Use of High-Impedance Screens for Enhancing Antenna Performance with Electromagnetic Compatibility
Ming-Shing Lin,
Chung-Hao Huang and
Cheng-Nan Chiu
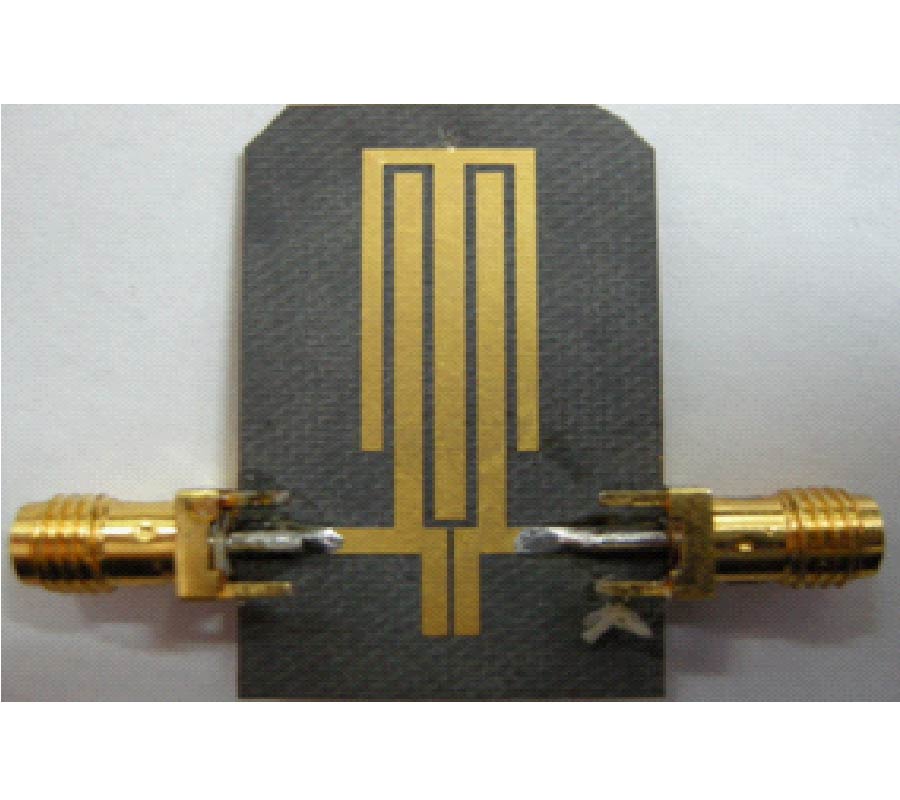
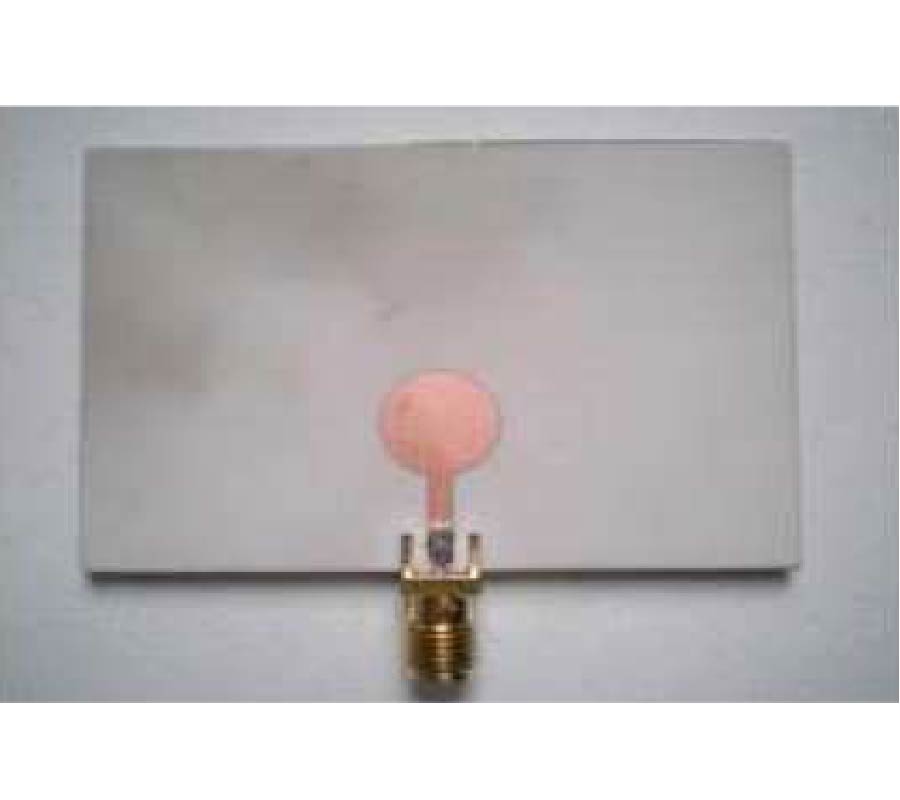
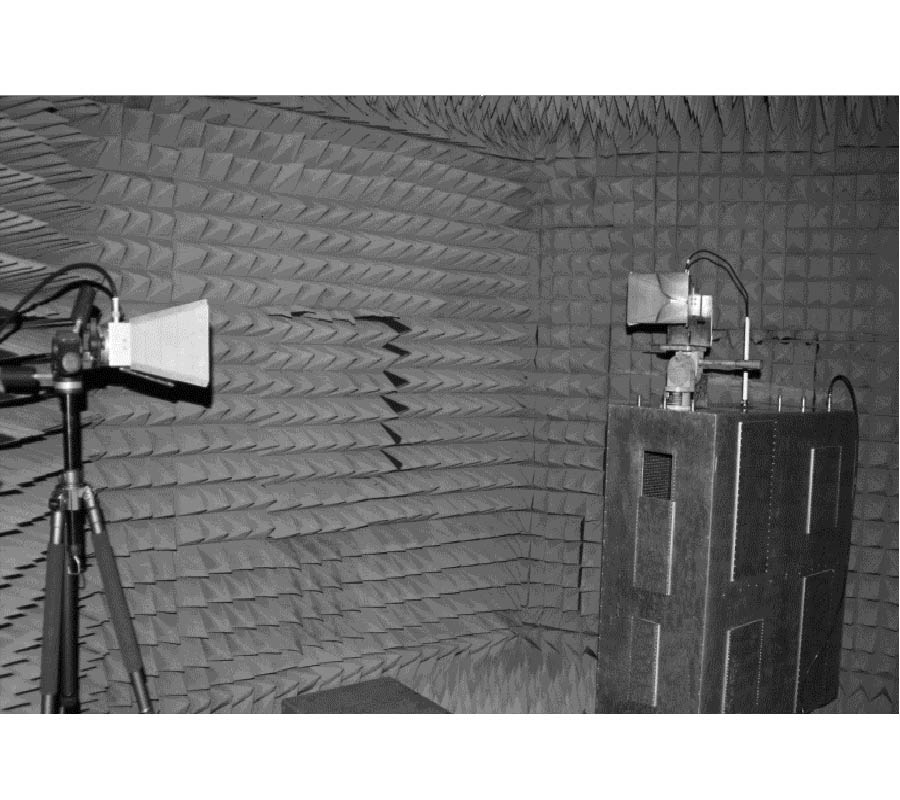
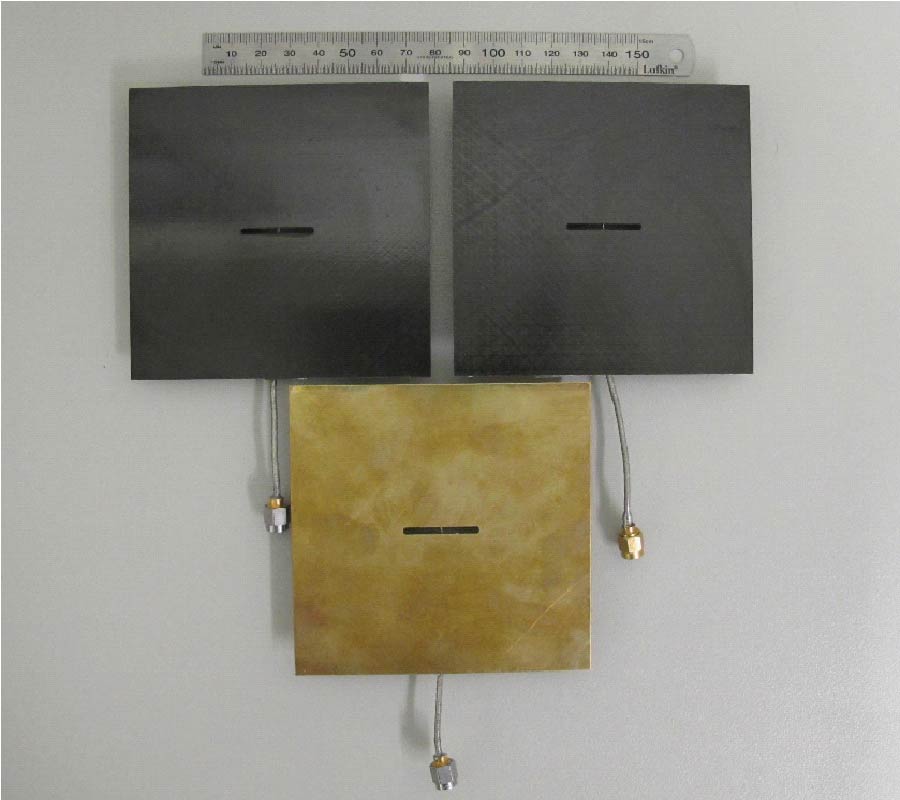
When developing a wireless communication system, a designer should consider the associated radiated power density, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and specific absorption rate (SAR). In this paper, high-impedance surfaces (HISs) are designed as an EM protection screen to reduce the interaction between an antenna and the user behind the screen. The effects of an HIS screen with a finite number of cells placed near a monopole antenna for the application of the 2.4 GHz WLAN band were thoroughly investigated. The screen is first-ever proposed not only to reduce the backward radiation from the antenna, but also to shift the impedance-matching band of the antenna and to adjust the corresponding bandwidth. As a result, the SAR behind the screen is noticeably lowered, and the out-of-band spurious emission from the antenna can be reduced. Two typical kinds of HIS structures, mushroom-shaped and Jerusalem Cross HISs (abbreviated as MSHIS and JCHIS, respectively), were investigated by numerical simulations and measurements. Three different measurement techniques were proposed for predicting the operating frequency band of an HIS. Some HIS-added antenna prototypes were constructed and studied. It was found that the MSHIS and JCHIS can adjust the impedance-matching band of the antenna, do not affect the radiation performance in the forward direction, and can significantly reduce the backward radiated power. In addition, the measured maximum SAR has been significantly reduced from 0.976 W/kg for the monopole antenna without an HIS to 0.037 and 0.038 W/kg, respectively, for the antenna with an MSHIS and a JCHIS.