ELF-EMFs Induced Effects on Cell Lines: Controlling ELF Generation in Laboratory
Marco Farina,
Marcello Farina,
Maria A. Mariggio,
Tiziana Pietrangelo,
Joseph J. Stupak,
Antonio Morini and
Giorgio Fano
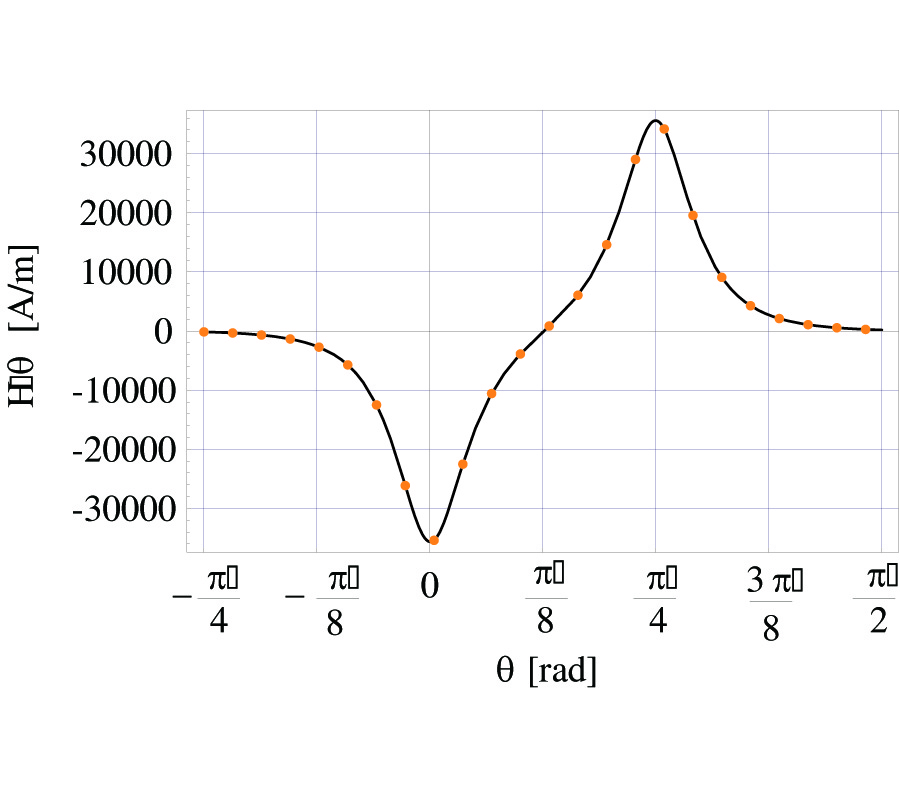
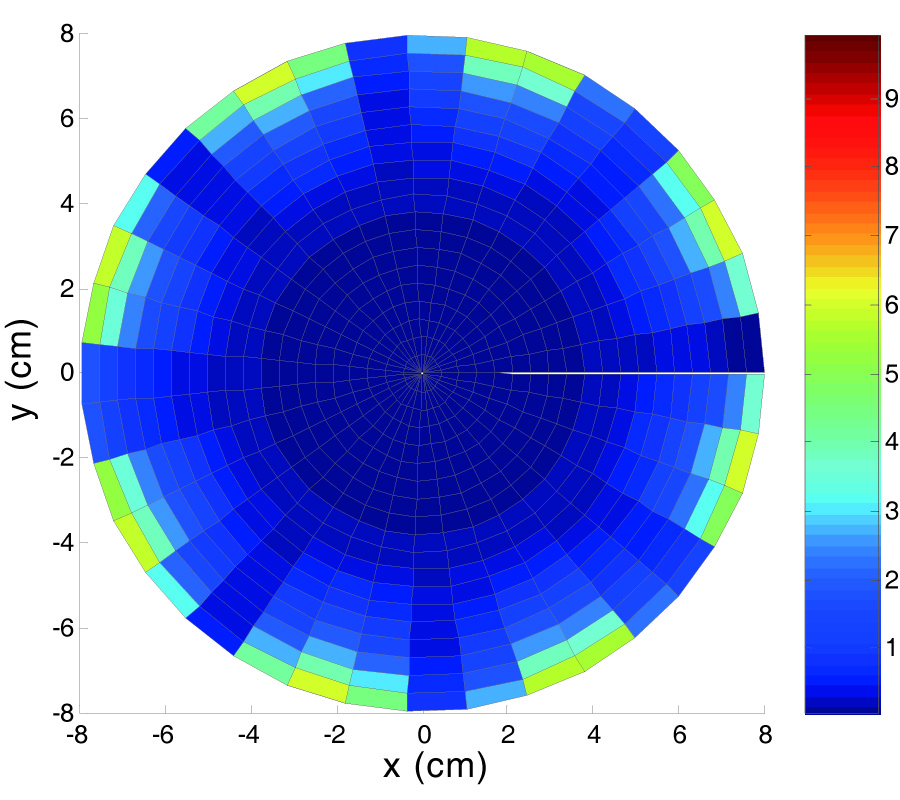
The aim of this paper is to discuss the effects of the exposure to Extremely Low Frequency ElectroMagnetic Fields (ELF-EMFs) on non- and excitable cells using in vitro cell models, namely neuron-like cell line (PC12), glioblastoma GL15 as glial model and C2C12 myocytes as muscle model, focusing our attention on standardized protocols for ELF-EMFs generation and exposure. A major issue in laboratory -and likely in natura- studies about possible biological effects of ELF waves is the difficulty in providing standard, reproducible environmental conditions. Hence, as part of the work we have developed an exposure system including a probing scanner, able to sample a given volume and to measure the time-varying magnetic field vector. The system allows detection, monitoring and removal of electromagnetic noise sources, as well as means to assess field homogeneity in terms of intensity and polarization.