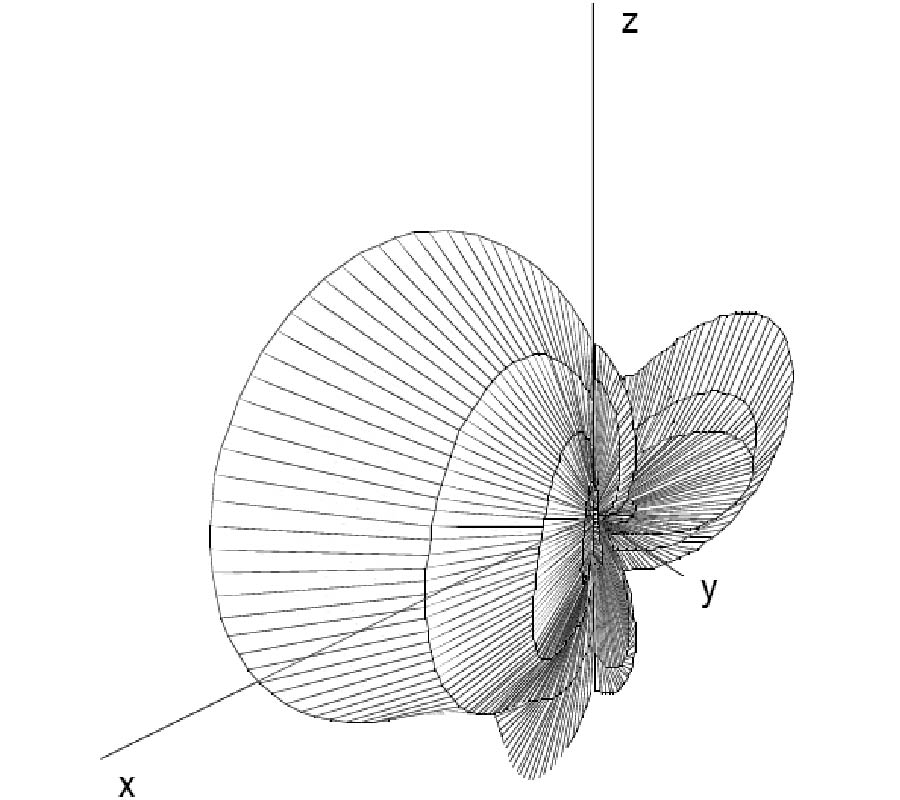
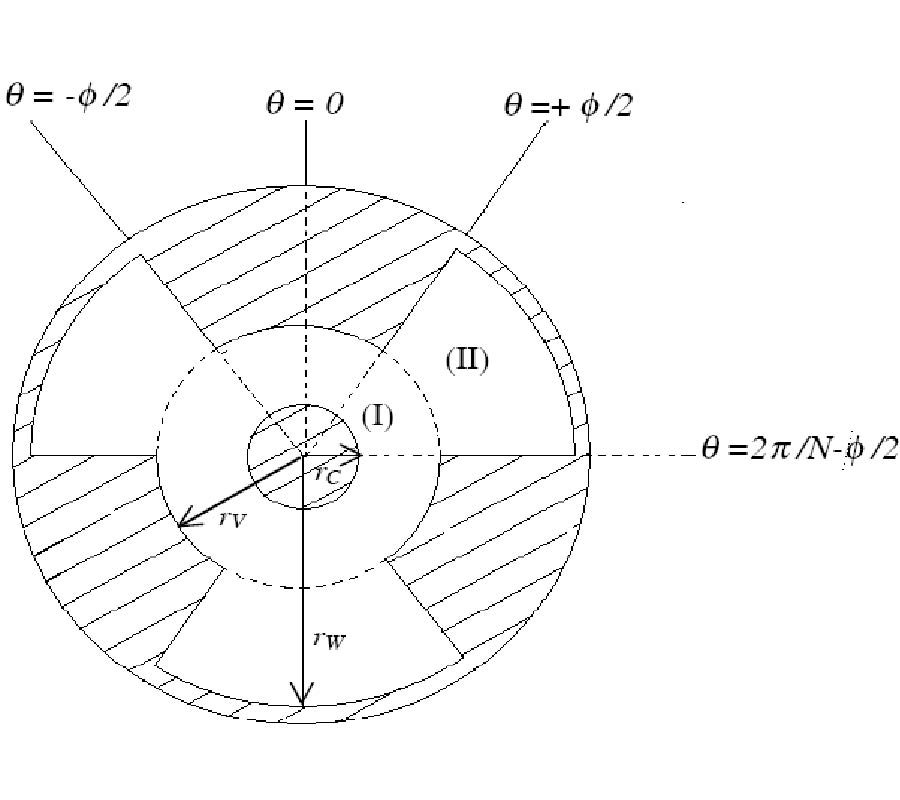
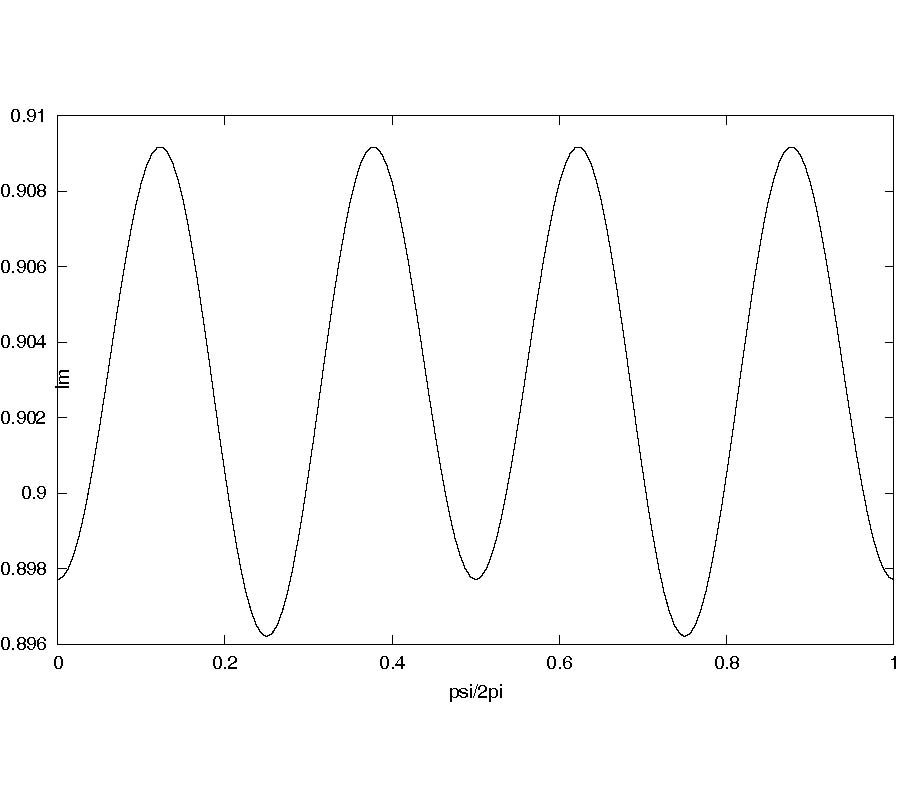
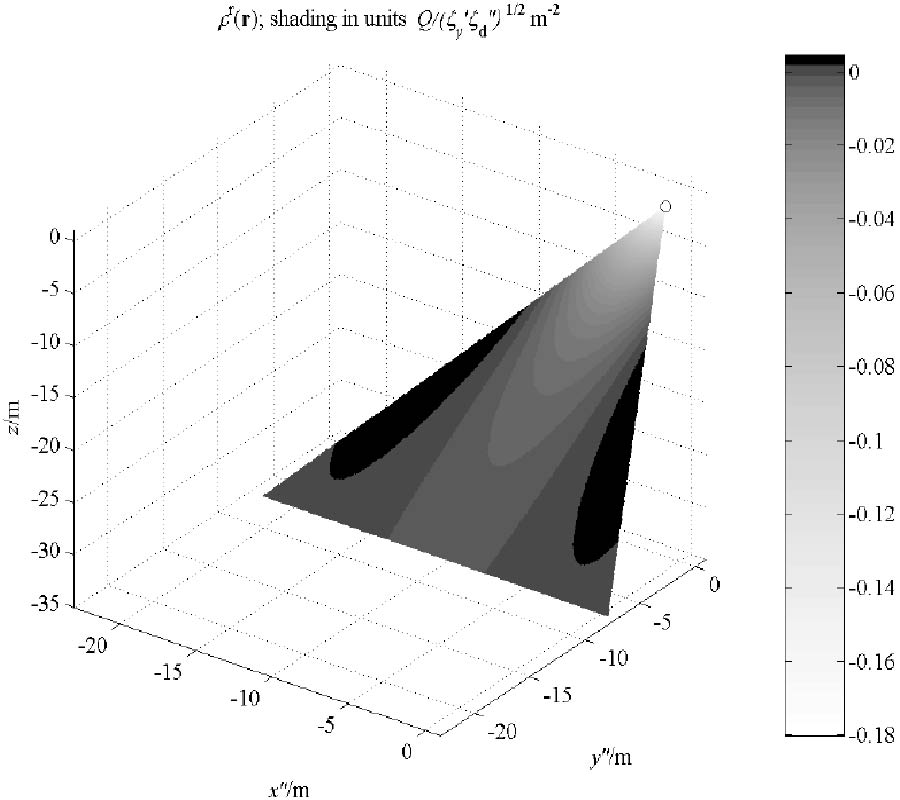
Electromagnetic Field Solution in Conformal Structures: Theoretical and Numerical Analysis
Filiberto Bilotti
,
Andrea Alu
and
Lucio Vegni
A full-wave evaluation of the electromagnetic field in conformal structures with linear loading materials is presented in this paper. The analysis is performed considering at first conformal components with conventional isotropic and homogeneous media in the generalized orthogonal curvilinear reference system. In this first case, a summary of the possible analytical solutions of the vector wave equation obtainable through various factorization techniques is given. Then, the attention is focused on conformal structures involving non-conventional media (anisotropic, chiral, bianisotropic) and in this case the field solution is demanded to a new generalization of the transmission line approach. As an aside, exploiting a contravariant field formulation, which allows writing Maxwell's equations in the generalized reference system as in the Cartesian one, a useful relationship between the local curvature of the geometry and a suitable inhomogeneity of a related planar structure is presented. Finally, some results, obtained simulating the behavior of patch radiators mounted on curved bodies through the combined application of an extended Method of Line (MoL) numerical algorithm and the theoretical approach here derived, are presented.