An Innovative Portable Ultra Wide Band Stereophonic Radio Direction Finder
Shubhendu Joardar
,
Minakshi Jaint
,
Vasudev Bandewar
and
Ashit Bhattacharya
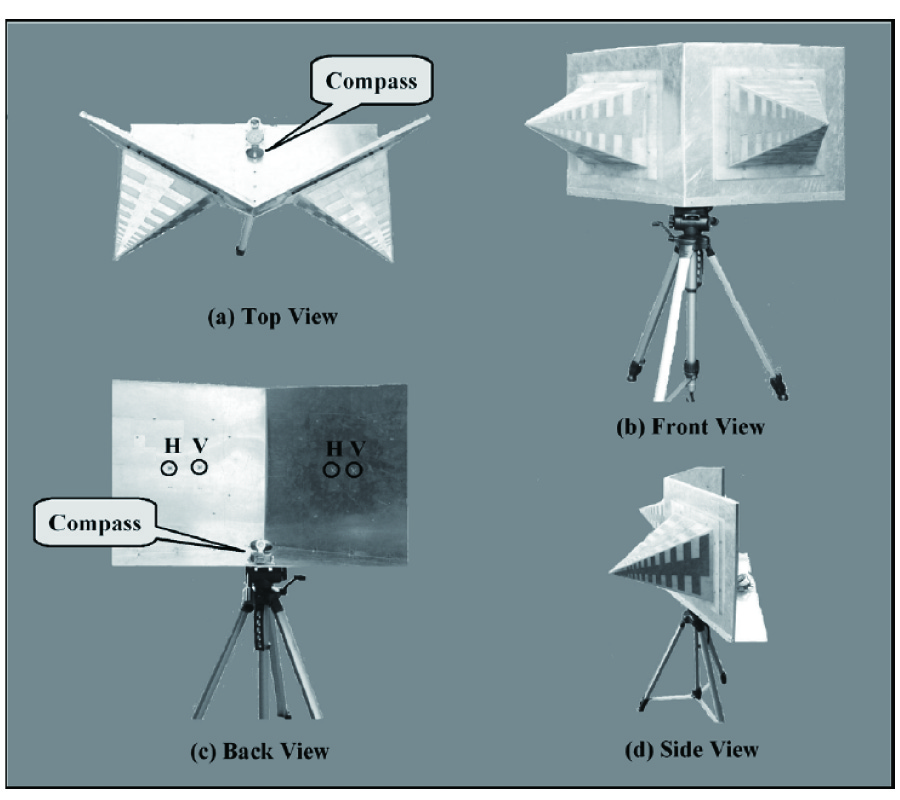
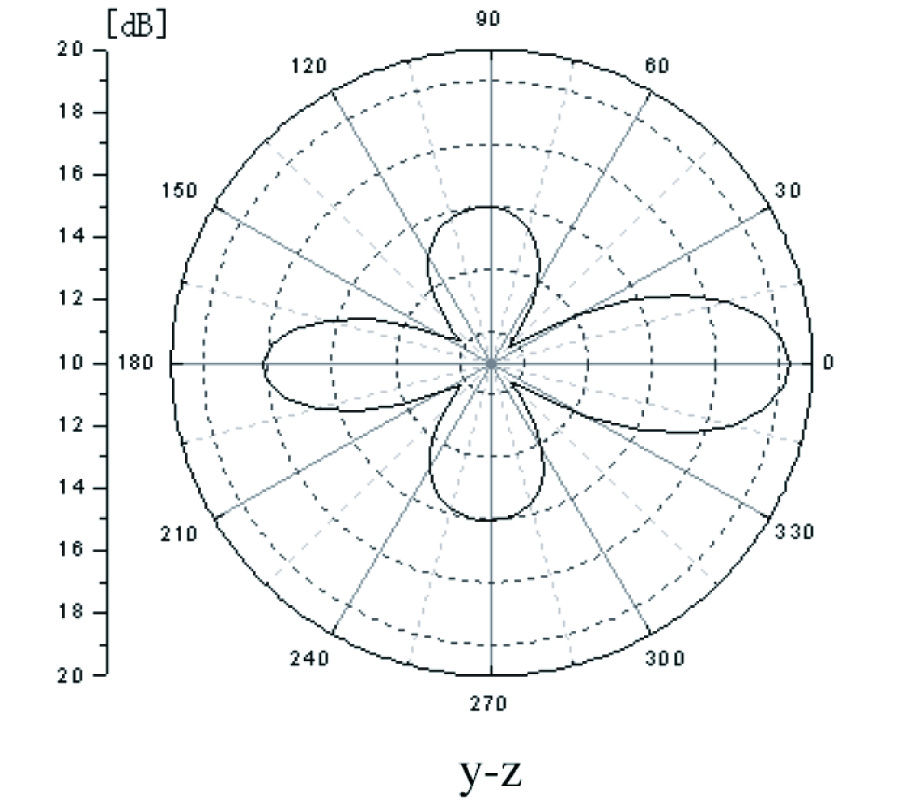
A portable ultra wide band radio direction finder has been constructed based on the principle of stereophonic direction recognition of sound by human ears. The instrument consists of two log periodic antennas having identical electrical properties. They are positioned in a plane, preferably parallel to the ground. The directivities of the antennas are aligned at slightly different directions with respect to each other. Their output powers are compared at the source frequency for the respective polarizations. The back lobes of the antennas have been reduced by symmetrically positioning two metallic plates (reflectors) behind the antennas. The antennas, reflectors and a compass are mounted over a video camera stand such that they could be manually positioned in the azimuth. Since the antennas are of identical make, ideally the radiation pattern of either antennareflector combination should behave as a flipped image of the other set. For any particular polarization and frequency, the outputs from the antennas are compared with each other. The antenna assembly is rotated between 0 and 360◦ in the azimuth until the power difference gets minimized. This position relates to the direction of the source and is indicated on the compass, provided there exits a single radio source at that frequency.