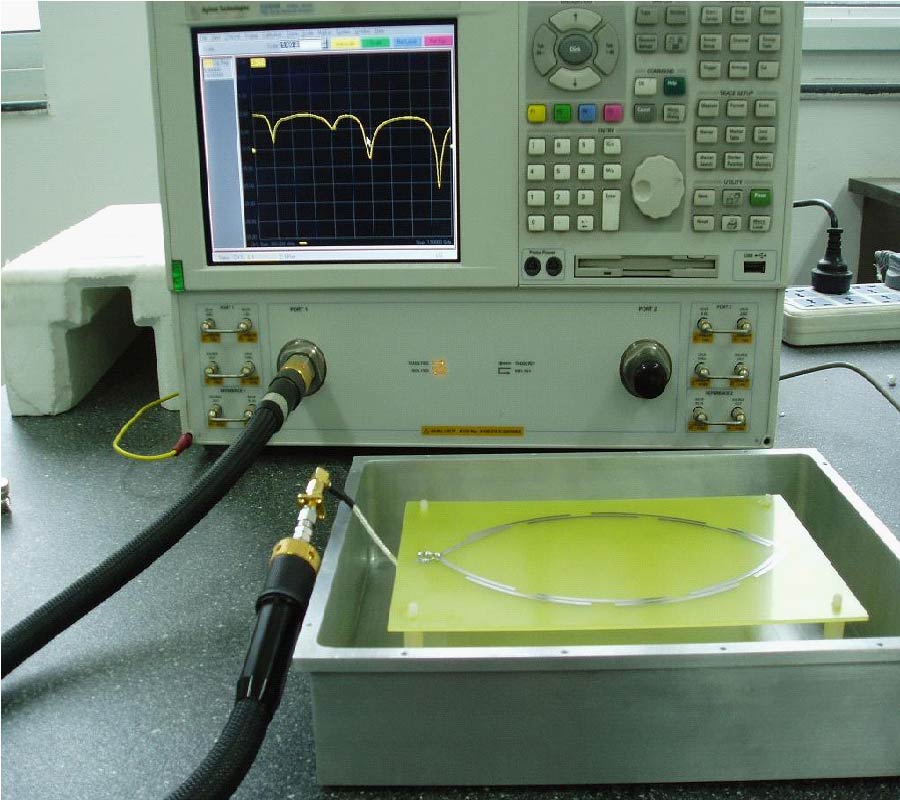
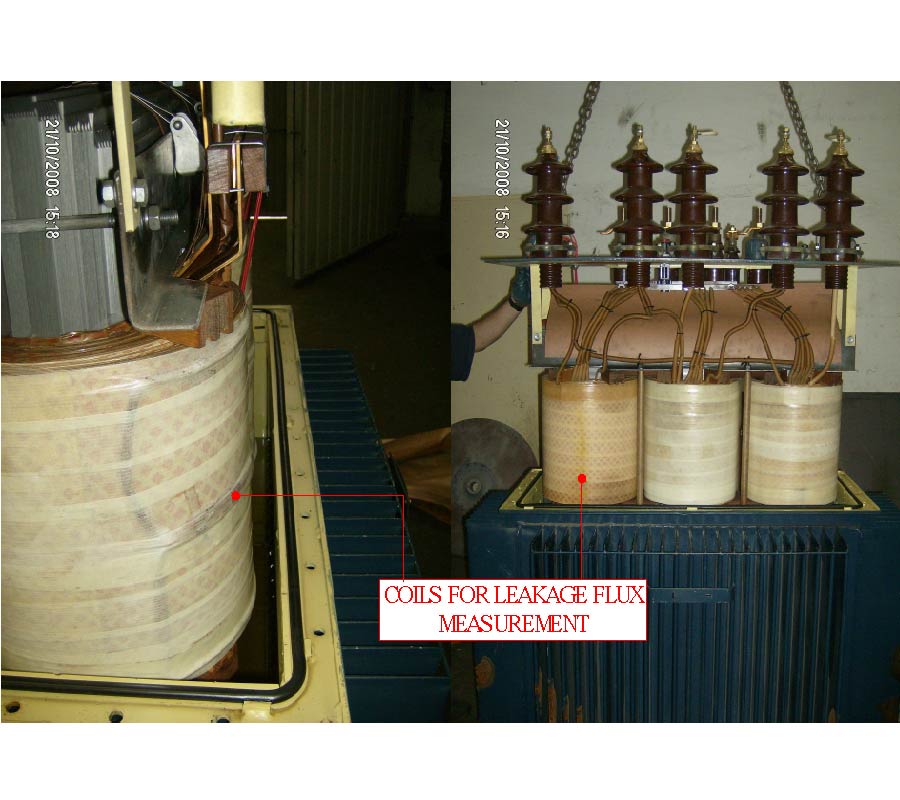
Insulation Fault Diagnosis in High Voltage Power Transformers by Means of Leakage Flux Analysis
Manes Fernandez Cabanas,
Francisco Pedrayes González,
Manuel García Melero,
Carlos H. Rojas García,
Gonzalo Alonso Orcajo,
José Manuel Cano Rodríguez and
Joaquín González Norniella
Power transformers in service are subjected to a wide variety of electrical, mechanical and thermal stresses capable of producing insulation faults. This type of failure figures amongst the most costly faults in distribution networks since it produces both machine outage and electrical supply interruption. Major research effort has therefore focused on the early detection of faults in the insulating systems of large high voltage power transformers. Although several industrial methods exist for the on-line and off-line monitoring of power transformers, all of them are expensive and complex, and require the use of specific electronic instrumentation. For these reasons, this paper will present the On-Line analysis of transformer leakage flux as an efficient alternative for assessing machine integrity and detecting the presence of insulating failures during their earliest stages. An industrial 400 kVA-20 kV/400V transformer will be used for the experimental study. Very cheap, simple sensors, based on air core coils, will be used to measure the leakage flux of the transformer, and non-destructive tests will also be applied to the machine in order to analyse pre- and post-failure voltages induced in the coils.