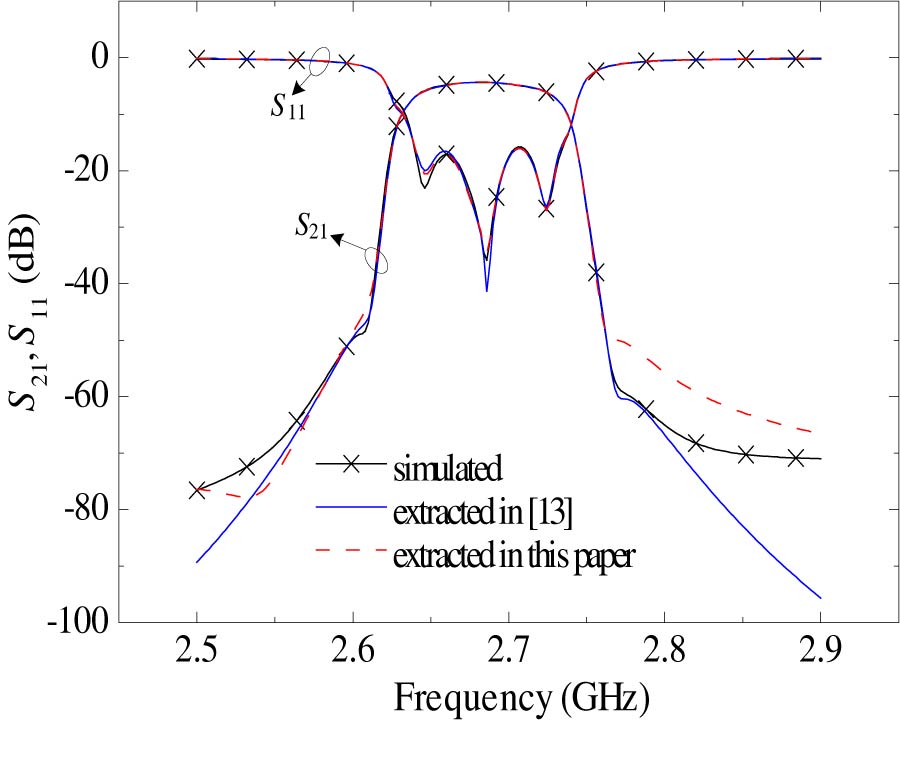
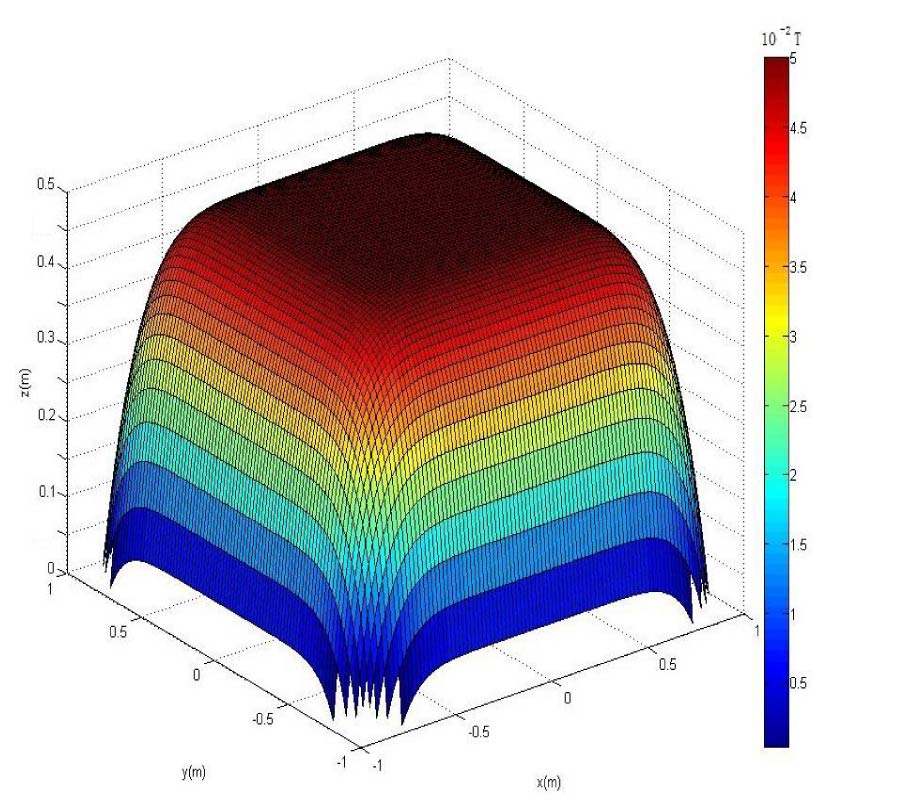
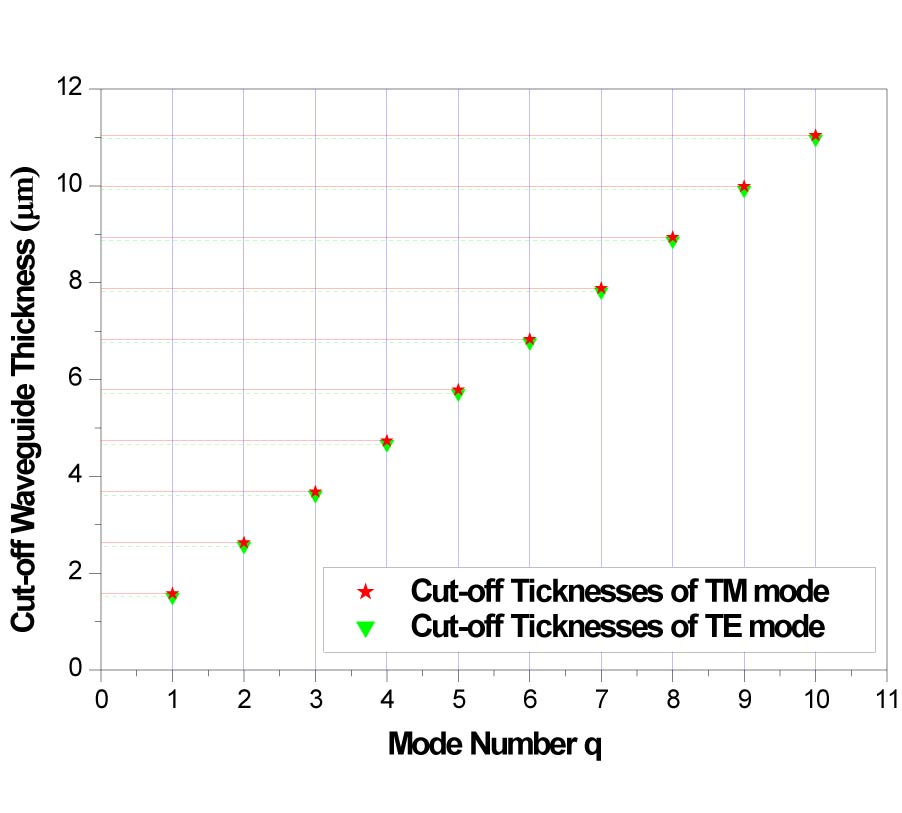
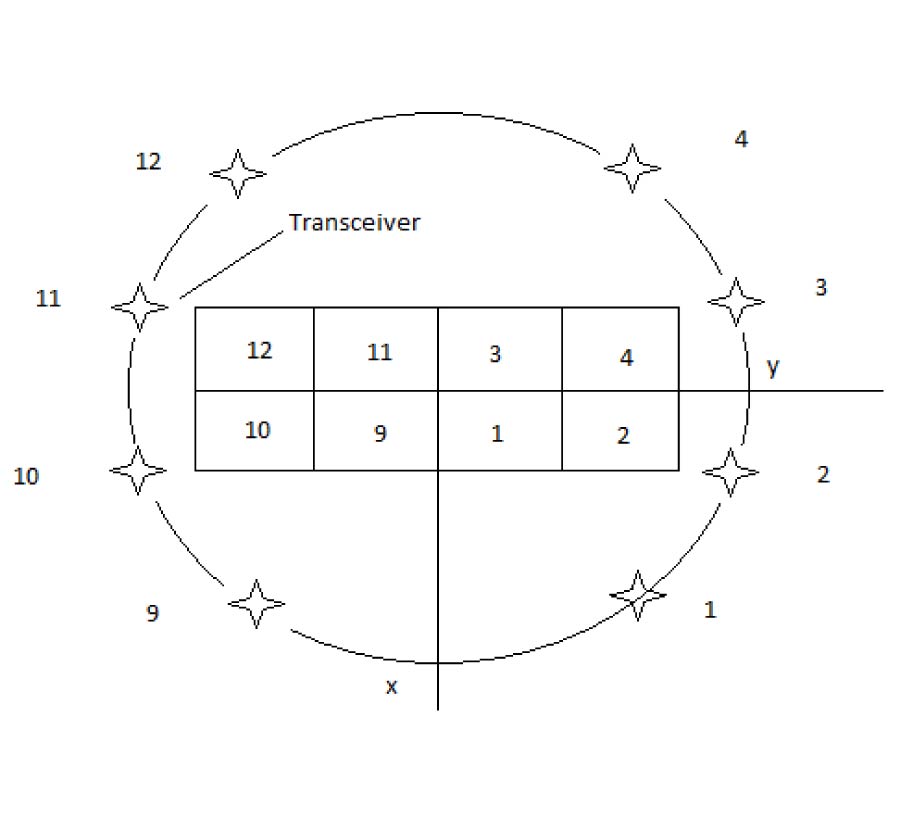
Efficient Analysis of Rectangular-Shape Metamaterials Using P-CBFM/P-FFT Method
Ke Xiao,
Huiying Qi,
Sheng Shui Wang,
Ying Liu,
Liang Ding and
Shun-Lian Chai
In this paper, we introduce an efficient algorithm to analyze metamaterials, which can be finite periodic structures with tightly coupling between nearby cells. Firstly, the algorithm, based on method of moments (MoM), uses hybrid volume-surface integral equation (VSIE) to analyze composite dielectric-conductor objects. Then, the characteristic basis function method (CBFM) and precorrected-fast Fourier transform (p-FFT) algorithm are combined to accelerate the calculation of equations, based on which, metamaterials composed of connected periodic cells can be analyzed efficiently.