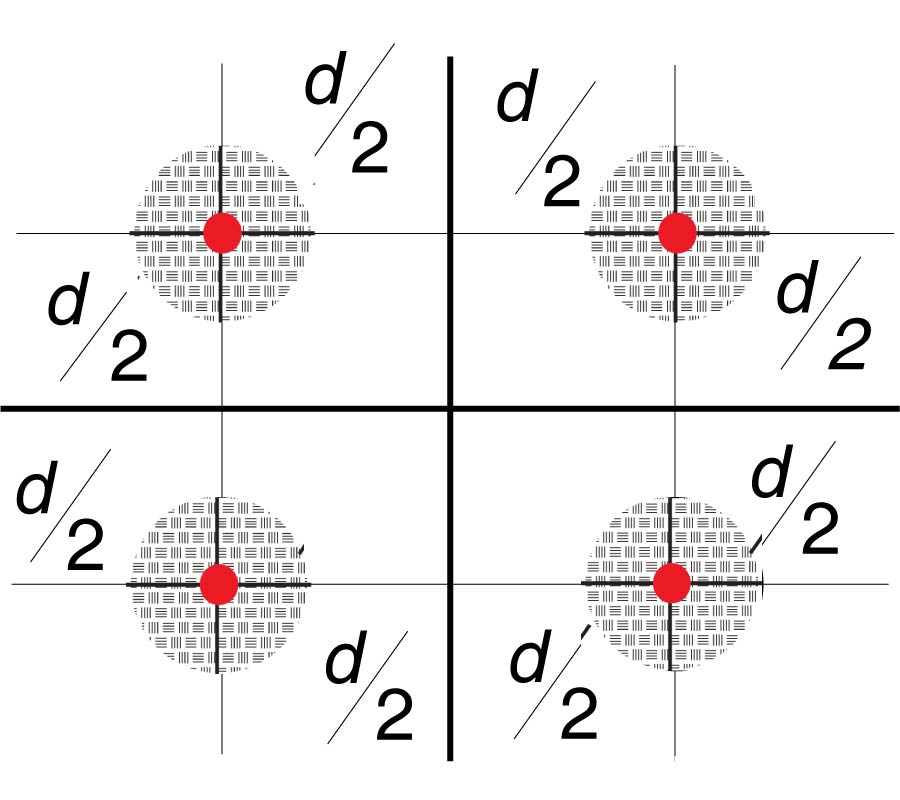
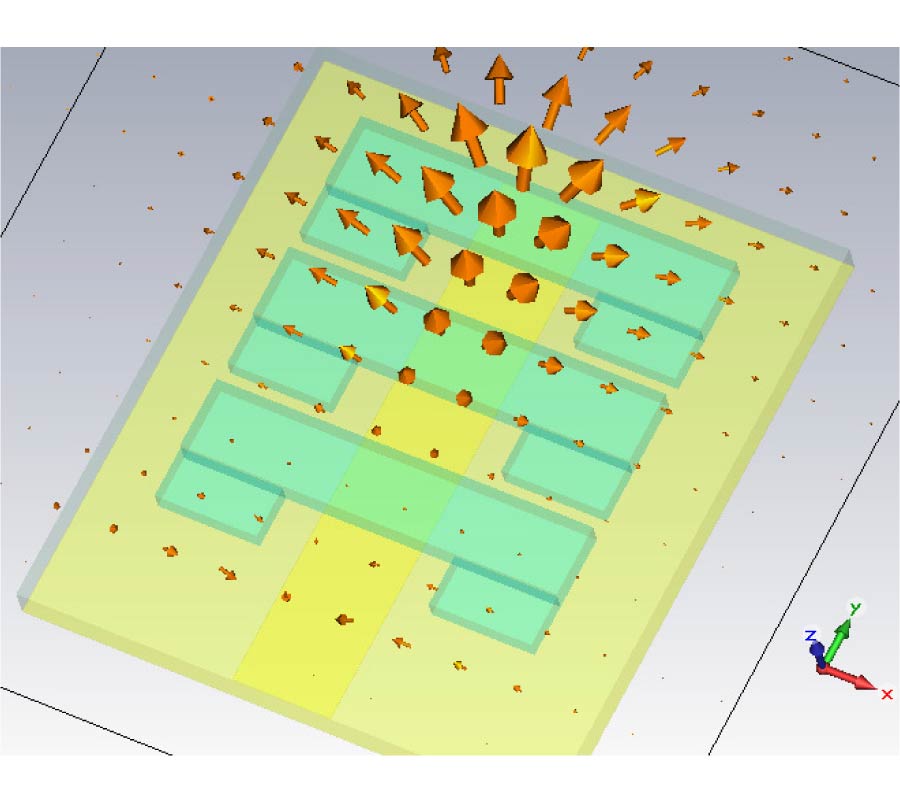
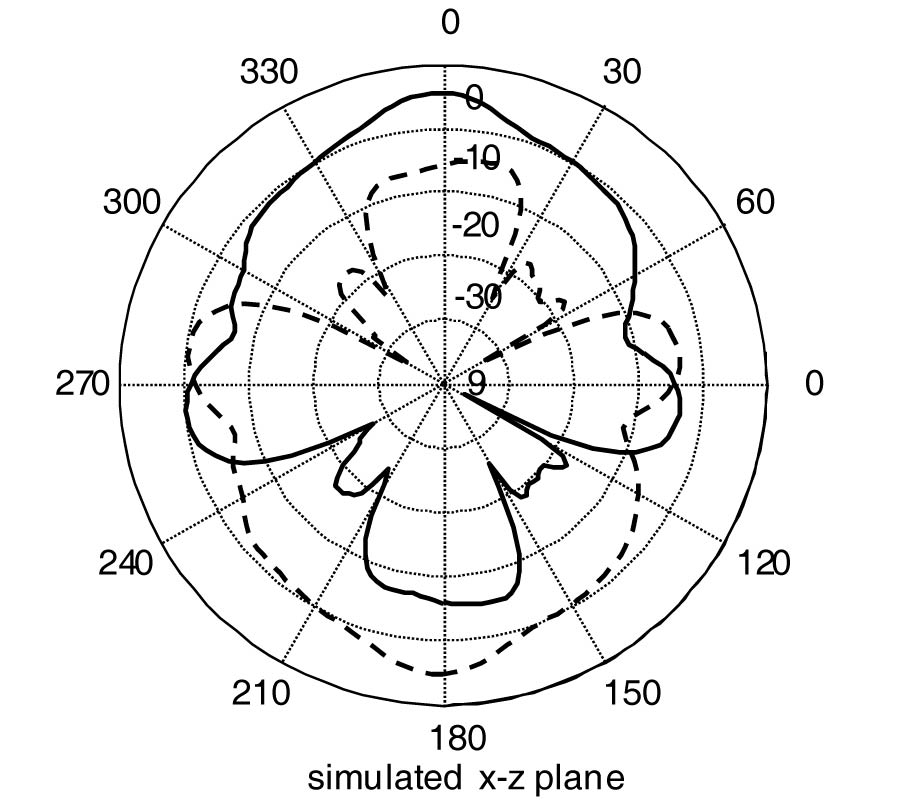
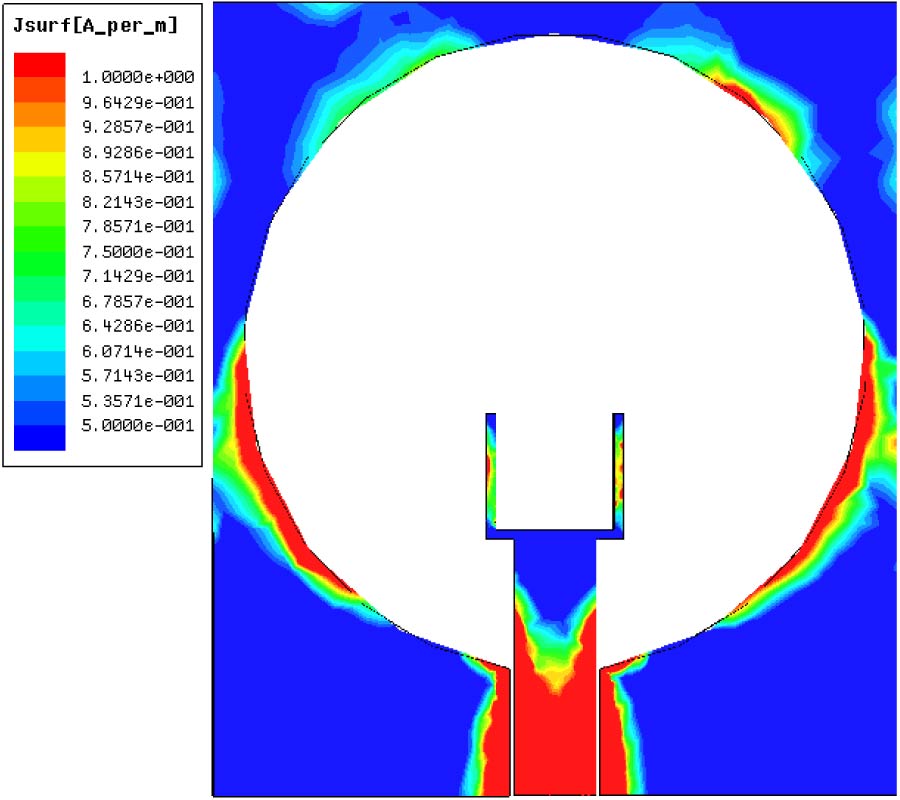
Investigation of the Characteristics of Barium Strontium Titanate (BST) Dielectric Resonator Ceramic Loaded on Array Antennas
Fwen Hoon Wee,
Mohd Fareq Bin Abd Malek,
Srimala Sreekantan,
Azlan Umar Al-Amani,
Farid Ghani and
You Kok Yeow
We investigated a dielectric resonator ceramic microstrip patch antenna. The antenna was formed using barium strontium titanate (BST), which has a dielectric constant of 15. A new approach, i.e., the use of a high temperature dielectric probe kit, was used to determine the dielectric constant of BST. A computer simulation technology (CST) microwave studio was used to simulate the BST array antennas, taking into consideration the dielectric constant. We also measured the gain of the antennas loaded with two-, four-, and six-element arrays of the BST antenna and found that the gain of a six-element BST array antenna was enhanced by a gain of about 1.6 dB over the four-element BST array antenna at 2.3 GHz. The impedance bandwidths of these BST array antennas for voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) < 2 were in the application ranges, i.e., 2.30 to 2.50 GHz, established for Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access (WiMAX) and Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). Compared with the conventional array antenna with the same aperture size, the performance of the antenna obviously was improved, and the design is suitable for array applications, including base stations, for example.