Application of Ultra-Thin Assembled Planar Metamaterial for Wireless Power Transfer System
Jun-Feng Chen,
Zhaoyang Hu,
Shengming Wang,
Minghai Liu,
Yongzhi Cheng,
Zhixia Ding,
Bin Wei and
Songcen Wang
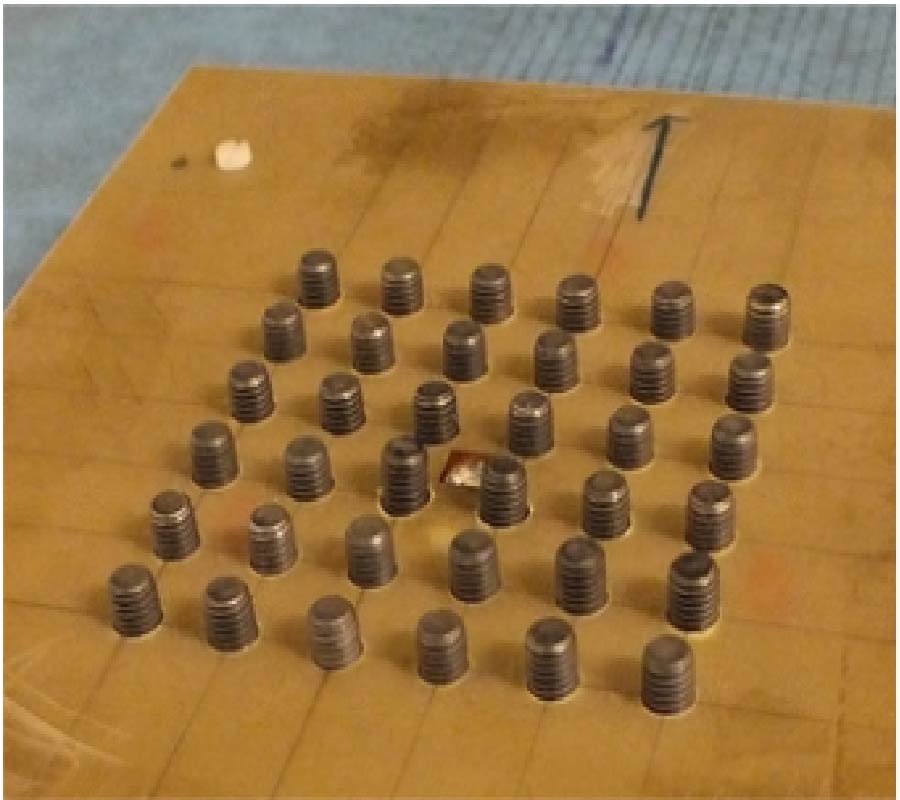
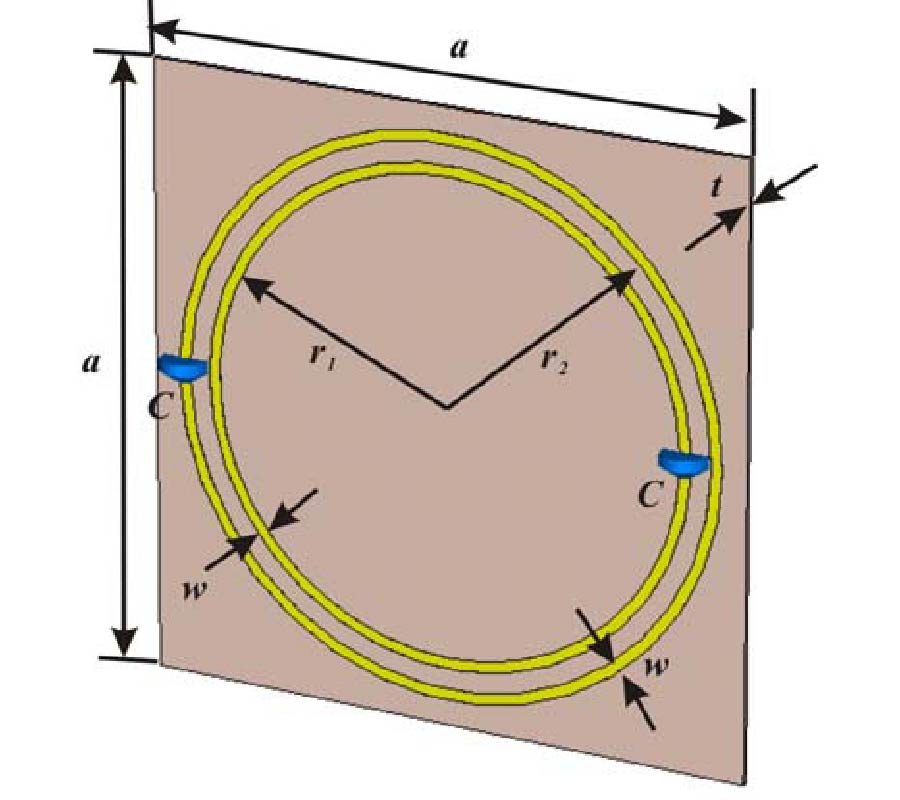
Magnetically coupled resonant wireless power transfer (WPT) has been employed in many applications, including wireless charging of portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, etc. However, the power transfer efficiency (PTE) decreases sharply due to divergence of magnetic field. Electromagnetic (EM) metamaterial (MM) can control the direction of magnetic fields due to its nega-tive effective permeability. In this paper, MMs with negative effective permeability at radio frequencies (RF) are applied to a WPT system operating at around 16.30 MHz for improvement of PTE. This ul-tra-thin and assembled planar MM structure consists of a single-sided periodic array of the capaci-tively loaded split ring resonators (CLSRRs). Both simulation and experiment are performed to cha-racterize the WPT system with and without MMs. The results indicate that the contribution of high PTE is due to the property of negative effective permeability. By integrating MM in the WPT system, the experimental results verify that the measured PTE with one and two MM slabs have respectively 10% and 17% improvement compared to the case without MM. The measured PTEs of the system at different transmission distances are also investigated. Finally, the proposed MM slabs are applied in a more practical WPT system (with a light bulb load) to reveal its effects. The results verify the efficiency improvement by the realized power received the load.