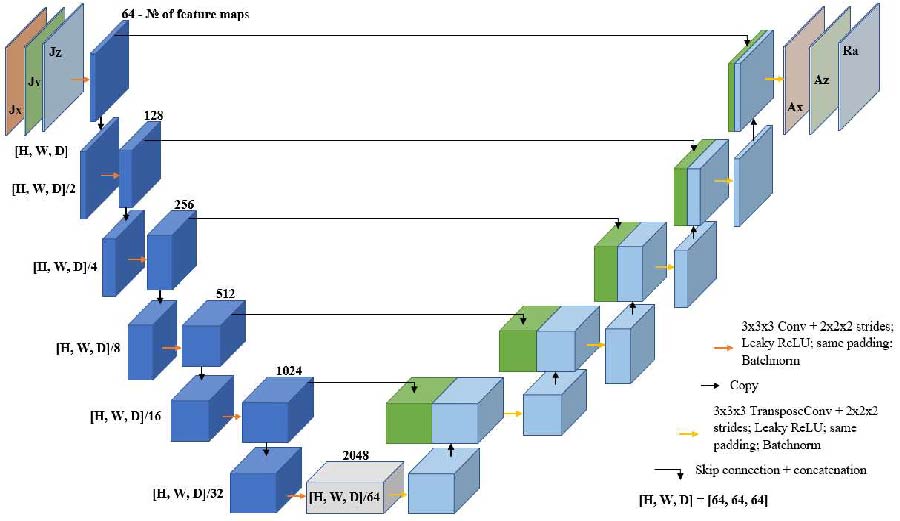
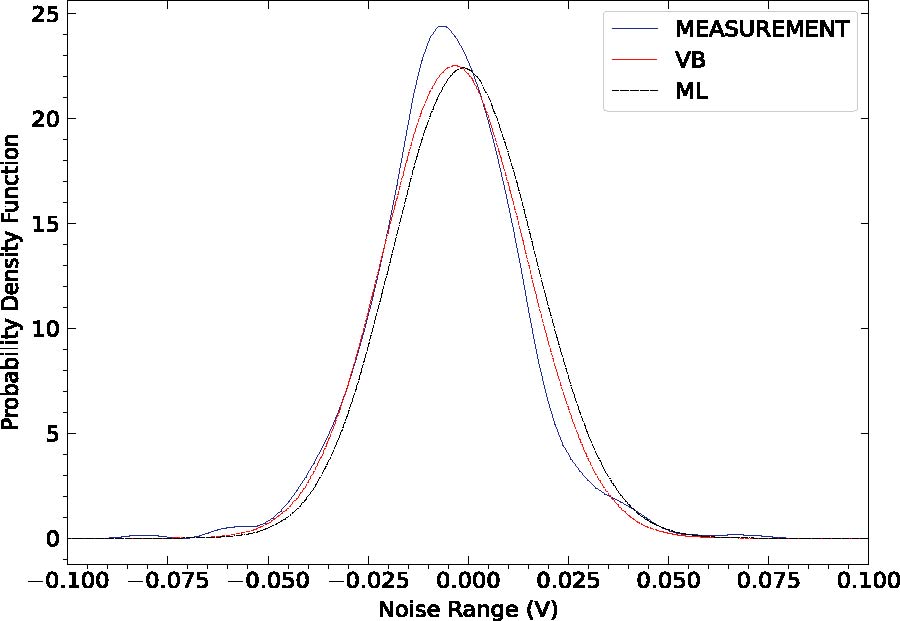
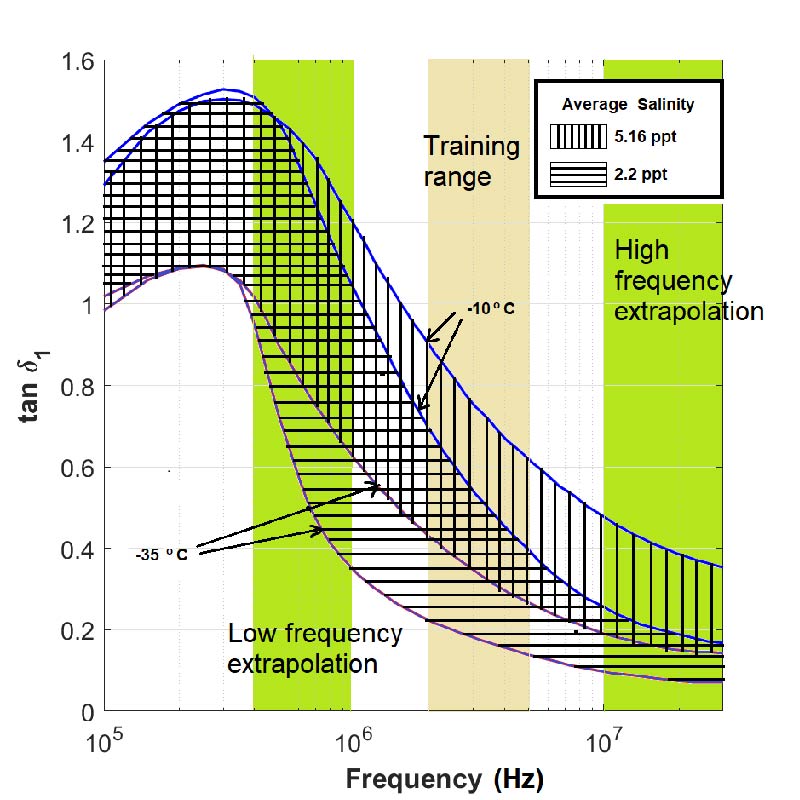
Estimation of Thickness and Dielectric Characteristics of Sea Ice from Near-Field EM Measurements Using Deep Learning for Large Scale Polar Ice Probing
Mohammad Shifatul Islam,
Sadman Shafi and
Mohammad Ariful Haque
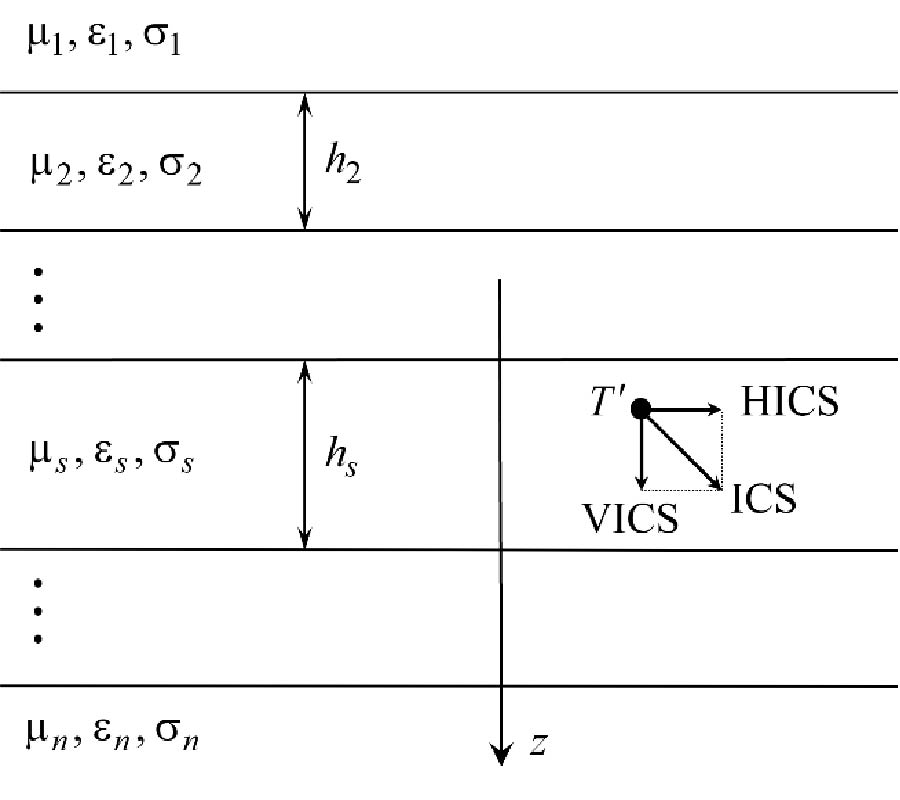
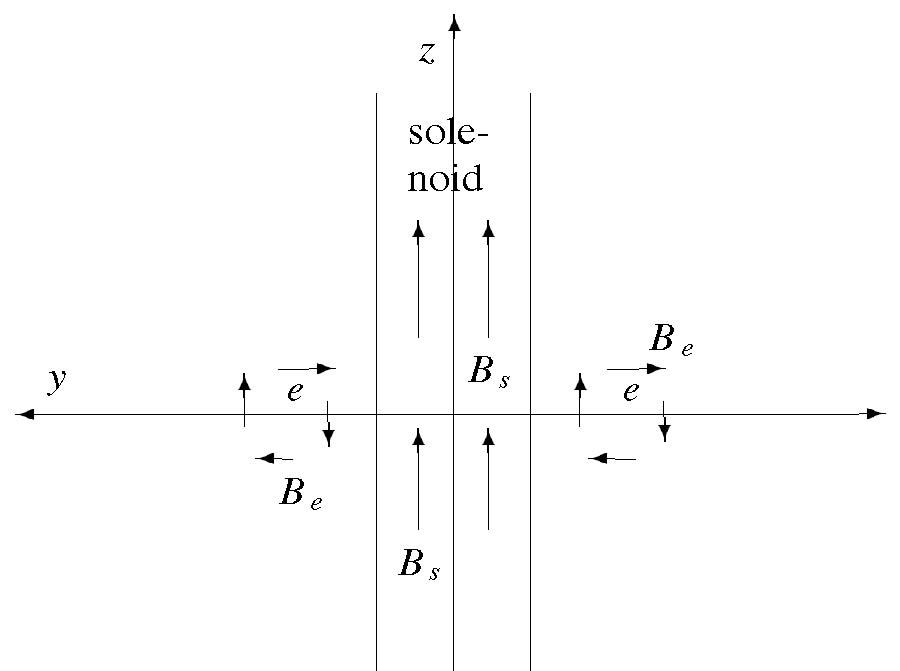
The near and far field EM responses over layered media have long been exploited in diversified applications such as remote sensing, monitoring and communication. In this work, we utilize the near field dependence of the EM fields of a three layered structure resembling air-sea ice-sea water to estimate the thickness and dispersion characteristics of sea ice using deep learning technique. We explore two key methods of field measurement termed as the fixed and scaled sweep methods. In the fixed radial sweep method, the receiver distance and height from the source are kept constant, and in the scaled sweep method both the receiver distance and height are set as a scaled function of the operating wavelength. A synthetic training dataset has been generated (using analytical computation and FEM simulation) in the low MHz band, which is used to train a deep learning model. The model is tested on different test datasets with frequencies inside, below and above the training limits. Even though the fixed sweep method is simpler to implement, the scaled sweep appears to perform better across the wide range of test frequency, both in and outside the training range. When the test frequency is inside the training range, the percentage errors for thickness, dielectric constant, and loss tangent were found to be <2%, <10%, and <5%, respectively, for the fixed radial sweep, whereas for the scaled sweep the percentage error is < 1% for all three measurement parameters. When the test frequency deviates further from the training range, the percentage error gradually increases. Later, we investigate the problem of determining sea ice thickness assuming a priori knowledge of sea ice dielectric parameters, and results show that the model estimates the thickness of the sea ice bulk with error as low as 0.1%.