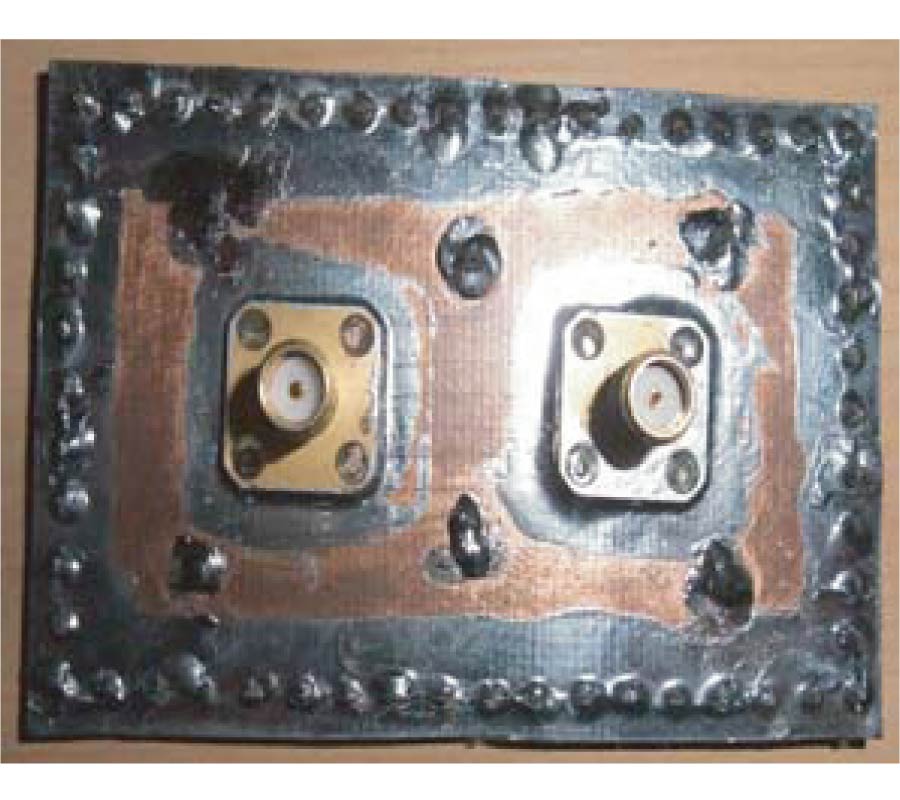
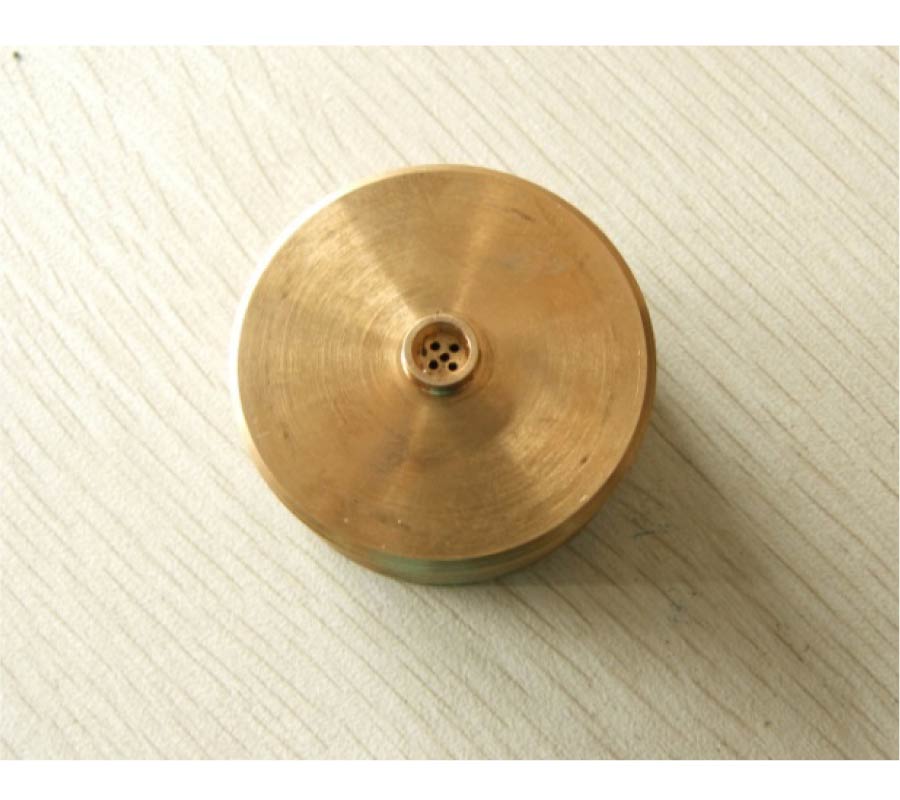
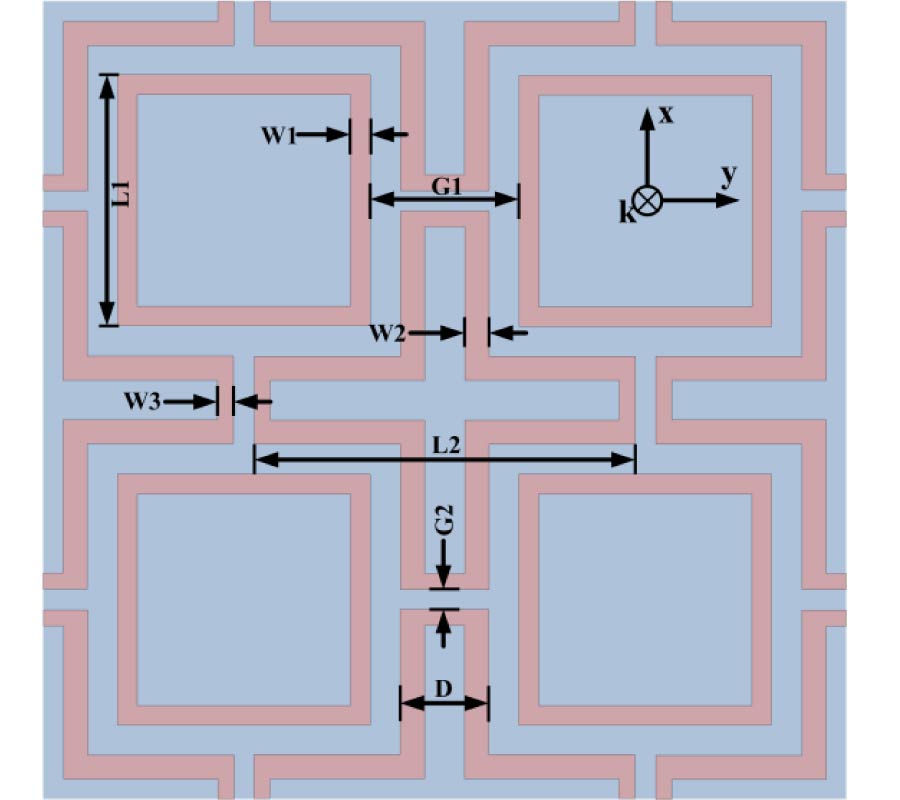
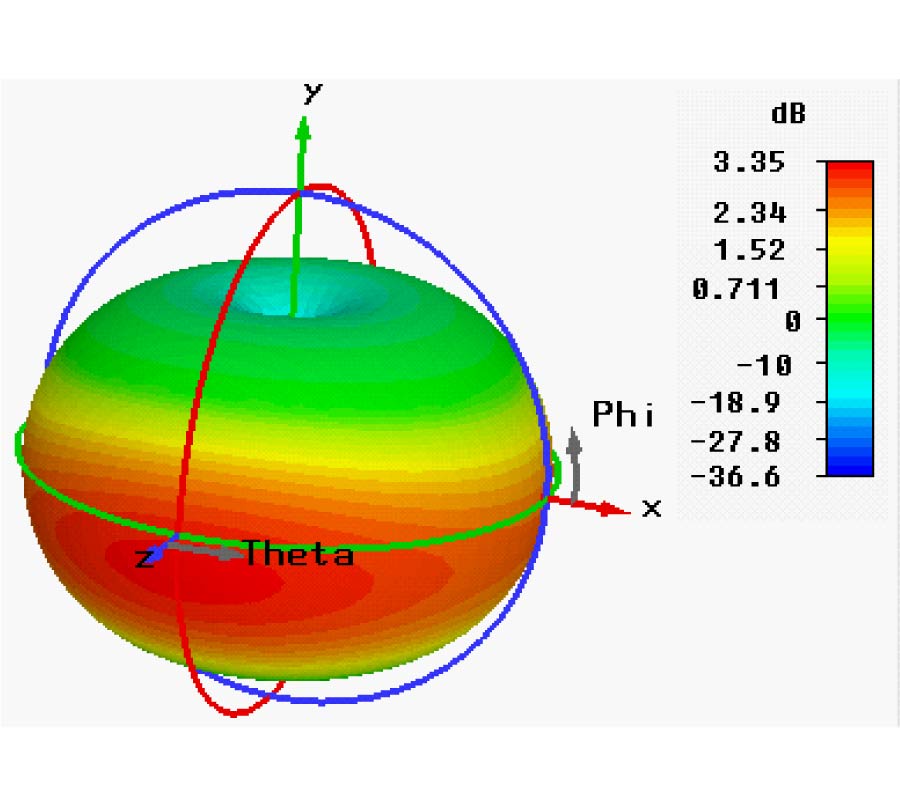
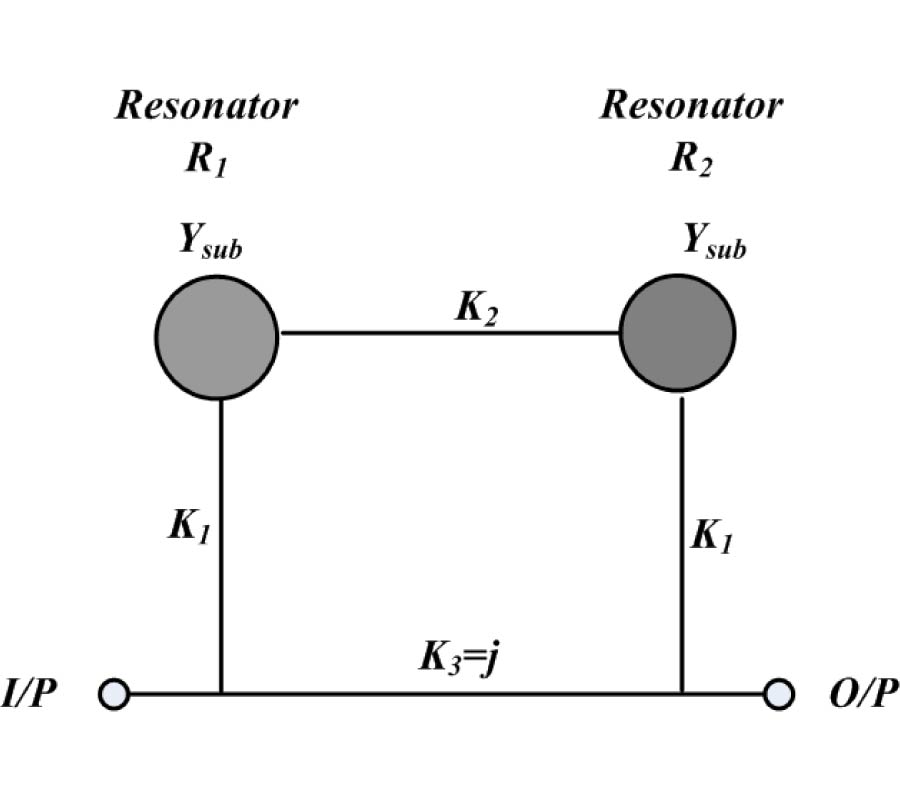
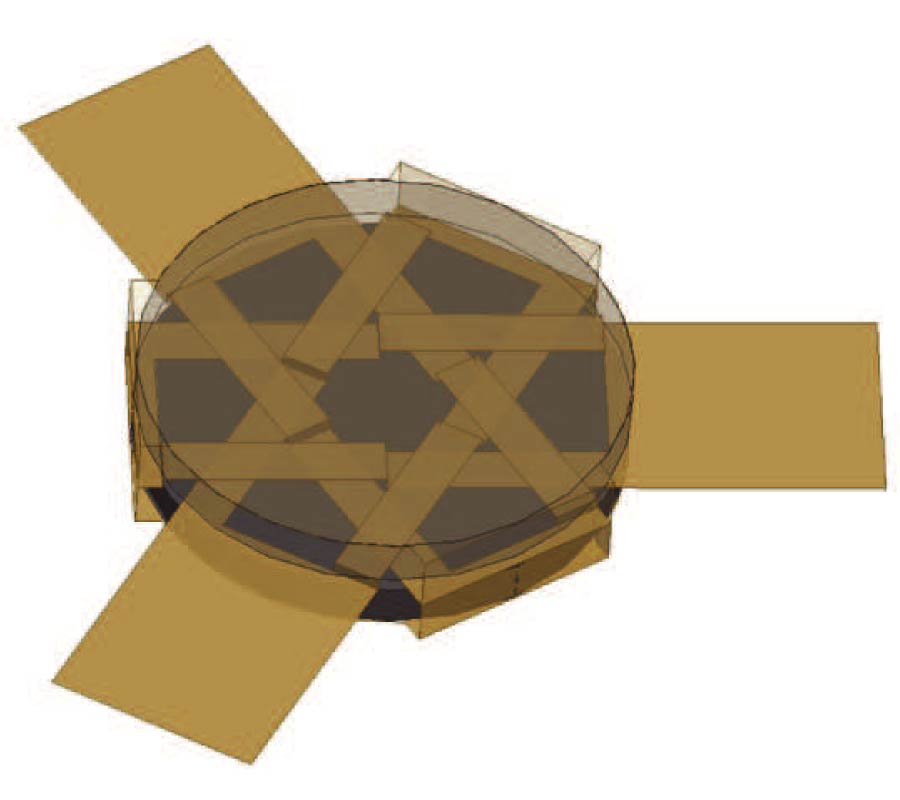
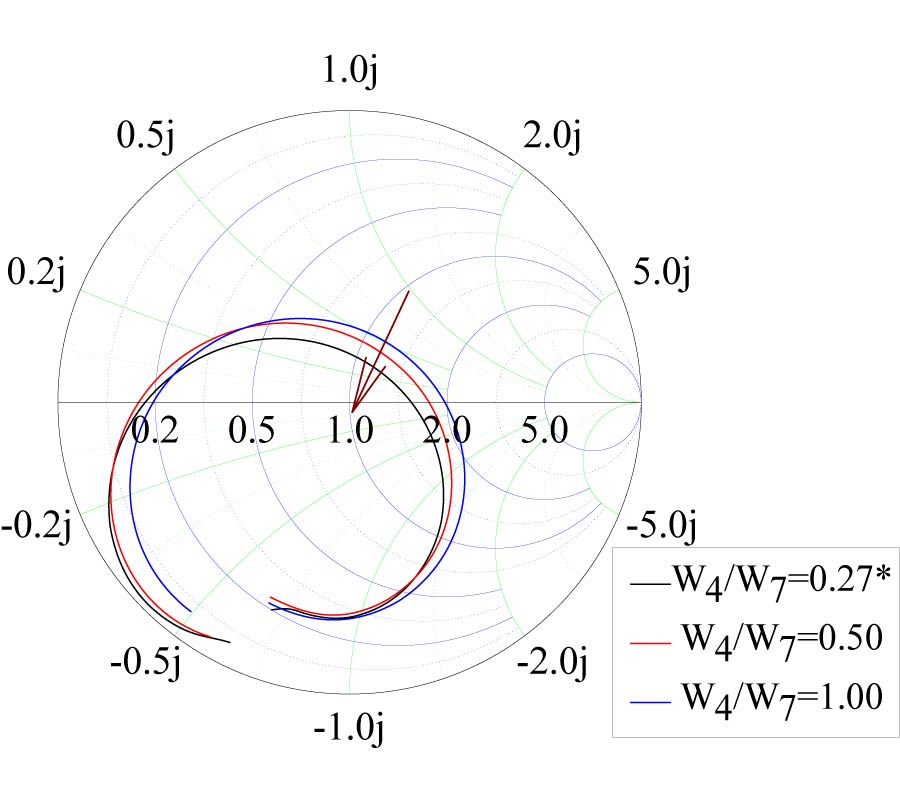
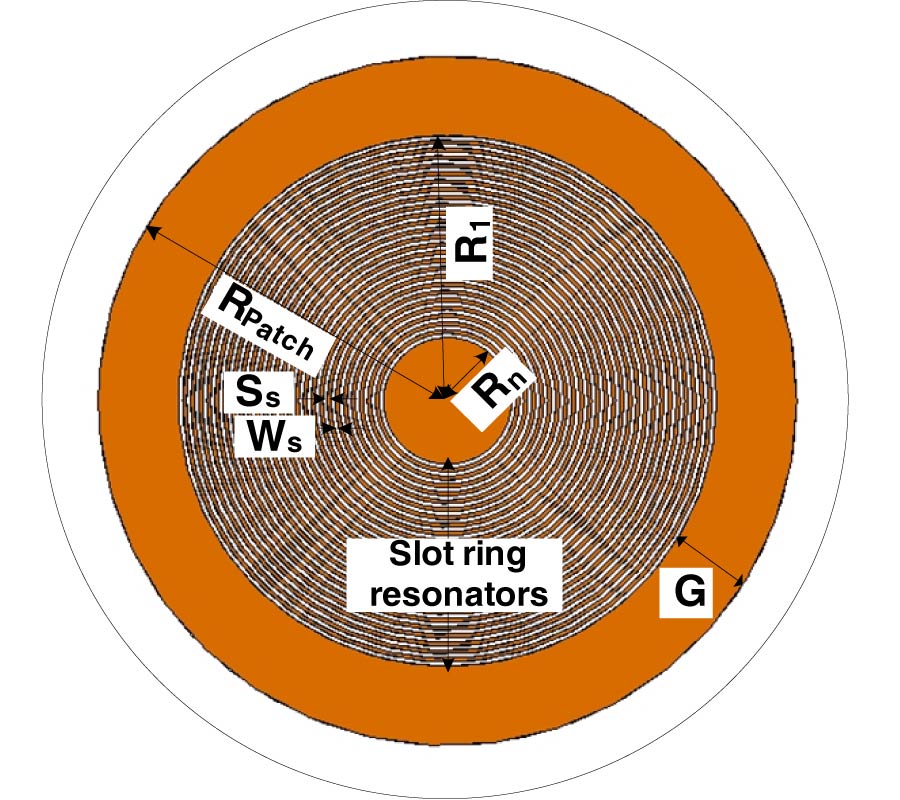
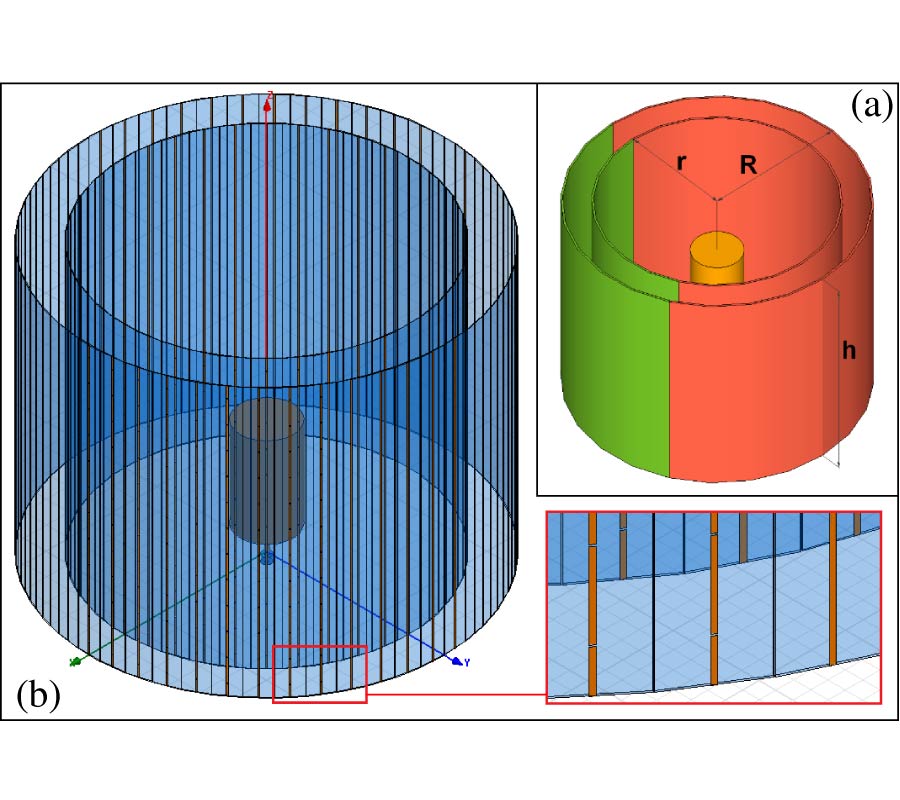
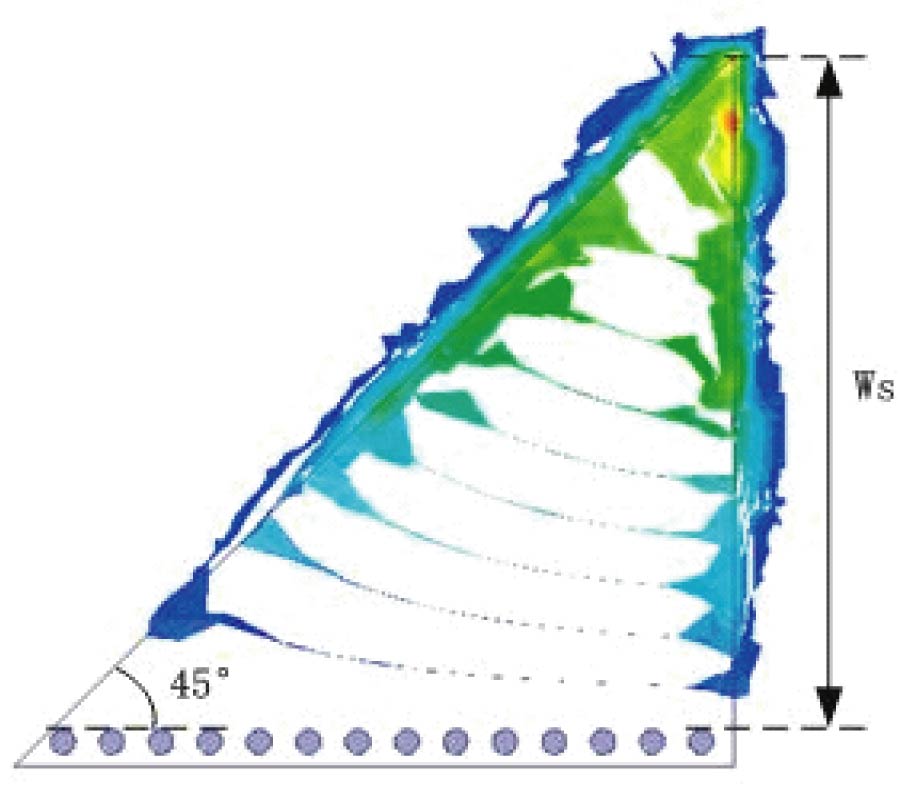
Design of Omnidirectional High-Gain Antenna with Broadband Radiant Load in C Wave Band
Shu Lin,
Meng-Qian Liu,
Xi Liu,
Yi-Chen Lin,
Yu Tian,
Jia Lu and
Zhihua Zhao
three novel structures of coplanar waveguide (CPW) cross-coupling-fed antenna with different kinds of broadband radiant loads, which are applied in C wave band, are presented. The simulated results by CST MICROWAVE STUDIO® indicate that these structures of antenna are able to expand bandwidth, improve gain and maintain good omnidirectional radiation characteristics while the sizes of the structures are relatively small. The antenna surface current simulated by CST is extracted, explaining the mechanism of broadband, high-gain and omnidirectional radiation characteristics of the antenna. Three structures of antenna with different kinds of broadband radiant loads are designed, manufactured and measured. The antenna is printed on FR-4 epoxy substrate with 0.5 mm thickness. According to the measured results of these three structures, the operating bandwidths with a reflection coefficient lower than -10 dB are 4.27~4.90 GHz, 4.04~5.07 GHz and 4.05~4.87 GHz. The relative bandwidths are up to 13.7%, 22.6% and 18.4% respectively. The H-plane maximum omnidirectional gains are 6.6 dB (4.8 GHz), 6.8 dB (4.6 GHz) and 7.8 dB (4.6 GHz), and the maximum magnitudes of un-roundness are 3.0 dB, 2.8 dB and 2.8 dB (4.5 GHz) respectively. The measured and simulated results do not differ much from each other. The overall sizes of the antennas are 133.5 mm × 4.4 mm (triangular load), 148.2 mm × 8 mm (cutting semi-circular load) and 145.65 mm × 6.1 mm (circular load) respectively, and the gains per electronic length on the polarization direction are 3.2 dB, 3.0 dB and 3.5 dB, which are relatively high. These three structures of antennas are suitable for communication systems working in C wave band.