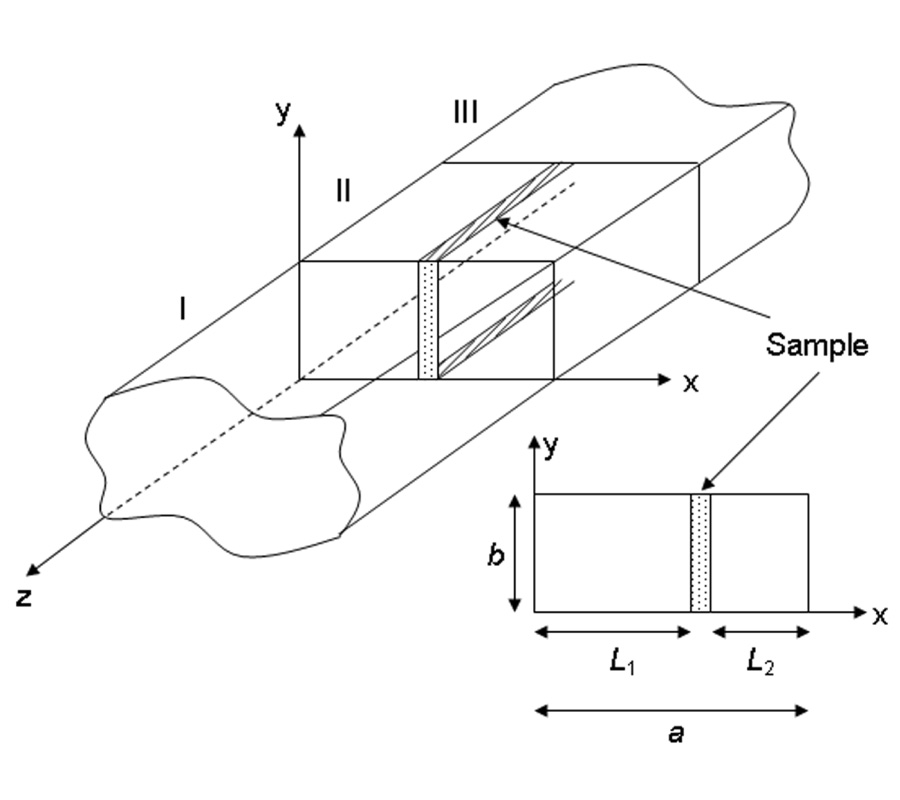
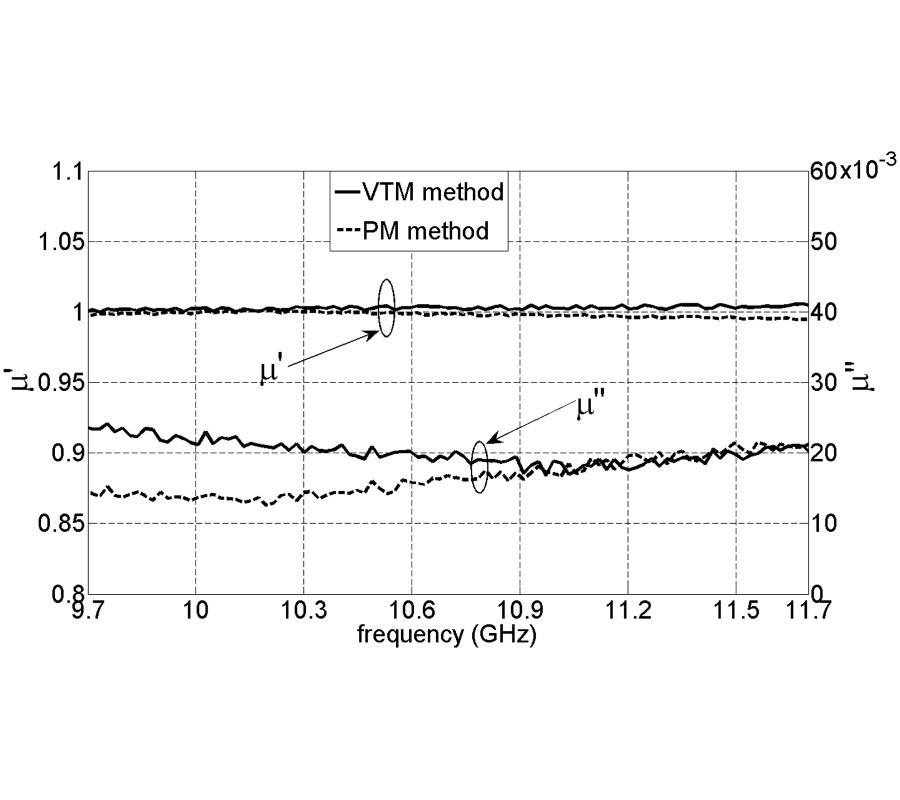
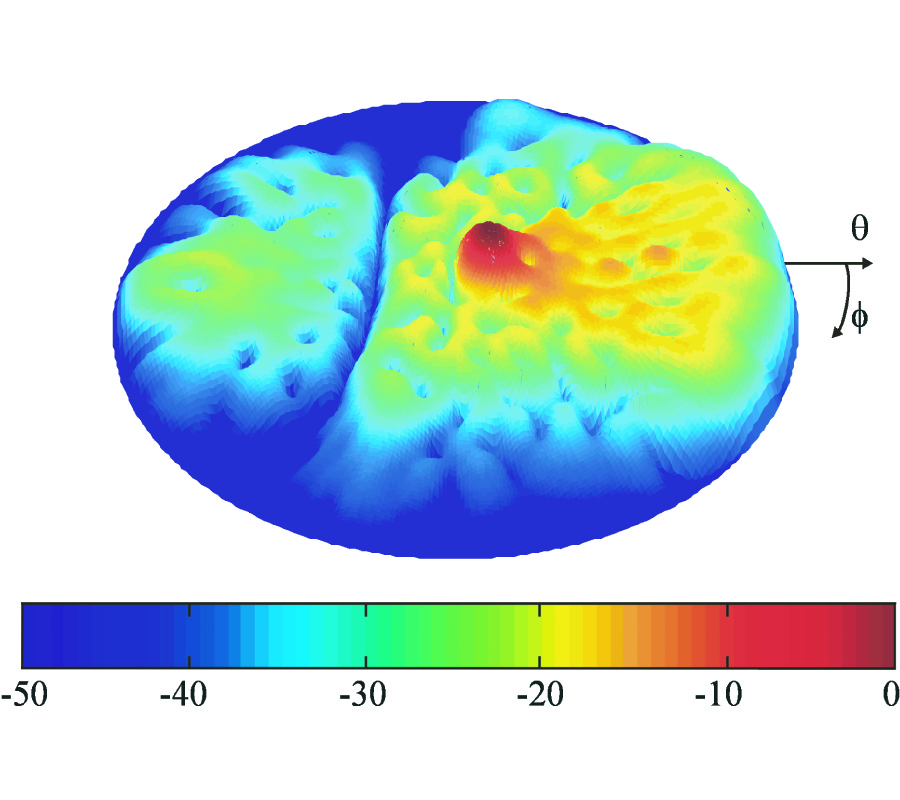
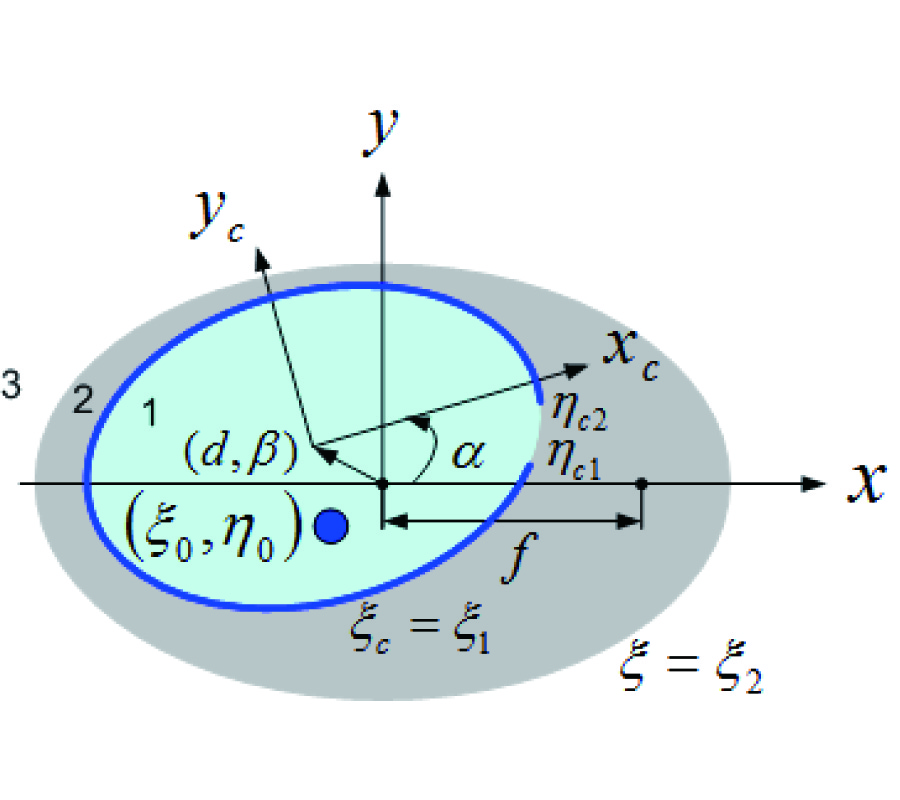
A Metamaterial-Based E-Plane Horn Antenna
Ruey-Bing Hwang,
Hung-Wang Liu and
Cheng-Yuan Chin
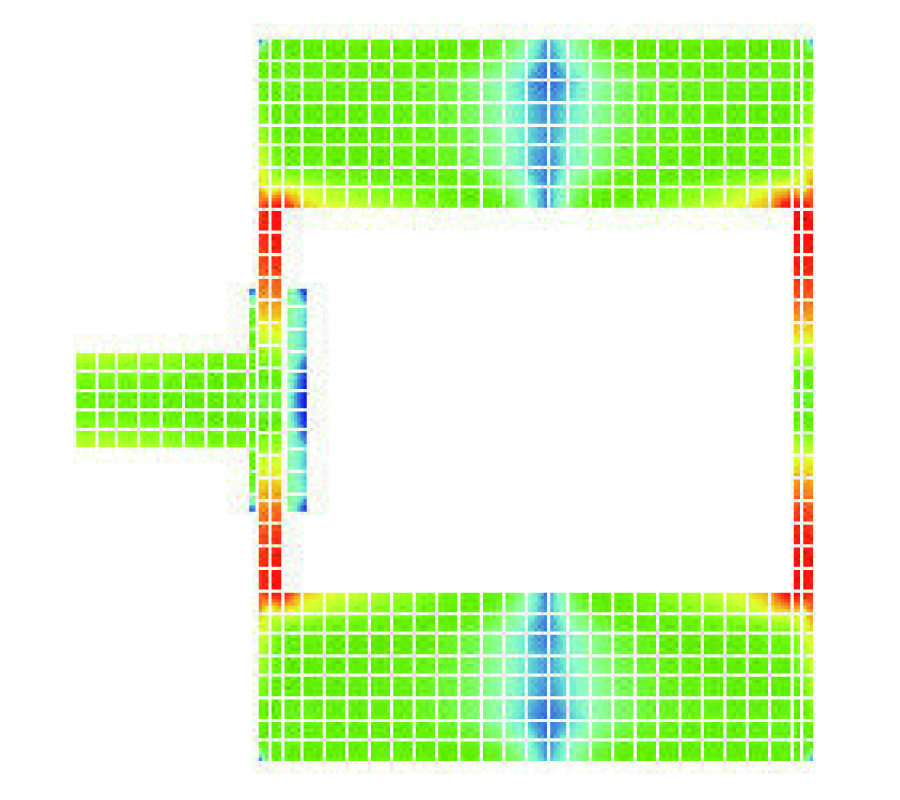
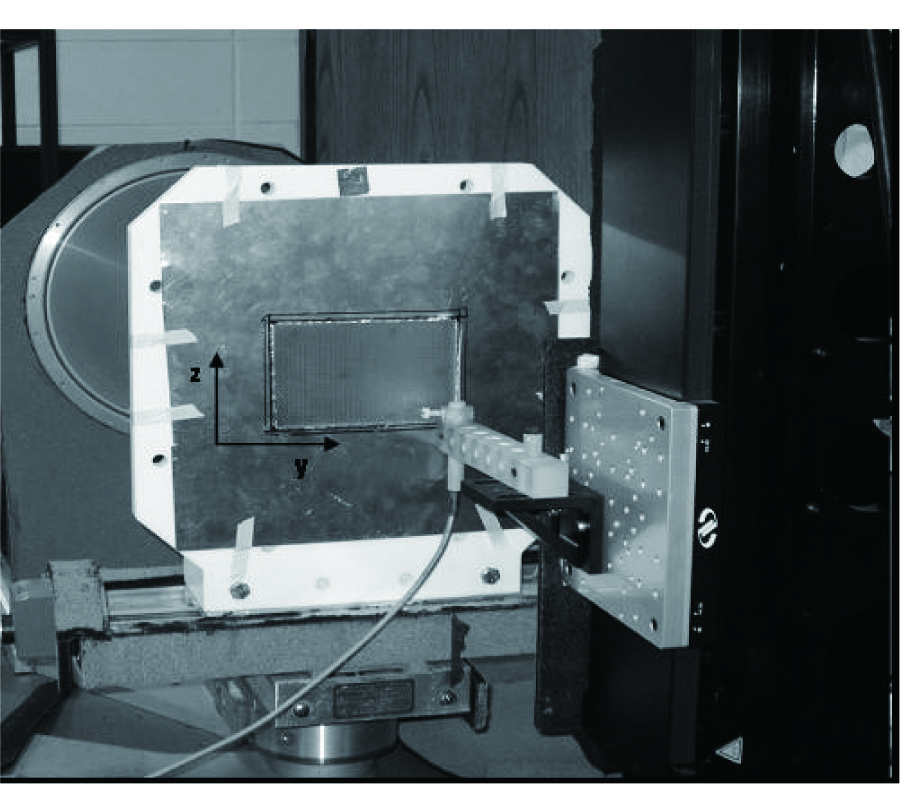
In this paper, we reported an E-plane horn antenna incorporating a metamaterial. Such a metamaterial is made up of metallic cylinders organized in a two-dimensional square lattice. After properly designing the lattice constant and unit cell pattern, we synthesized a medium with the effective refractive index smaller than unity. Therefore, once the waves were excited within the metamaterial, the refractive waves tend to be perpendicular to the interface between the metamaterial and uniform medium. Based on this concept, a 4-way beam splitter was designed to equally distribute the input power into 4 different directions. We then guide each of the power into individual E-plane flared opening to radiate a directional beam pattern in each sector. We have fabricated this antenna and measured its radiation characteristics including the return loss and far-field pattern. The excellent agreement between the measured and simulated results was obtained. Due to the properties of robust, low-loss, and low-cost, this antenna may have promising application in a point-to-multiple-point downlink system.