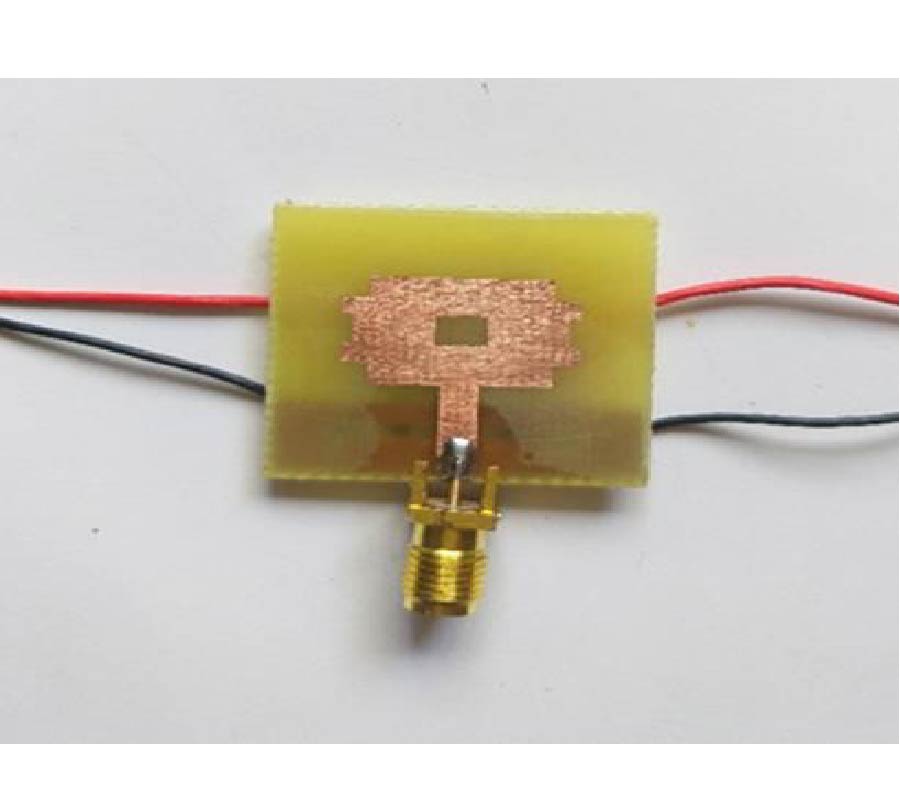
Wide-Band Frequency Tunable Antenna for 4G, 5G/Sub 6 GHz Portable Devices and MIMO Applications
Shivleela Mudda,
K. M. Gayathri and
Mudda Mallikarjun
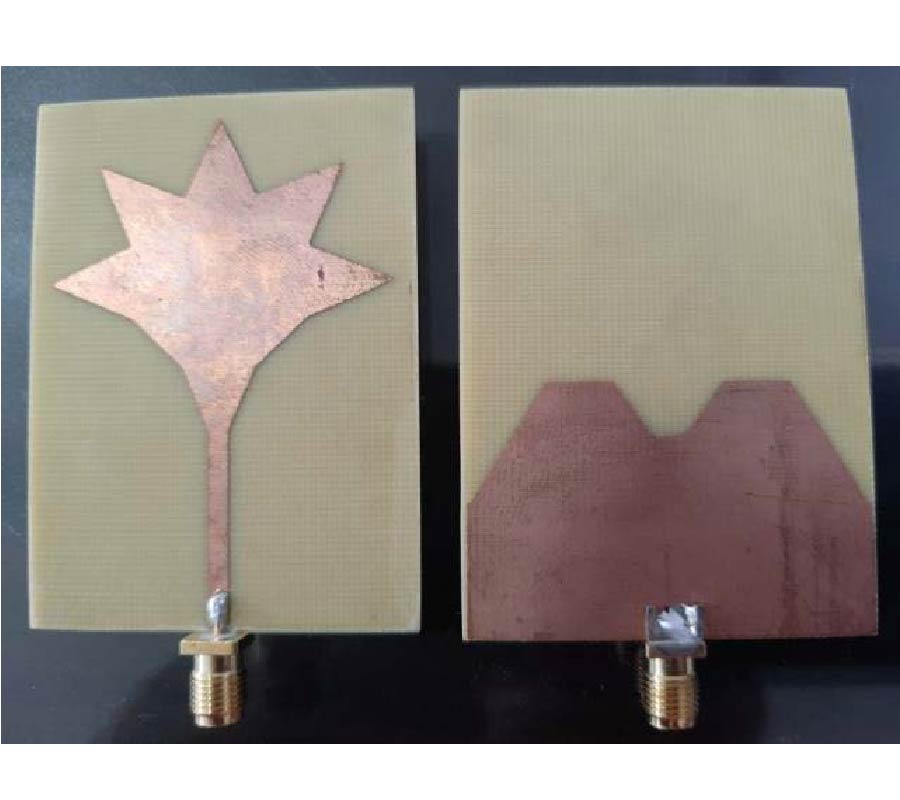
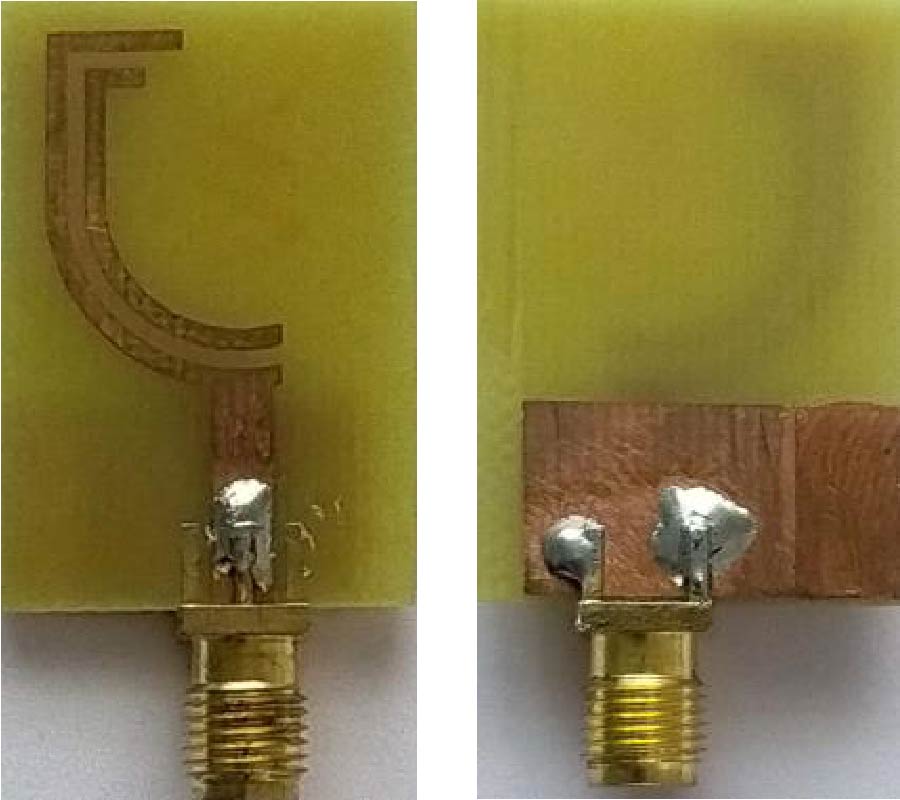
A compact (25×28×1.57 mm3) and wide-band multimode frequency tunable antenna with defected ground structure (FRDGS) for 4G and 5G conformal portable devices and multi-band wireless systems is presented in this article. In a previous study, frequency reconfigurable antenna designs only used the method of adding slots on the patch or ground. In this study, a combination of multiple slots, partial ground, and defective ground structure techniques were utilised to attain the advantages of compactness, wide impedance bandwidth, and steady radiation pattern. Multiple slots on the top layer of the substrate and F-shaped slot etched at the bottom makes the proposed antenna. Two PIN diodes are inserted in the F-shaped slot for frequency reconfiguration, allowing the antenna to switch between different resonances. Ansys high frequency structure simulator 15.0v is used to simulate the antenna parameters. This antenna performance is demonstrated using measured and simulated data. The simulated and measured results clearly show that the proposed antenna can switch between six dissimilar resonant frequency bands via various modes of operation across the frequency spectrum from 2.3 to 8.9 GHz. The antenna works in a variety of commercial bands, such as WLAN/Bluetooth (2.4-2.5 GHz), LTE/4G (2.3-2.7 GHz), S-band (2-4 GHz), Radio Navigation (2.7-2.9 GHz), and 5G/sub-6 (3.3-4.9 GHz), according to simulations and experiments. The proposed design features narrowband, wideband, and ultra-wideband properties with a consistent radiation pattern, adequate gain (1.6 to 5.8 dB), and high radiation efficiency (86 to 94%) in a small package. Furthermore, the performance comparison of the proposed antenna with that of the state-of-the-art antennas in terms of compactness, frequency reconfigurability, number of operating bands, and impedance bandwidth demonstrates the novelty of the proposed antenna and its potential application in multiple wireless applications.