2026-01-05 Fellow Article
Latest Published
By Sachleen Singh
Andrew Forbes
Progress In Electromagnetics Research, Vol. 185, 1-16, 2026
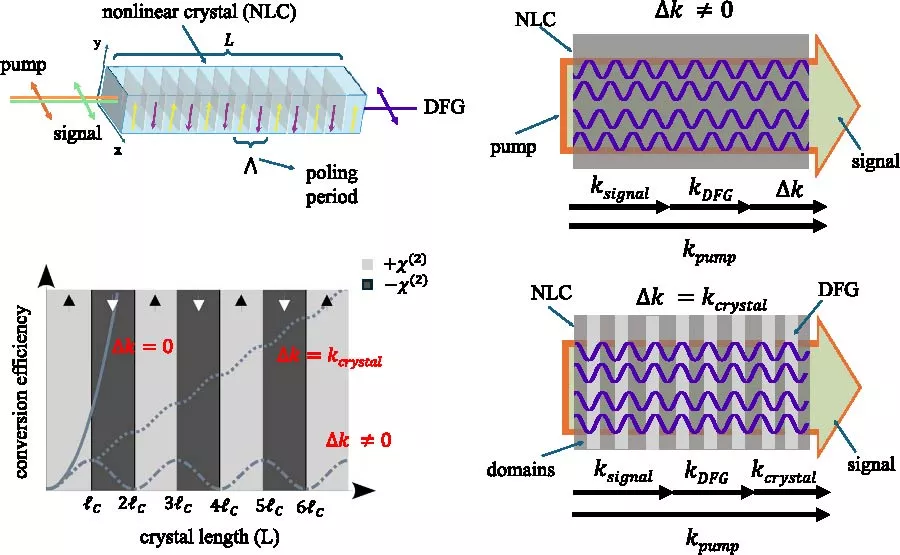
Abstract
The control of all of light's degrees of freedom and its harnessing for applications is captured by the emergent field of structured light. The modern toolkit includes external modulation of light with devices such as metasurfaces and spatial light modulators, their intra-cavity insertion for structured light directly at the source, and their deployment to engineer quantum structured light at the single photon and entangled state regimes. Historically, this control has involved linear optical elements, with nonlinear optics only recently coming to the fore. This has opened unprecedented functionality while revealing new paradigms for nonlinear optics beyond plane waves. In this review we look at the recent progress in structured light with nonlinear optics, covering the fundamentals and the powerful applications they are facilitating in both the classical and quantum domains.