Effects of Power-Frequency Magnetic Fields on Body Mass in Rats: a Pooled Analysis
Tsutomu Nishimura
,
Harue Tada
,
Satoshi Teramukai
,
Kaneo Mohri
and
Masanori Fukushima
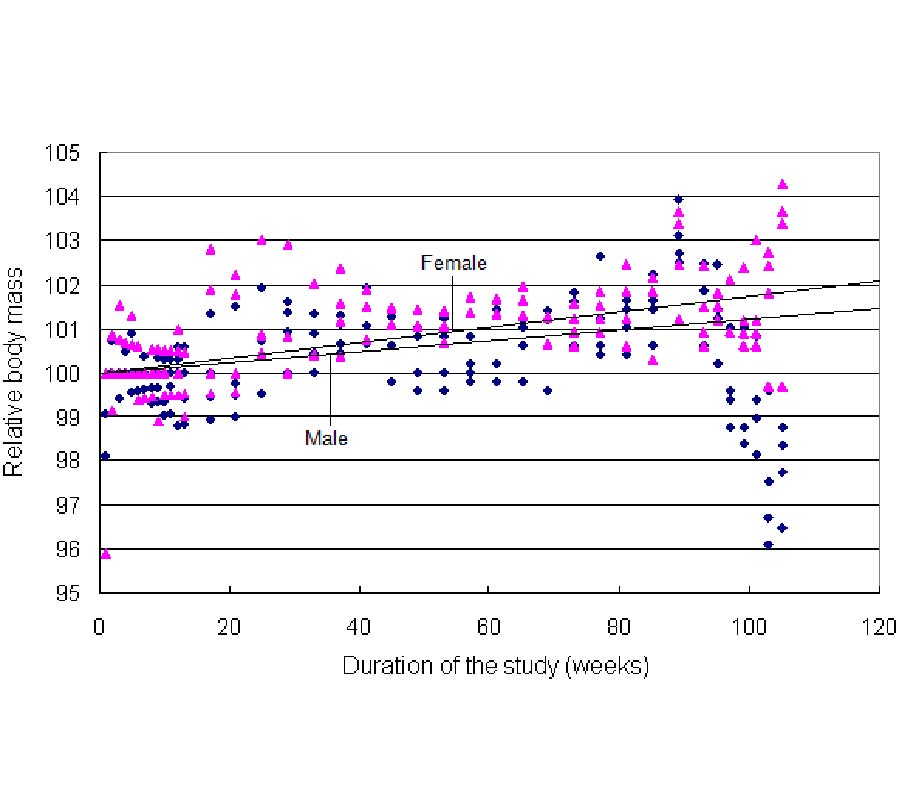
There is some evidence that exposure of various animals to a power-frequency magnetic field can cause increases in body mass. However, the precise nature of the relationship is not clear, particularly for long-term exposure. To clarify the relationship between long-term power-frequency magnetic field exposure (2 years) and animal body mass, we conducted a pooled analysis of data in two studies to examine the impact of power-frequency magnetic field exposure on body mass as compared with sham-exposed rats of both sexes. Relative body mass was the response variable, and the study duration (in weeks), magnetic flux density ($\upmu$T), and daily exposure time (hours/day) were the explanatory variables with adjustment for the study. We analyzed by sex. The P-value (P) was defined as the probability of having observed our data (or more extreme data) when the null hypothesis was true. In multiple linear regression analyses of male and female rats, performed separately, we obtained estimates of the effect on relative body mass of study duration (coefficients 0.0225 and 0.0201, respectively; both P<0.0001), magnetic flux density (coefficient 0.0002 for males, P<0.0001; coefficient -0.0002 for females, P=0.0015), and daily exposure time (coefficient 0.046 for males, P=0.0007; coefficient -0.072 for females, P<0.0001). Our pooled analysis has shown that there is a possible relationship between duration of exposure to power-frequency magnetic fields and body mass in rats.