Millimeter Wave Antennas: A
State-of-the-Art Survey of Recent Developments, Principles, and Applications
Reena Aggarwal,
Ajay Roy and
Rajeev Kumar
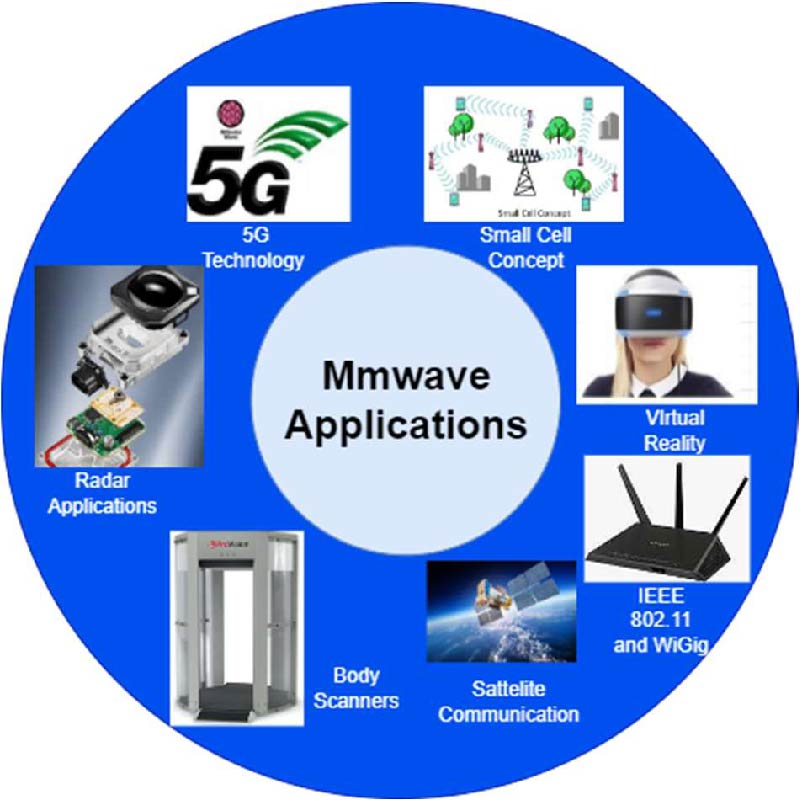
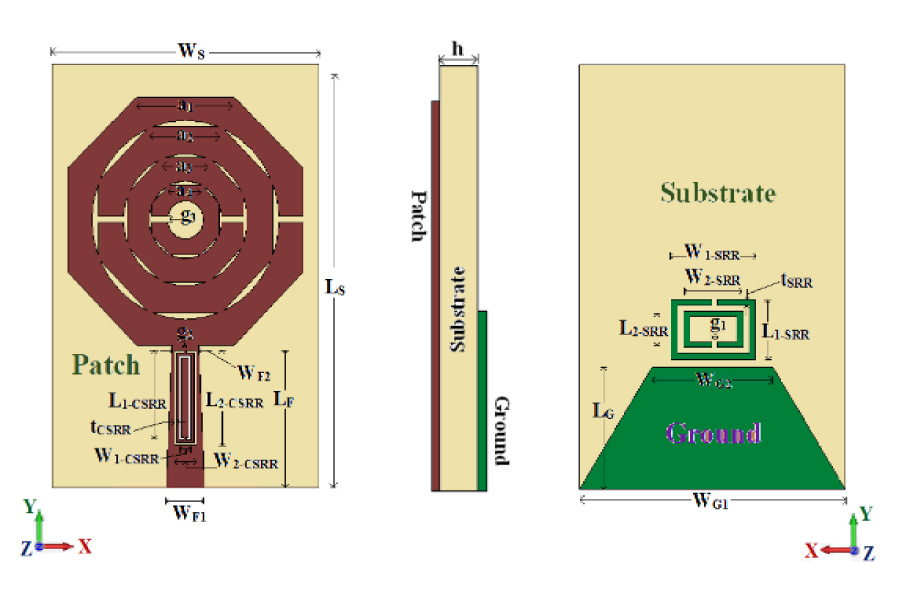
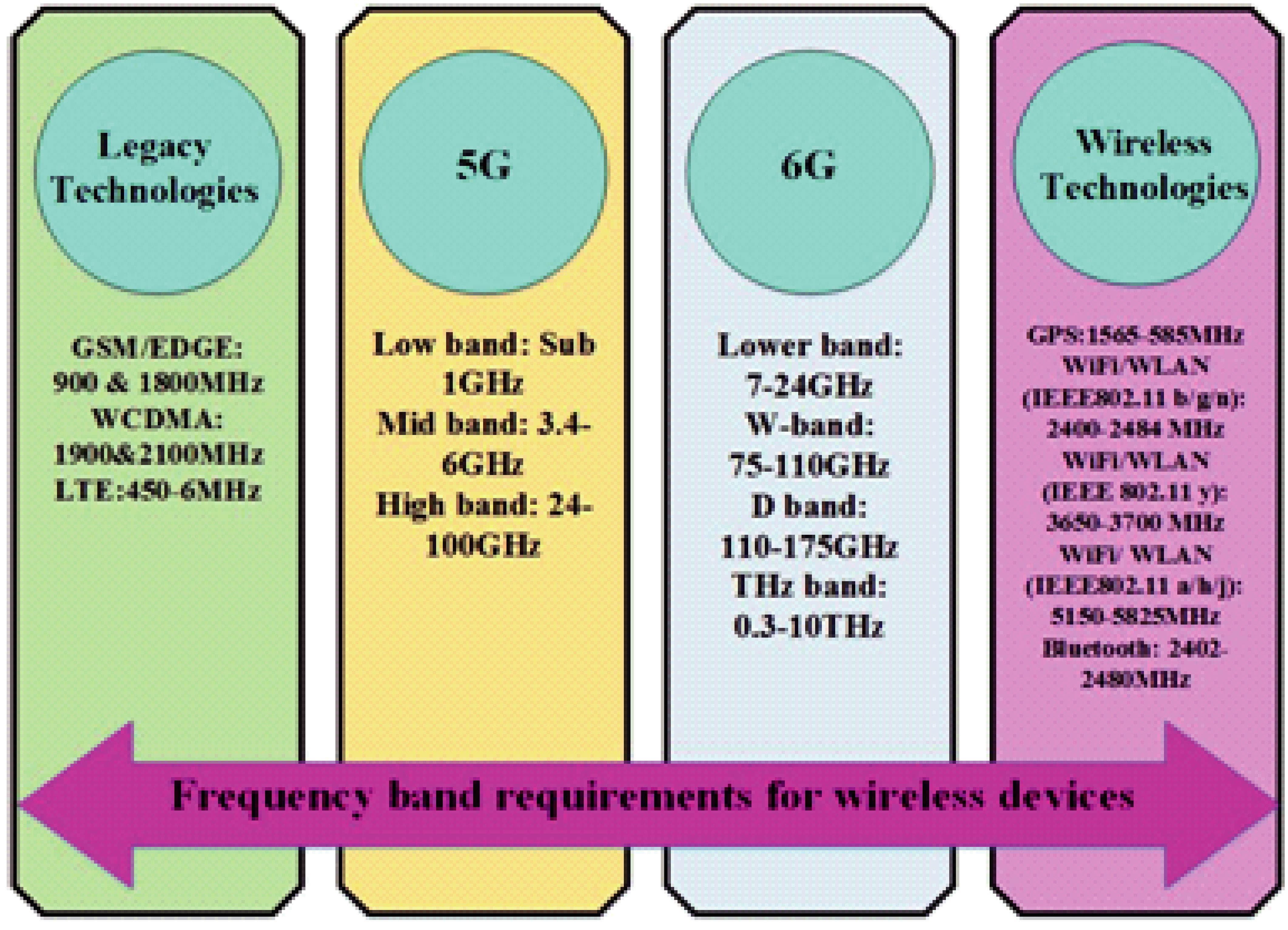
The increasing volumes of data generated by social networking, cloud computing, e-commerce, and online video broadcasting necessitate the implementation of higher data rates. As the current 4G network encounters congestion and potentially struggles to accommodate the substantial data demand, there is a growing interest in millimeter wave (mmWave) technology. The 30-300 GHz mmWave spectrum is characterized by its broad bandwidth and low latency; it is having many applications in communication domains, also includes 5G cellular. Despite its atmospheric attenuation and non-line-of-sight (NLOS) propagation, the majority of nations have begun to implement mmWave 5G in the band of 28/38 GHz as a result of its reduced path loss exponent, minimal signal spread, and decreased atmospheric attenuation. While the patch antenna (single-element) is a compact and easily transportable choice for mmWave applications, its radiation efficiency, gain, and bandwidth are all subpar. Array antennas have effectively addressed these limitations by exhibiting significant enhancements in bandwidth, gain, and radiation efficiency. It is still limited in the maximum data rates it can accommodate. The rate of data can be increased by a factor of one thousand using Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology, which is enabled by geographical diversity and multiplexing techniques. As a result, comprehension of the structures of MIMO antennas operating at mmWave is imperative for the continued enhancement of performance. In comparing the efficacy of these designs, bandwidth, isolation, efficiency, gain, and radiation pattern are considered. In this paper, the most recent planar MIMO antenna designs, which are categorized as defected ground structures, Slot/Patch/Stub, MIMO Antenna Array, Dielectric Resonator Antenna, and Meta-Surface/Metamaterial Structures, are described. This paper also addresses the effects that slots, partial ground, and decoupling structures have on levels of isolation, bandwidth, and impedance matching. A comprehensive analysis of the design considerations and subsequent advancements is also provided in this paper.