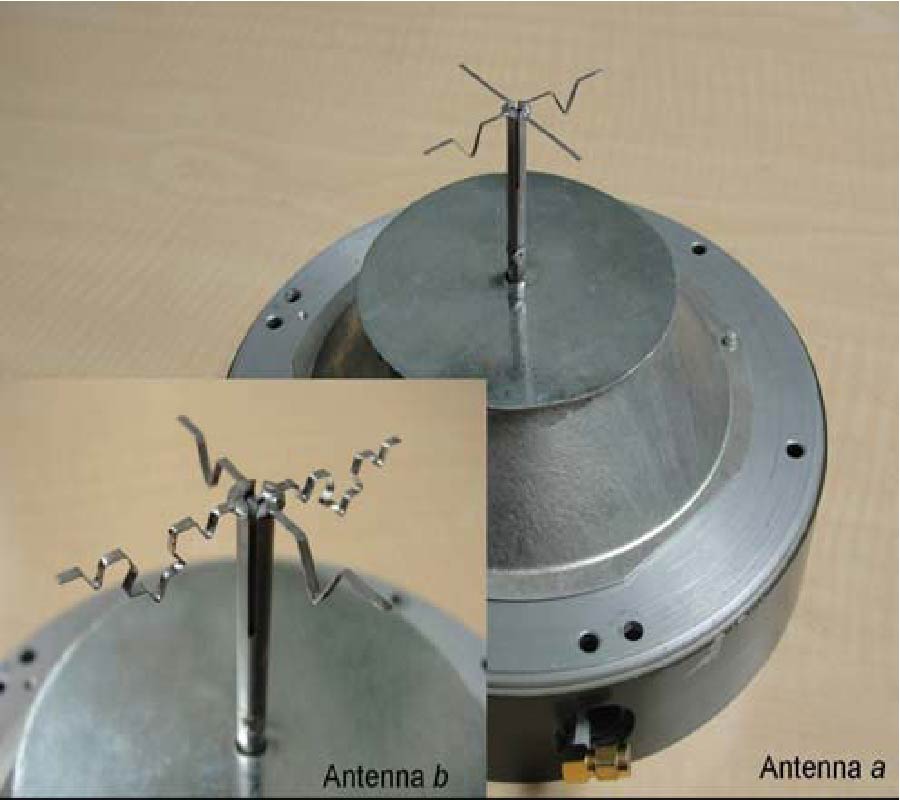
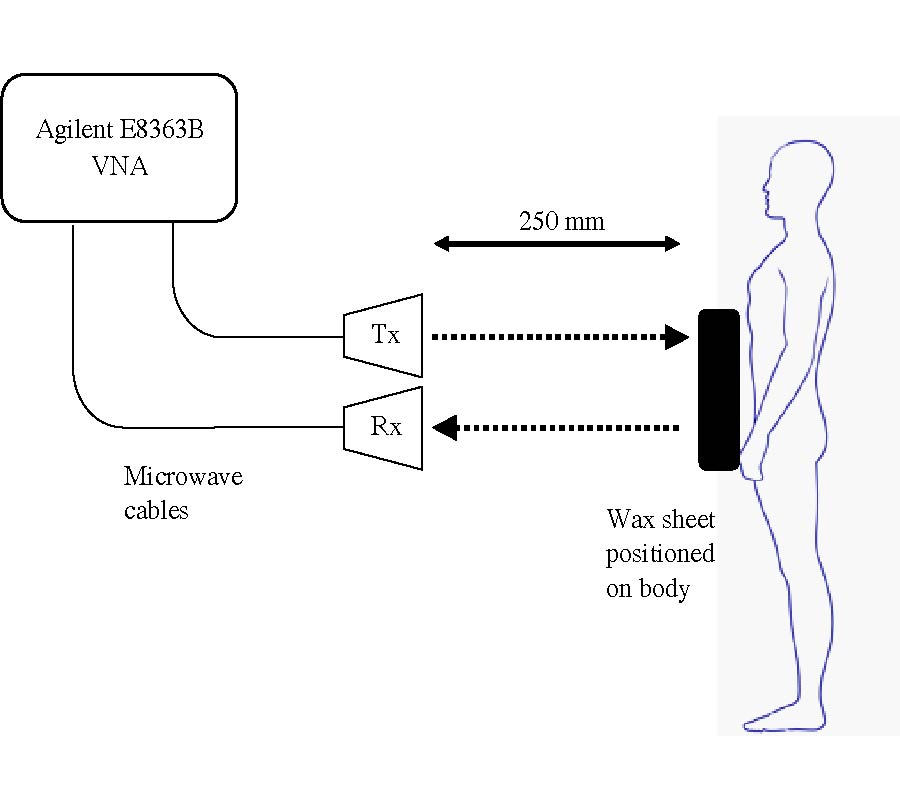
The insertion loss of different materials is measured at 2.4, 3.3 and 5.5 GHz bands. Directive antennas with a nominal gain of 19 dB are used in the measurement campaign. The height of the antennas has been selected to have the minimum possible reflection from around surfaces. Thick concrete wall, thick concrete column and tree's insertion loss are measured. It is noticed that the insertion loss increases with the increment of the operating frequency. For tress, the insertion loss for the leafless tress is 6 to 10 dB lower than the deciduous trees.