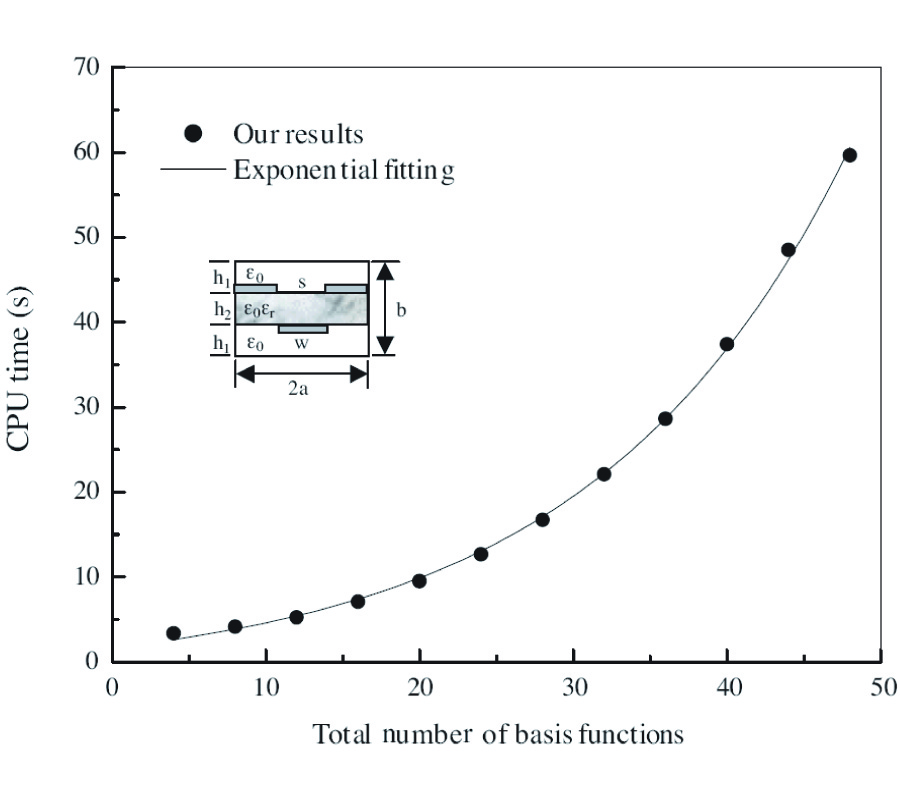
Analysis of the Mixed Coupling in Bilateral Microwave Circuits Including Anisotropy for Mics and Mmics Applications
Mohamed Lamine Tounsi,
R. Touhami,
A. Khodja and
Mustapha Yagoub
Higher integration and smaller layout size, two major trends in today's industry, lead to more prominent electromagnetic coupling with direct applications in the RF/microwave area such as directional couplers, filters, multiplexers, shifters, delay lines, etc. In the present work, an efficient hybrid-mode method is presented for a rigorous characterization of the coupling in multilayer bilateral microwave circuits including anisotropy effects. Various types of planar configurations were considered including microstrip, finline and coplanar structures, but the proposed approach can easily be extended to any form of coupled lines. To fully characterize bilateral multilayer circuits in millimetre wave region with an arbitrary number of conductors, closed forms of dyadic Green's functions were determined in the spectral domain, with use of the Galerkin technique. The computed results show good agreement with data available in the literature. Furthermore, two original configurations based on three line bilateral couplers were computed and validated using neural network models.