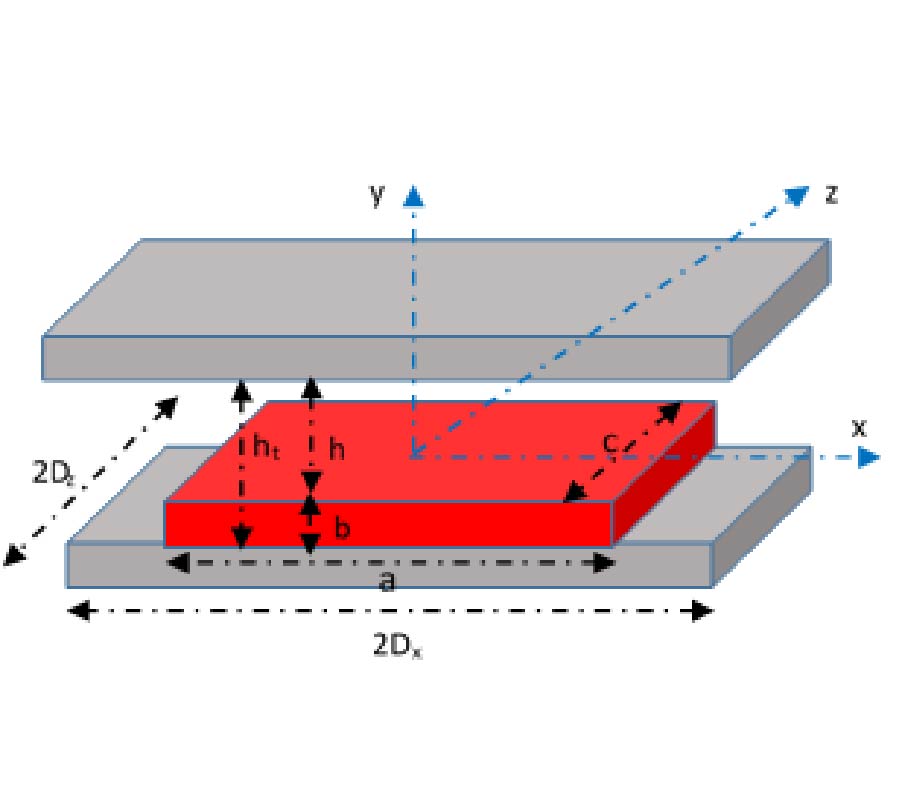
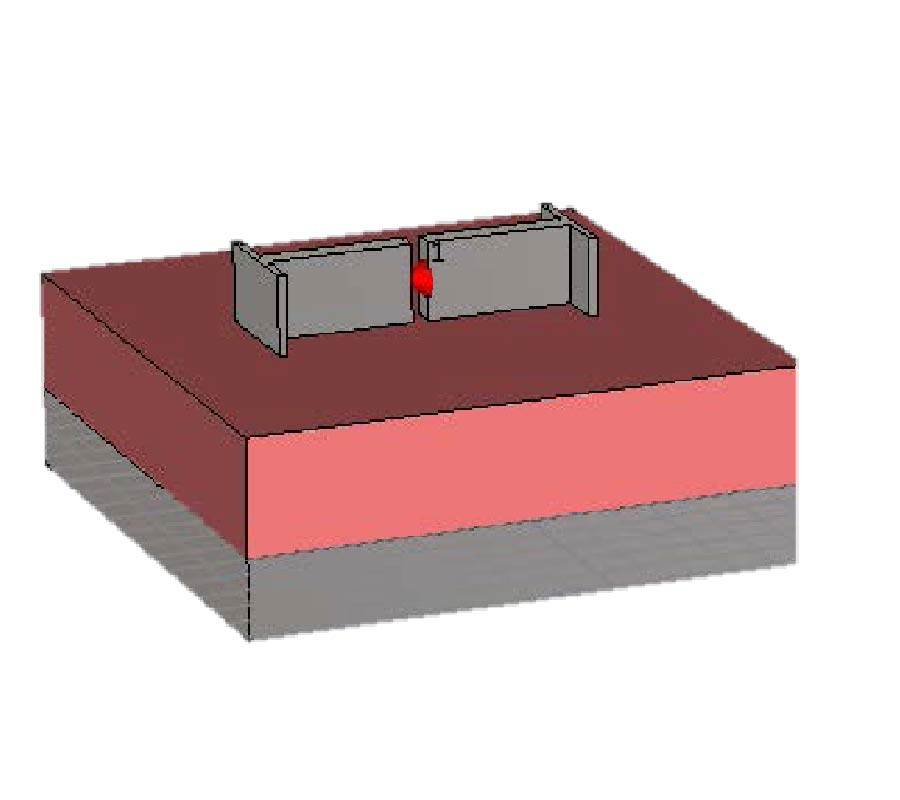
Investigation of Plasmonic Metal Conductors and Dielectric Substrates on Nano-Antenna for Optical Wireless Communication
Shekhara Kavitha,
Kanduri Venkata Sairam and
Ashish Singh
In this manuscript, plasmonic metal conductors such as Silver, Gold, Aluminum, Copper, Chromium, Tungsten, Titanium, and Nickel are investigated on a T-shaped nano dipole antenna using dielectric materials such as Silicon Dioxide, Zinc Oxide, Indium Tin Oxide, and Silicon Nitride. The optical properties of the conductors and dielectric materials are modeled using Drude and Lorentz dispersive models, respectively. It is observed that the Aluminium metal supports high quality plasmonic oscillations for a wide range of Terahertz frequencies. The Aluminium metal also shows high losses occurring at the Terahertz frequency among the other metals. The Gold and Silver can resonate in the visible region and have moderate losses compared to the other plasmonic metals. It is noticed that the near-zero permittivity point of the Silicon Dioxide substrate occurs at 2875 THz which is much greater than the other three substrates. Further, it is observed that on the Silicon Dioxide, Zinc Oxide, and Silicon Nitride substrates the Silver Nano dipole antenna shows the maximum directivity of 6.615 dBi, 5.671 dBi, and 5.709 dBi, respectively. The Aluminium nano-antenna gives the maximum directivity of 5.066 dBi on the Indium Tin Oxide substrate. The Silver-Silicon Dioxide Nano-antenna will be suitable for the terahertz optical wireless communication.