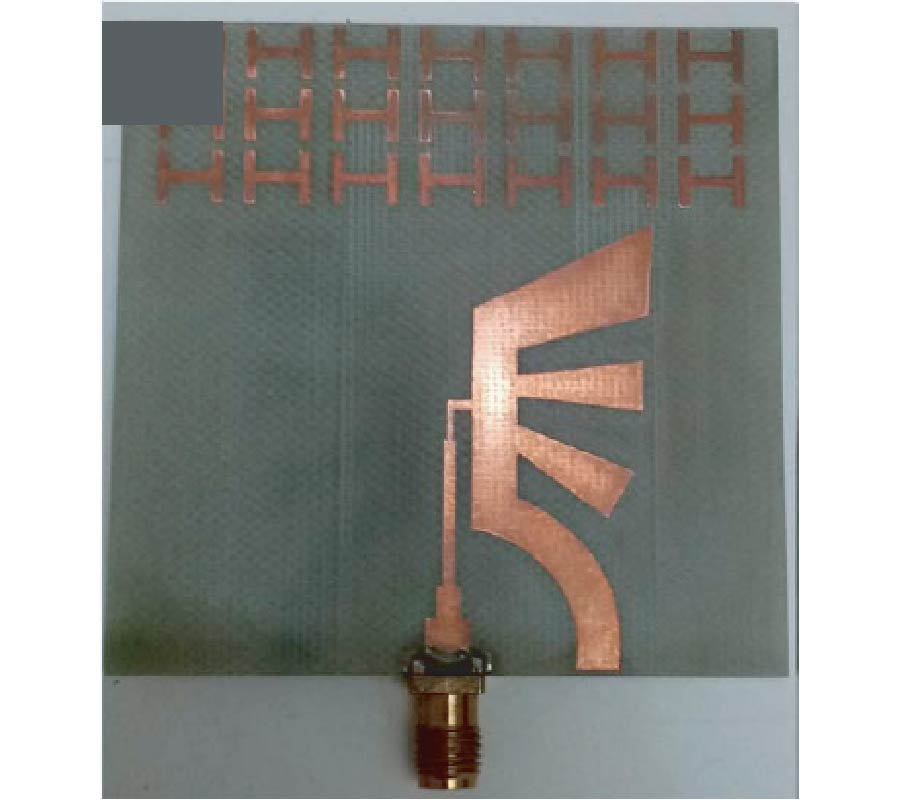
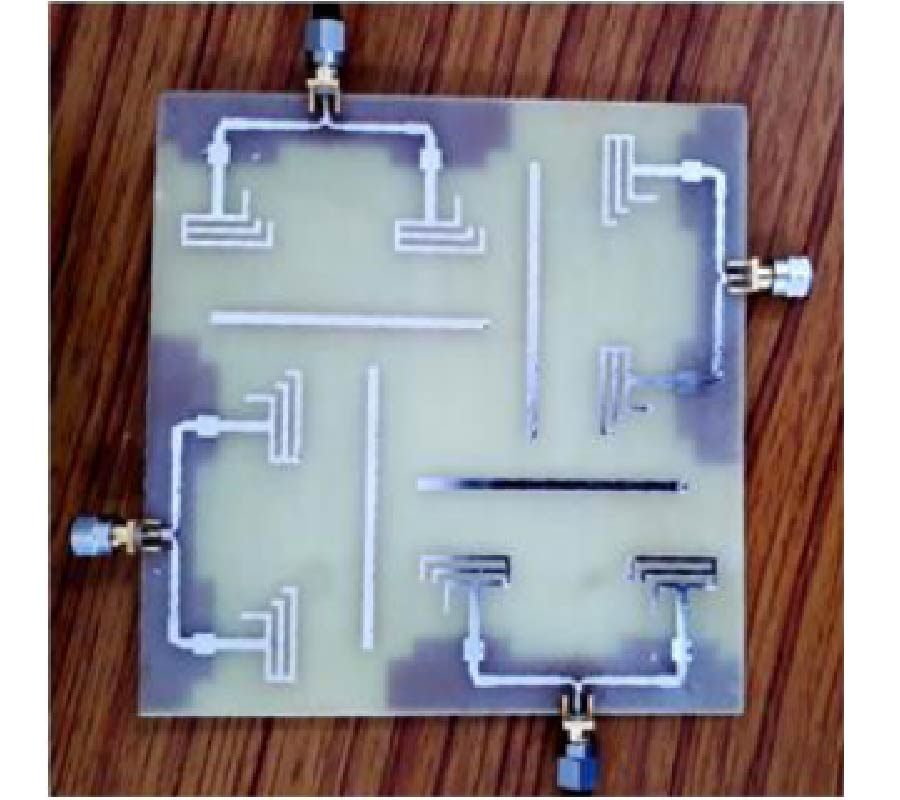
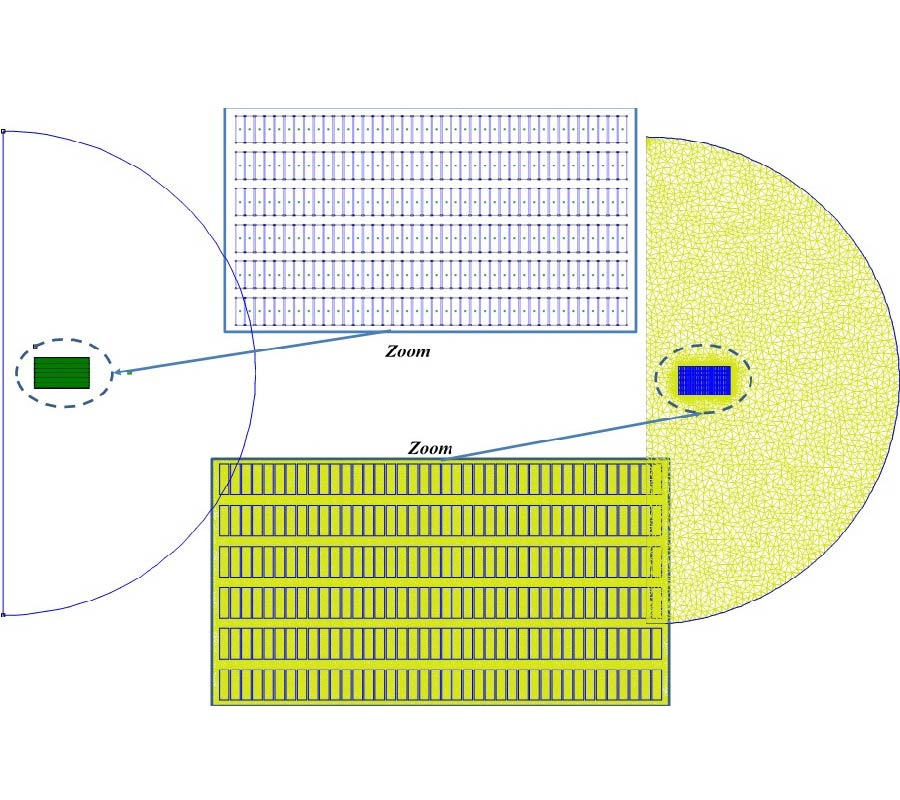
First Microwave Tomography Approach Towards a Truly Noninvasive, Pain-Free and Wearable Blood Glucose Monitoring Device
Asma Bakkali
,
Clément Buisson
,
Lourdes Mounien
,
Jean François Landrier
,
Victoria Tishkova
and
Pierre Sabouroux
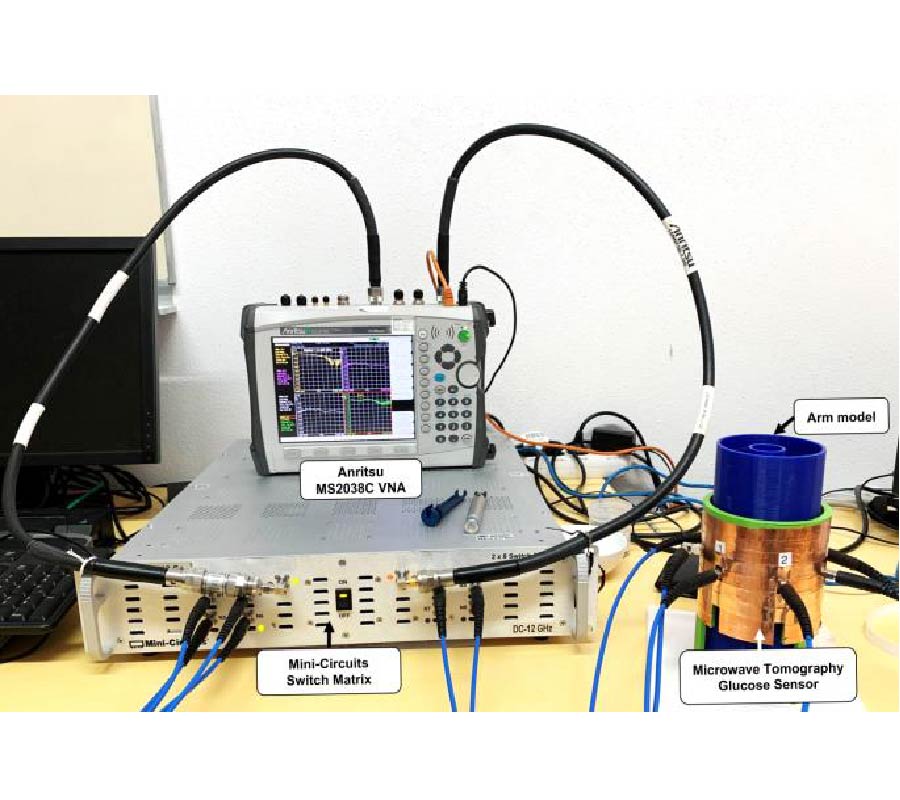
Despite the advancements in the field of glucose monitoring sensors, the development of noninvasive, wearable, continuous and comfortable systems is still a real challenge. New technologies are required for noninvasive, continuous and effective measurements remaining discreet, painless, comfortable to the patient and avoiding additional costs.This article presents a truly noninvasive microwavetomography prototype designed for glucose monitoring. The system is based on an array of dipole antennas placed in a circular configuration.The transmitted field data are collected using a switchmatrix connected to a vector network analyzer. A heterogeneous 3-D arm model and a 3-D electromagnetic solver have been used to model the human arm and to characterize the system. Blood electromagnetic properties are affected by the glucose concentration, a promising correlation between the dielectric properties of blood and glucose level should be investigated. By simulating the antenna array on the arm phantom, the characteristics of the S-Parameters were interesting at the frequencies of interest. The transmission coefficient amplitude decreases as the dielectric constant decreases from 63 to 40, and the conductivity increases from 1.5 S/m to 3.5 S/m. For each value of dielectric properties, a given transmission coefficient value can be clearly identified. Experimental measurements validated the arm phantom and confirmed the relationship between the response of the system and the dielectric properties of blood tissue. The armband sensor is designed as an inexpensive, noninvasive, and light weight device suitable for all patients with a high level of discretion. This work, under optimization for preclinical and clinical testing, demonstrates the proof of concept of an innovative microwave tomography system for noninvasive glucose monitoring. Compared to studies with a similar aim, this research may achieve distinct advances and offers promising hope in the field of noninvasive glucose sensors.