A Novel Compact Planar Six-Way Power Divider Using Folded and Hybrid-Expanded Coupled Lines
Hui Chen and
Yu-Xing Zhang
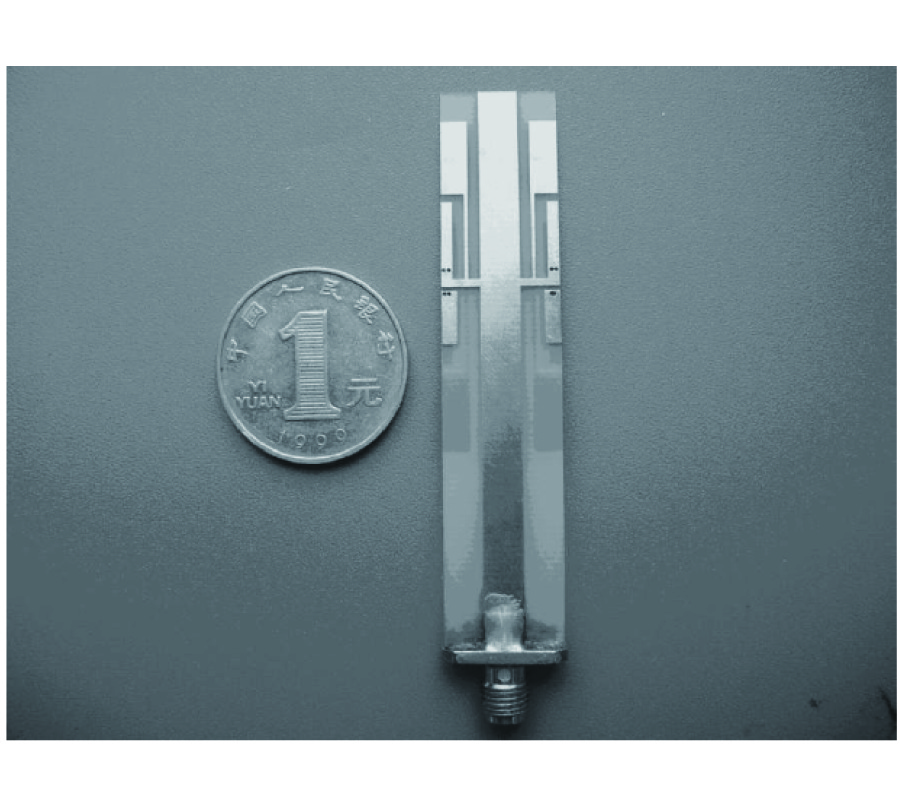
A novel planar six-way power divider is proposed. Based on the conventional planar microstrip coupled line technology, the proposed compact six-way power divider is comprised of two stages coupled transmission lines, which is different to the conventional multistage power divider using the same expanded structure, one stage folded two-coupled line, and the other hybrid-expanded symmetrical three-coupled line. Therefore, the proposed power divider is size reduction, and has a broad-band property, which is better than 40% of fractional bandwidth. Furthermore, compared to a traditional six-way power divider, it is designed and fabricated easily. From the simulated and measured results, the six-way planar power divider shows a good specifications, which are insert loss 8.1±0.2 dB from 2 GHz to 3 GHz, and return loss less than −18 dB, isolation less than −19.5dB at 2.5 GHz, respectively.