Planar Transmission Line Method for Characterization of Printed Circuit Board Dielectrics
Jianmin Zhang,
Marina Koledintseva,
Giulio Antonini,
James Drewniak,
Antonio Orlandi and
Konstantin Rozanov
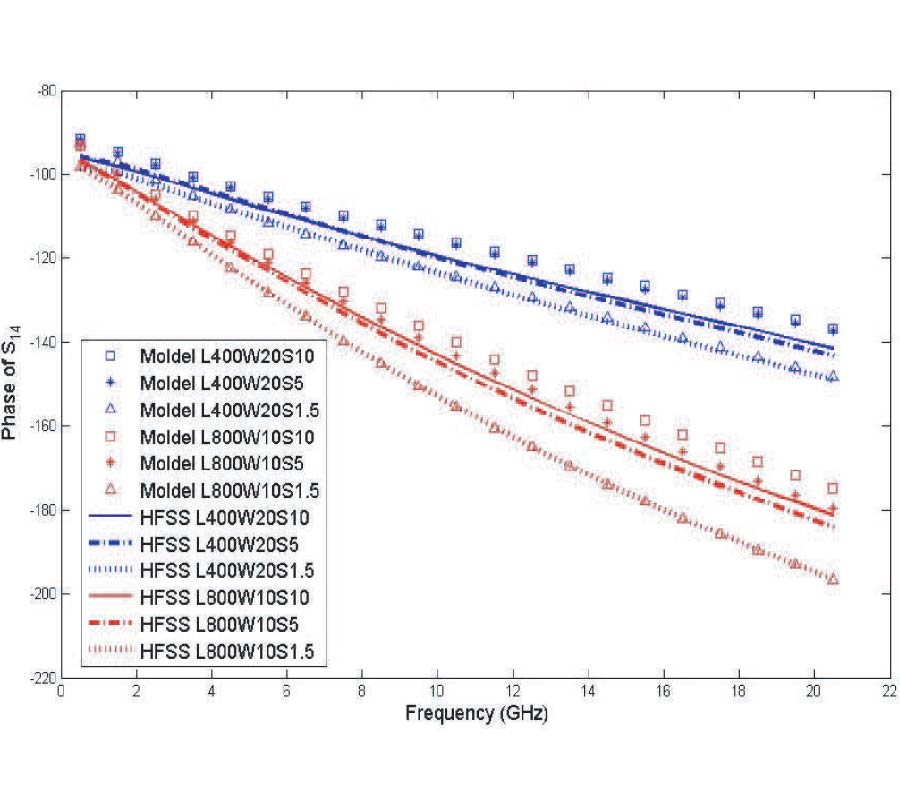
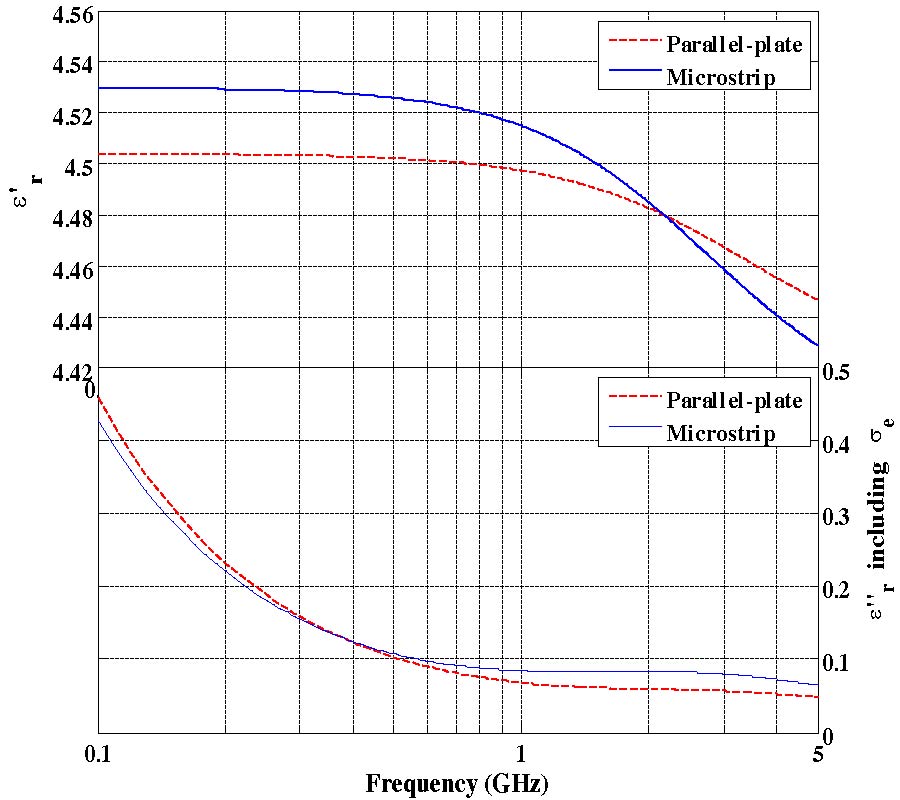
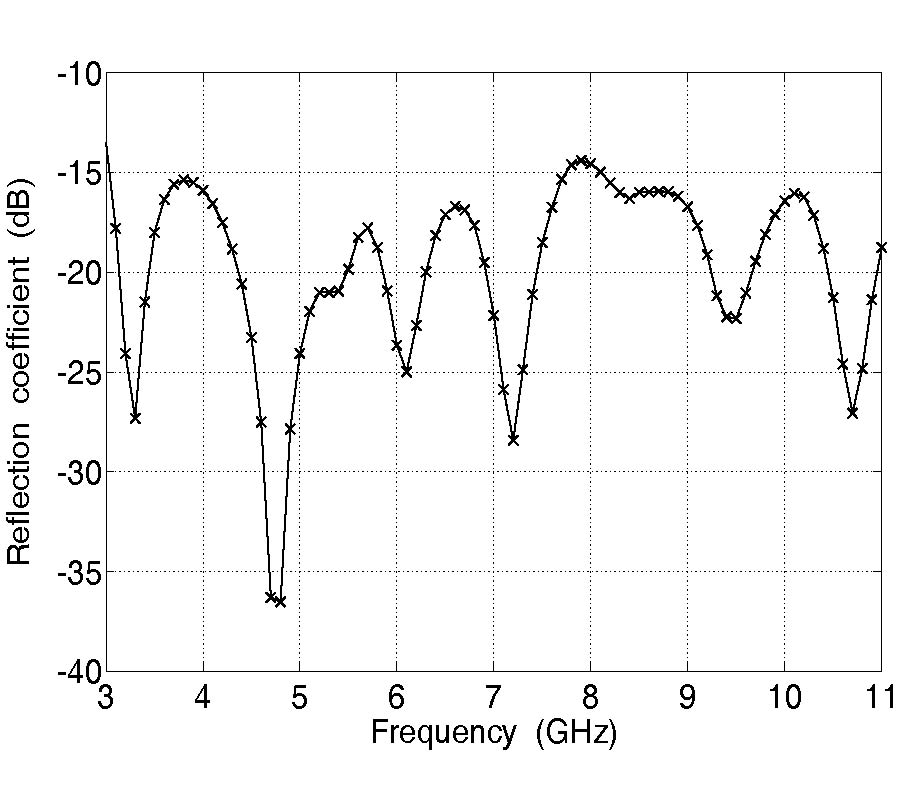
An effective approach to characterize frequency-dispersive sheet materials over a wide RF and microwave frequency range based on planar transmission line geometries and a genetic algorithm is proposed. S-parameters of a planar transmission line structure with a sheet material under test as a substrate of this line are measured using a vector network analyzer (VNA). The measured S-parameters are then converted to ABCD matrix parameters. With the assumption of TEM/quasi-TEM wave propagation on the measured line, as well as reciprocity and symmetry of the network, the complex propagation constant can be found, and the corresponding phase constant and attenuation constant can be retrieved. Attenuation constant includes both dielectric loss and conductor loss terms. At the same time, phase term, dielectric loss and conductor loss can be calculated for a known transmission line geometry using corresponding closed-form analytical or empirical formulas. These formulas are used to construct the objective functions for approximating phase constants, conductor loss and dielectric loss in an optimization procedure based on a genetic algorithm (GA). The frequency-dependent dielectric properties of the substrate material under test are represented as one or a few terms following the Debye dispersion law. The parameters of the Debye dispersion law are extracted using the GA by minimizing the discrepancies between the measured and the corresponding approximated loss and phase terms. The extracted data is verified by substituting these data in full-wave numerical modeling of structures containing these materials and comparing the simulated results with experimental.