On the Image Approximation for Electromagnetic Wave Propagation and PEC Scattering in Cylindrical Harmonics
Shaolin Liao
and
Ronald Vernon
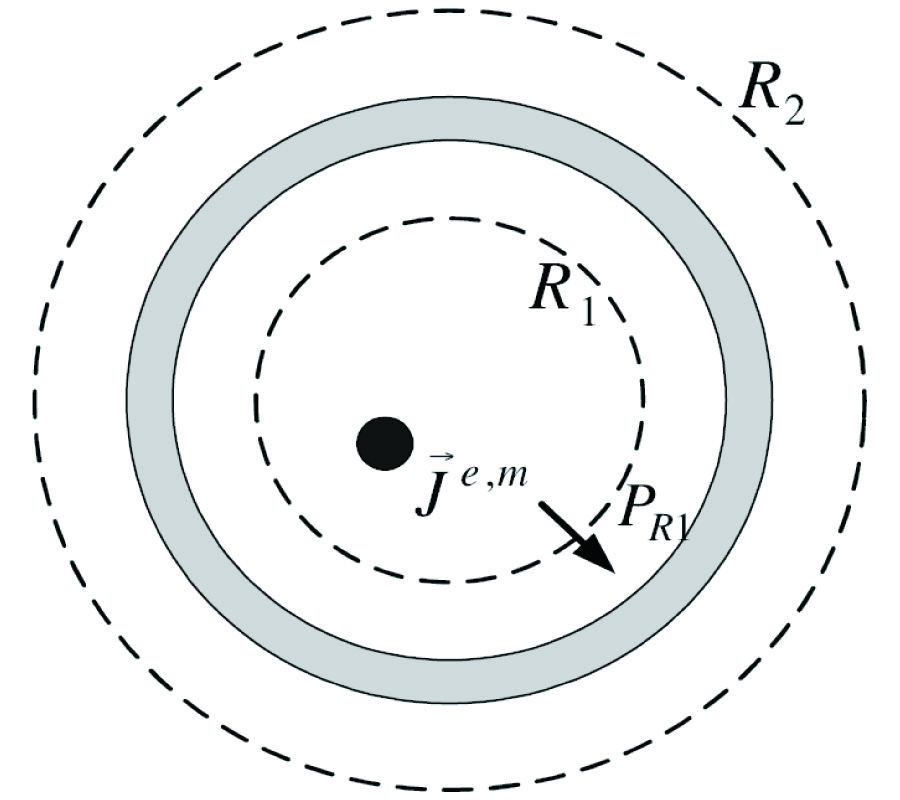
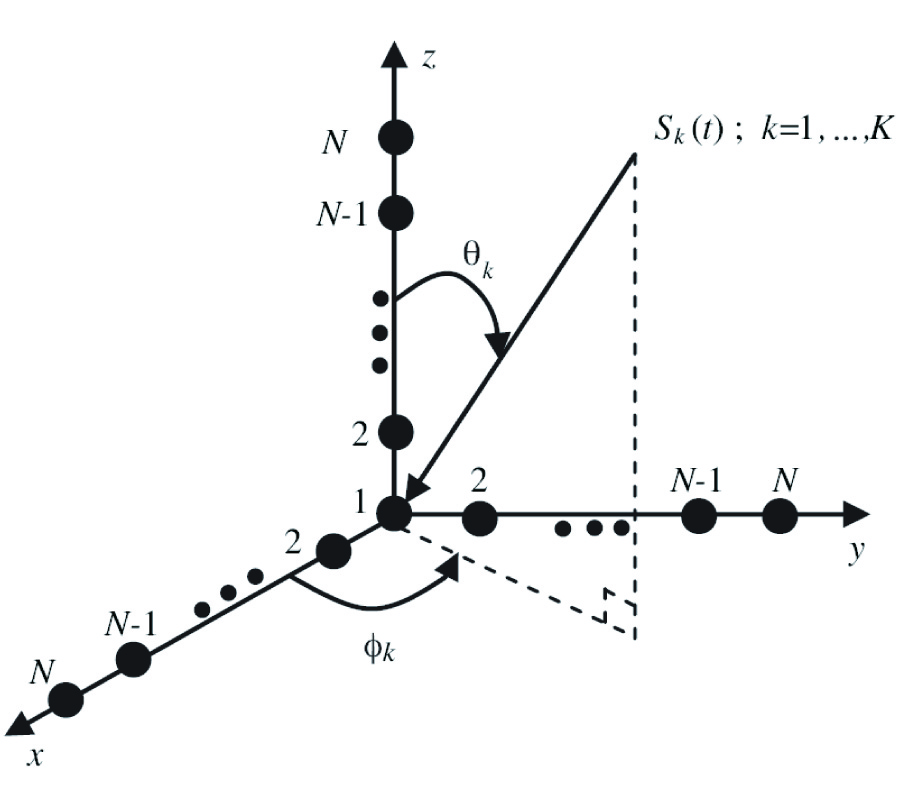
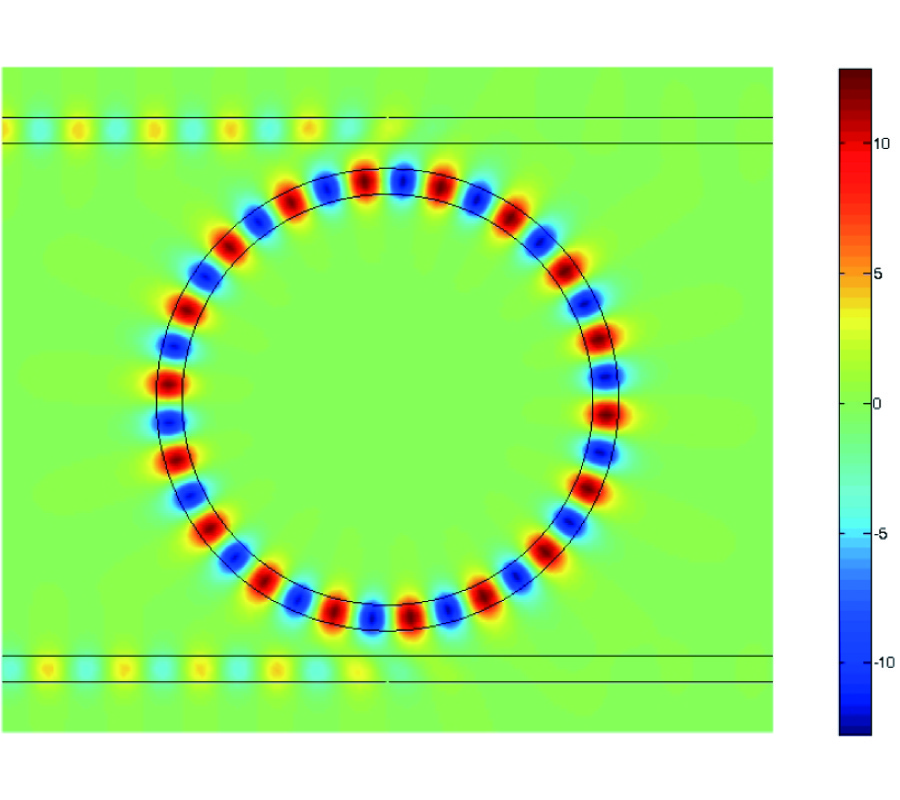
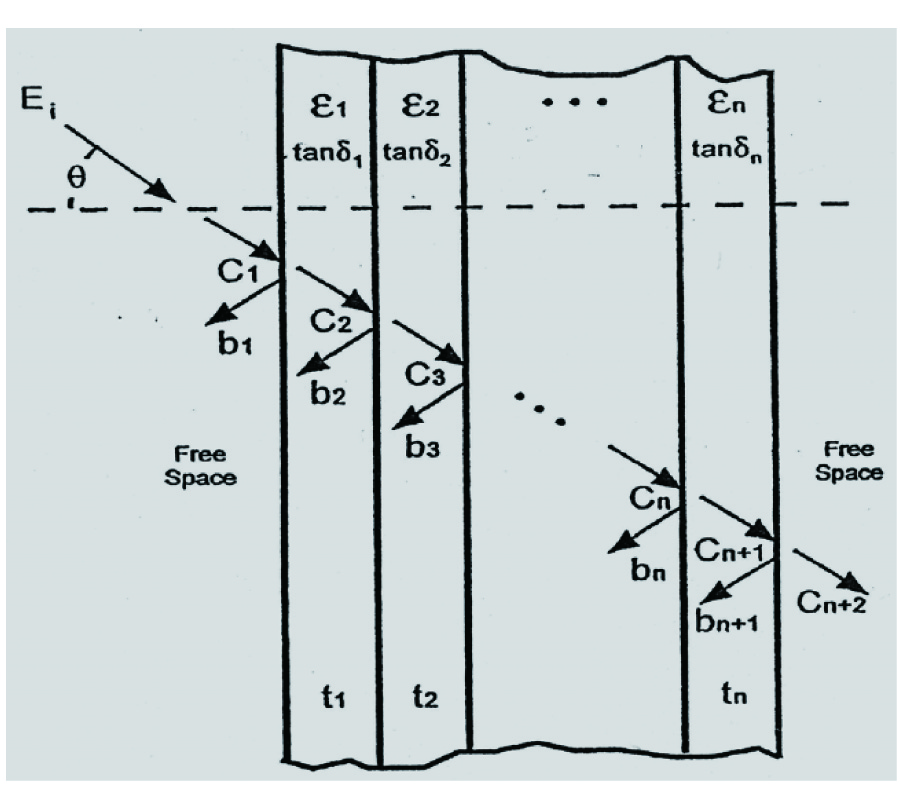
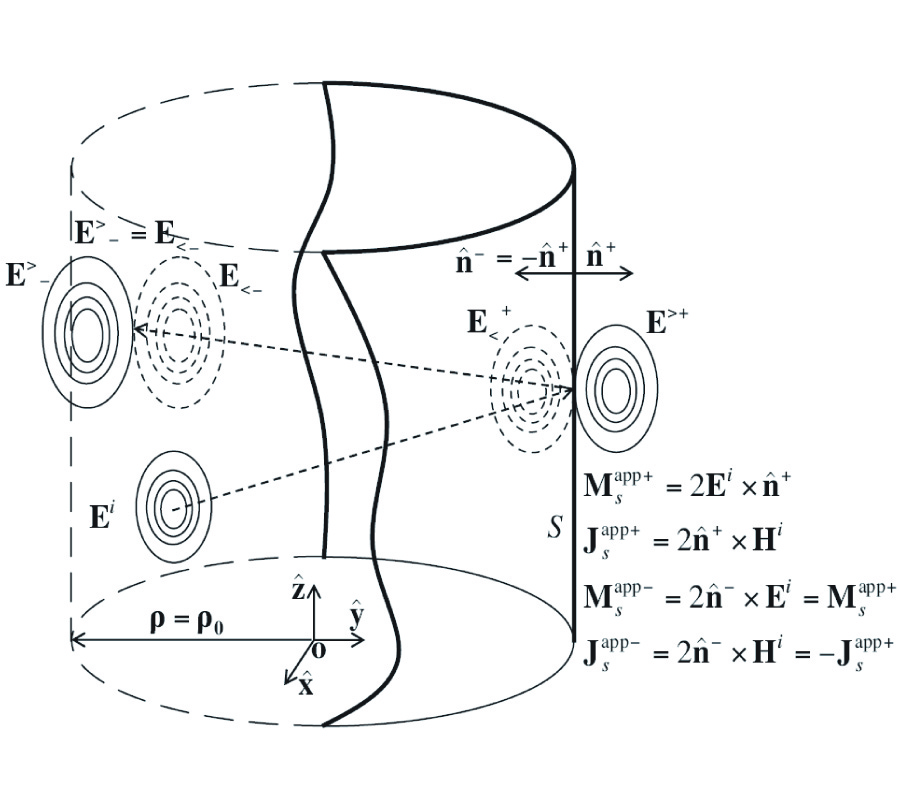
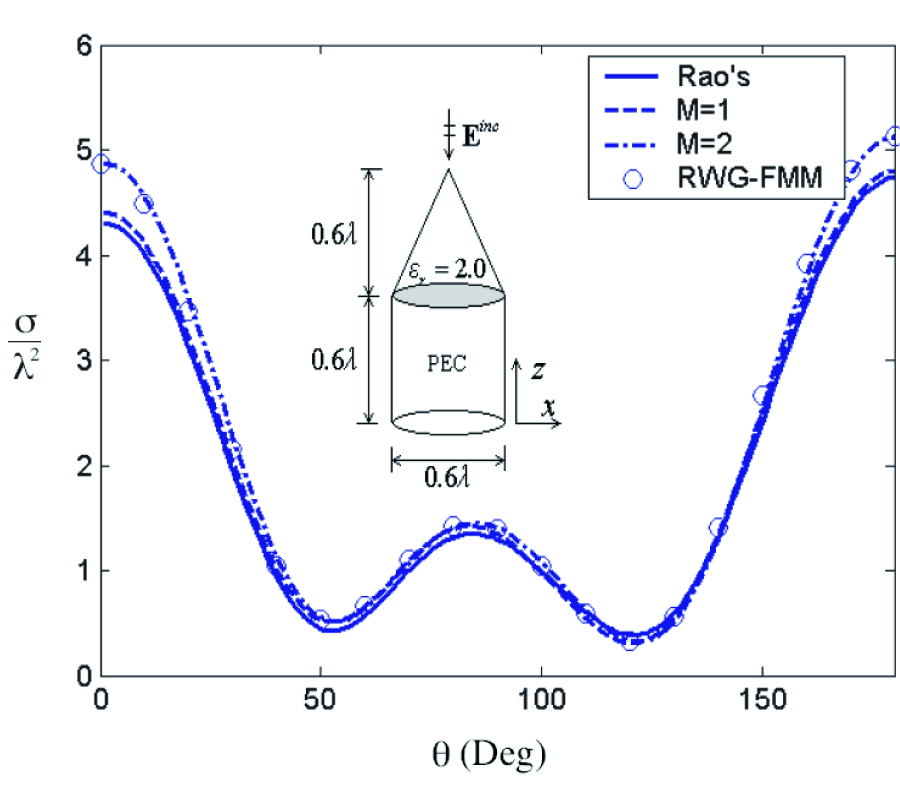
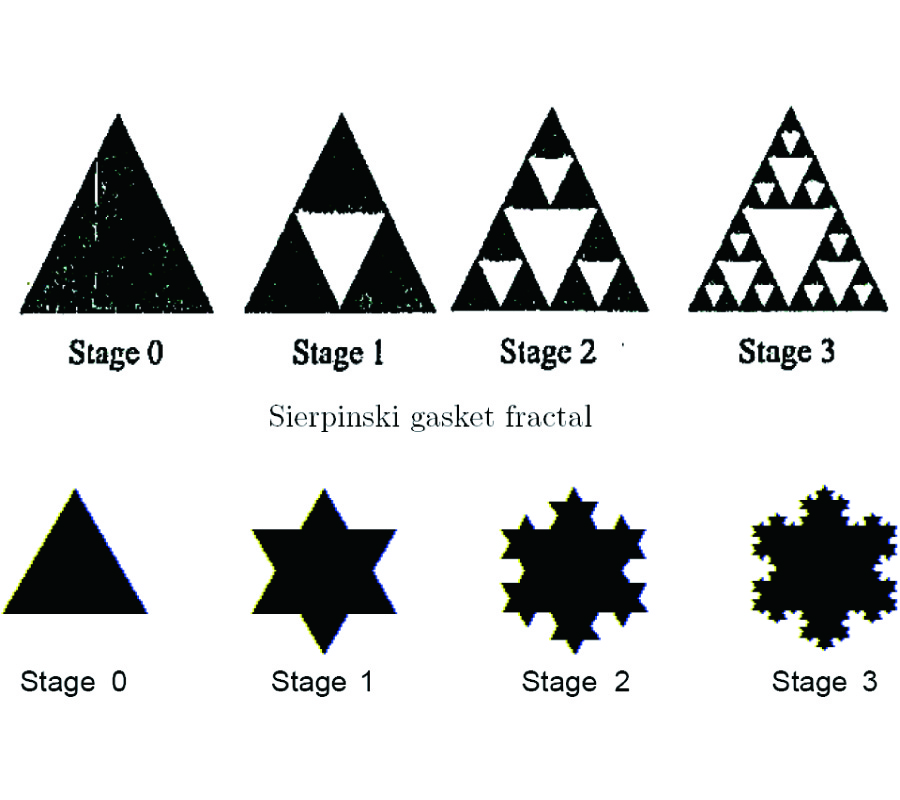
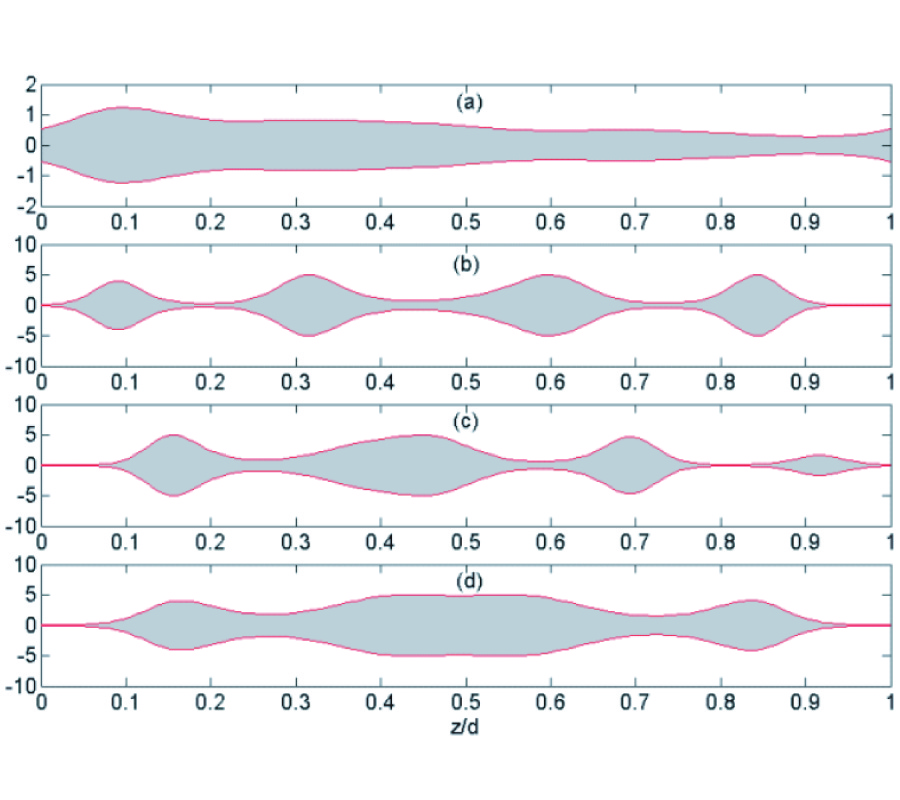
Aclosed-form formula, the discrepancy parameter, which has been defined as the ratio of the modal expansion coefficients between the electromagnetic field obtained from the image approximation and the incident electromagnetic field, has been proposed for the evaluation of the validity of the image approximation in the electromagnetic wave propagation, i.e., Love's equivalence principle, and the electromagnetic wave scattering, i.e., the induction equivalent and the physical equivalent, in the cylindrical geometry. The discrepancy parameter is derived through two equivalent methods, i.e., the vector potential method through the cylindrical addition theorem and the dyadic Green's function method, for both the TE and TM cylindrical harmonics. The discrepancy parameter justifies the fact that the image approximation approaches the exact solution for the cylindrical surface of infinite radius. For the narrow-band field with limited spectral component in k space, the cylindrical modal expansion of the electromagnetic wave into the TE and TM cylindrical harmonics can be separated into the forward-propagating wave that propagates forward and the back-scattered wave that is back-scattered by the PEC surface, within the image approximation. The discrepancy parameter shows that the validity of the image approximation depends on the property of the incident field and the radius of the cylindrical surface, i.e., the narrow-band field and the surface of a large radius are in favor of the image approximation, which has also been confirmed by the numerical result.