A Compact Dual-Polarized Broadband Antenna with Hybrid Beam-Forming Capabilities
Hong-Li Peng,
Wen-Yan Yin,
Jun-Fa Mao,
Di Huo,
Xu Hang and
Liang Zhou
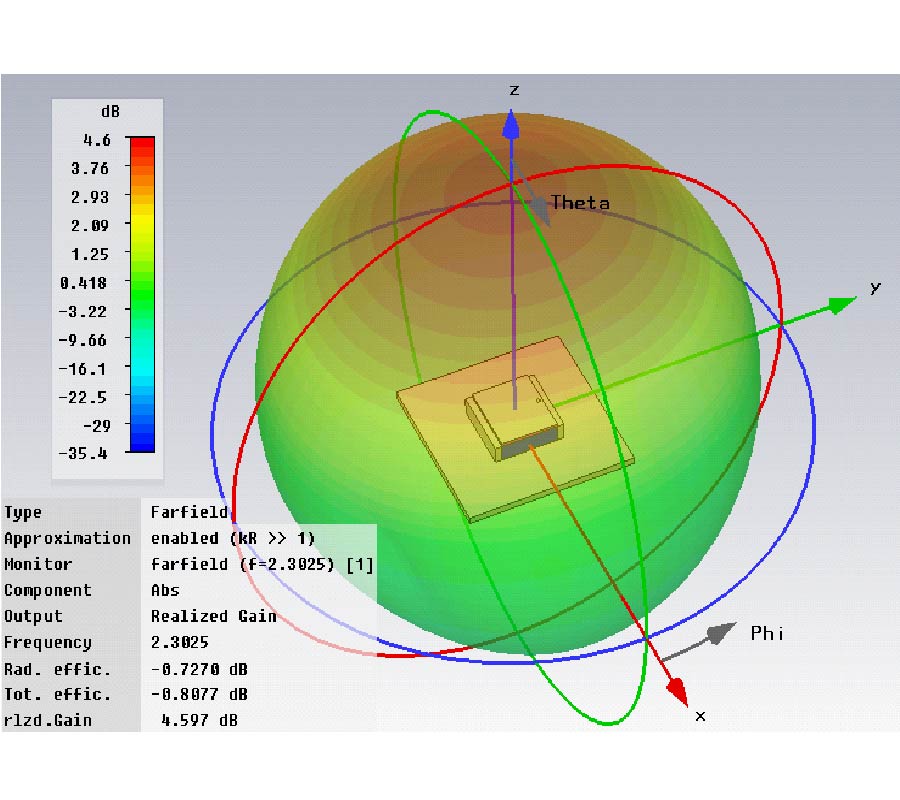
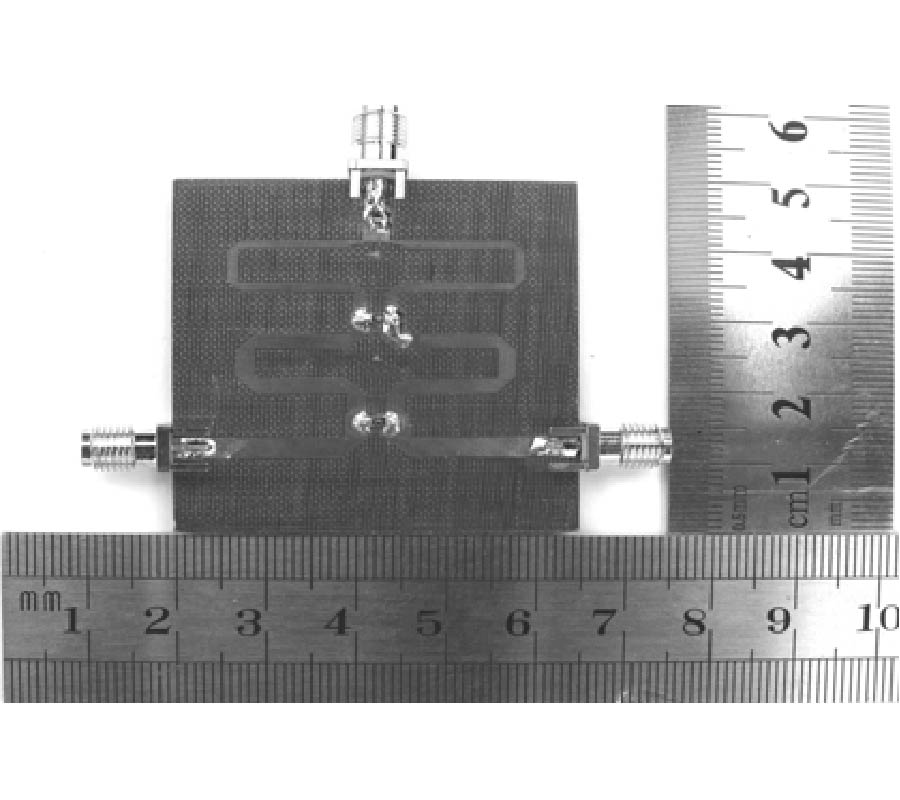
A broadband dual-polarized four-port (DPFP) antenna is presented in this paper, which consists of a radiation element and a feed network. It is very compact in size, with the diameter of 150.0 mm and the height of 47.0 mm, with the following unique properties: (1) it has hybrid beam-forming capability and operates at two modes, which depends on its excitation; (2) its operating frequency range is from 0.96 to1.78 GHz, and the return loss is about 10 dB; (\ref{eq3}) its insertion loss is (3±0.5) dB, with its balanced power splitting over the relative bandwidths of 37% at Mode 1 (180°±5° phase shifting) and 55% at Mode 2 (±5° phase shifting), respectively; (\ref{eq4}) an isolation of 30 dB at Mode 1 is obtained between the dual polarized ports, with the gain of 7.6 dBi and 42° of the 3 dB-bandwidth at 1.25 GHz; and (5) the gain difference between Modes 1 and 2 is about 7 dB, within the angle of -15° ≤ θ ≤ 15° for the same polarization at 1.25 GHz. For the application of DPFP, a hybrid beam forming algorithm is proposed with an angular precision of 3°, as validated by measurement.