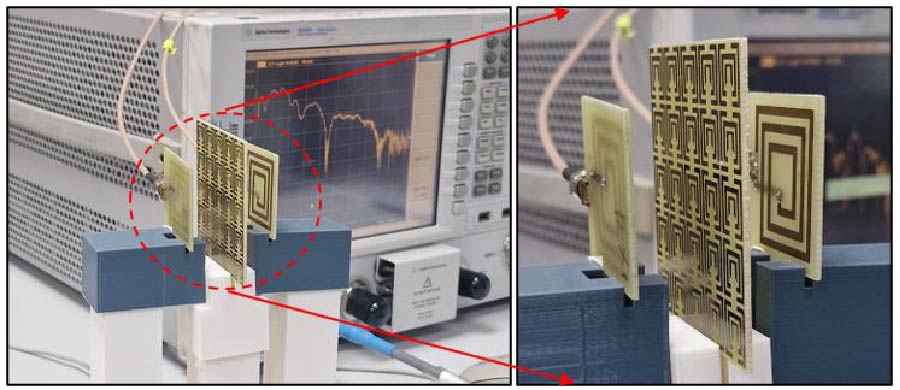
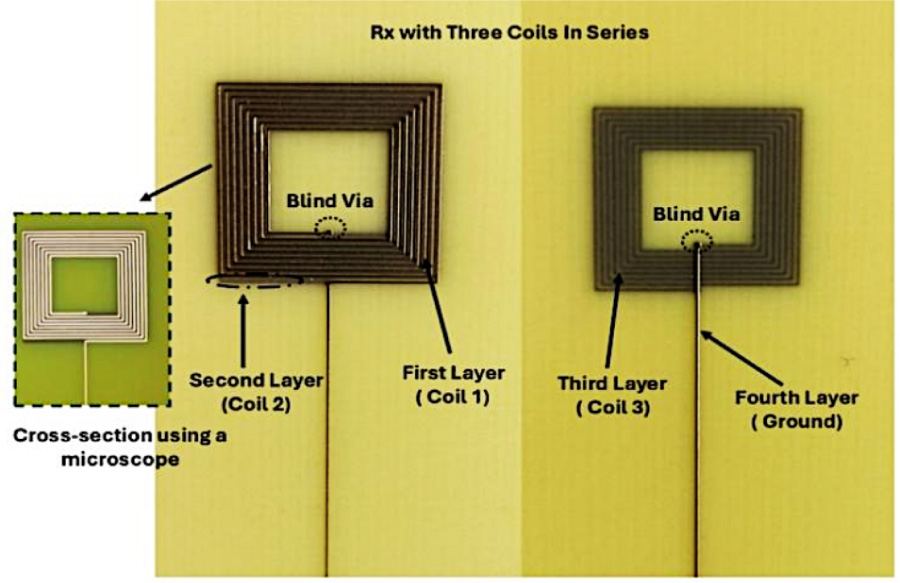
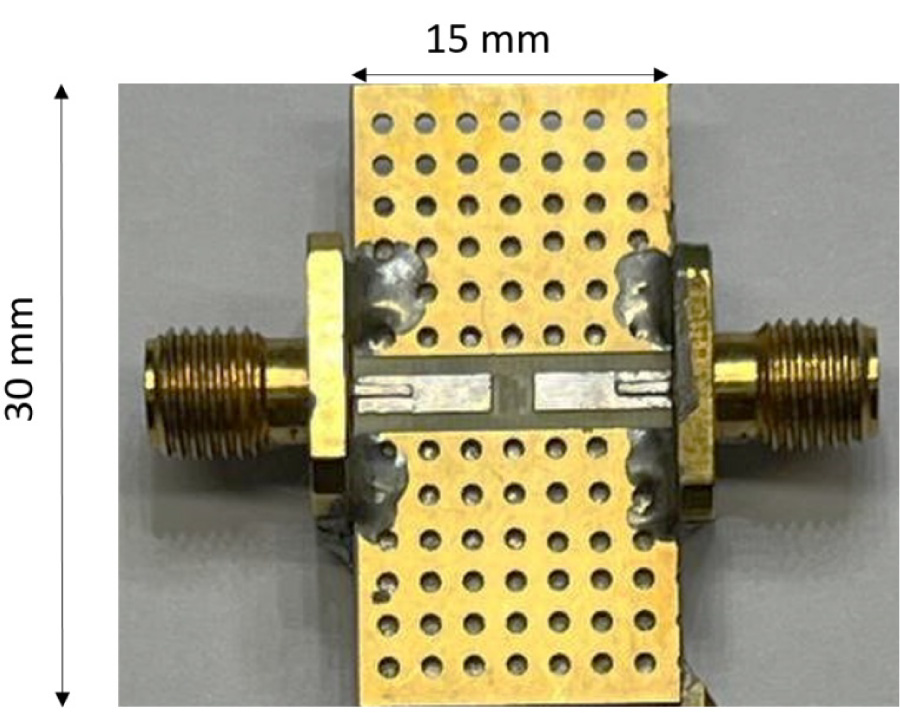
Multi-Layer Square Coil-Based Wireless Power Transfer for Biomedical Implants
Hala Kamal Abduljaleel,
Sadik Kamel Gharghan and
Ahmed Jamal Abdullah Al-Gburi
Biomedical devices (BDs) monitor vital signs and diagnose illnesses to improve patients' lives. These BDs rely on battery power, which is often short-lasting. To address this limitation, wireless power transfer (WPT) has been proposed in research as a solution for wirelessly recharging BD batteries. This paper aims to enhance WPT in a nonradiative near-field system for implanted BDs by designing and fabricating a triple-layer receiver coil operating in the 13.56 MHz ISM band. First, three square coil models --- single-layer, double-layer, and triple-layer—were developed and simulated using HFSS ANSYS software. The coil models were tested at air gaps ranging from 2 to 40 mm between the transmitter and receiver coils. The single-layer and double-layer coils, each with a receiver coil size of 10×10×0.5 mm, achieved transfer efficiencies of 76.19% and 80.03%, respectively, at an air gap of 10 mm. In contrast, the triple-layer coil, designed with a receiver coil size of 10×10×1.5 mm, attained a transfer efficiency of 87.83% at the same air gap. Additionally, the study analyzed the specific absorption rate (SAR), which was measured at 0.1823 W/kg for 1 g of tissue. Second, the triple-layer square coil was validated through fabrication and experimental testing in different environments, including air, acrylic, and biological tissue (beef). The results demonstrated transfer efficiencies of 80%, 77%, and 63% in air, acrylic, and tissue, respectively. Moreover, the experimental results closely matched the simulation ones, confirming that the triple-layer square coil model accurately represents real-world performance.